
Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(A) $Br{F_3}$
(B) ${(HP{O_3})_3}$
(C) $Xe{F_4}$
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: Molecules are generally held together by covalent bonds or shared pairs of electrons. These bonds are bidirectional, which means the atoms adopt specific positions relative to one another in order to maximize the bond strengths. So, each molecule will have a definite structure or spatial distribution of atoms.
Complete answer:
a) $Br{F_3}$:
The electronic configuration of bromine is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^5}$. $Br{F_3}$ has seven electrons in its outermost shell and after bond formation it will have two lone pairs and three covalent bonds of bromine and fluorine. As the electron pair is equal to five the hybridisation is $s{p^3}d$. The molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and the bond angle is ${86.2^ \circ }$. The structure of $Br{F_3}$ is given below:
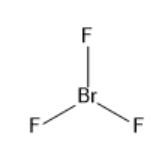
b) ${(HP{O_3})_3}$:
The compound is called trimetaphosphoric acid. It is made up of three Meta phosphoric acid arranged in a cyclic structure. The structure of ${(HP{O_3})_3}$ is given below:
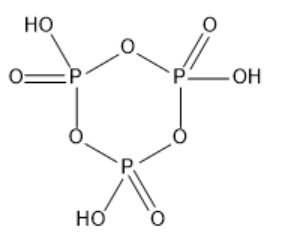
c)$Xe{F_4}$:
The valence shell of xenon has six electrons in the $5p$ orbital and two electrons in the $5s$ orbital. In the formation of$Xe{F_4}$, two electrons of the $5p$ orbital move to fill the vacant $5d$ orbitals. So, there will be four unpaired electrons. Hybridization will be$s{p^3}{d^2}$. The structure of xenon tetrafluoride is given below:
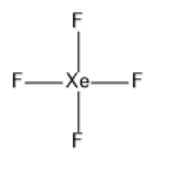
Note:
The concept of mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals having different energies, shapes, etc. than the component atomic orbitals, suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory is hybridization.
Complete answer:
a) $Br{F_3}$:
The electronic configuration of bromine is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^5}$. $Br{F_3}$ has seven electrons in its outermost shell and after bond formation it will have two lone pairs and three covalent bonds of bromine and fluorine. As the electron pair is equal to five the hybridisation is $s{p^3}d$. The molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and the bond angle is ${86.2^ \circ }$. The structure of $Br{F_3}$ is given below:

b) ${(HP{O_3})_3}$:
The compound is called trimetaphosphoric acid. It is made up of three Meta phosphoric acid arranged in a cyclic structure. The structure of ${(HP{O_3})_3}$ is given below:

c)$Xe{F_4}$:
The valence shell of xenon has six electrons in the $5p$ orbital and two electrons in the $5s$ orbital. In the formation of$Xe{F_4}$, two electrons of the $5p$ orbital move to fill the vacant $5d$ orbitals. So, there will be four unpaired electrons. Hybridization will be$s{p^3}{d^2}$. The structure of xenon tetrafluoride is given below:

Note:
The concept of mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals having different energies, shapes, etc. than the component atomic orbitals, suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory is hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




