
Draw the structures of the following compounds.
i)3-Methylbutanal
ii)p-Nitropropiophenone
iii)p-Methylbenzaldehyde
iv)4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
v)4-Chloropentan-2-one
vi)3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
vii)p,p-Dihydroxybenzophenone
viii)Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:The IUPAC (International System of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system is the most rational and widely used system of nomenclature in organic chemistry. The IUPAC name of any organic compound consists of three parts namely: word root, suffix (primary or secondary) and prefix (primary or secondary).
Complete step by step answer:
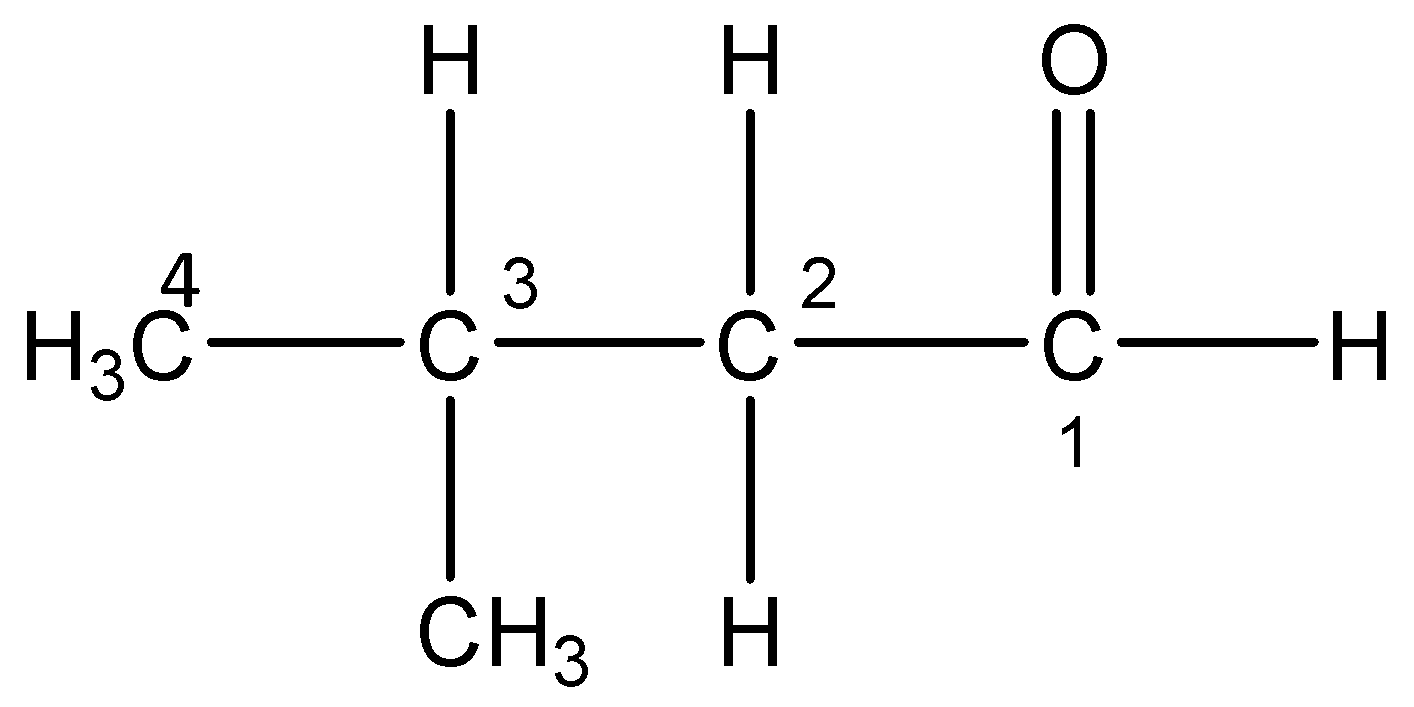
i)3-Methylbutanal:
The word root ‘but’ suggest that there are 4 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a methyl group is substituted at 3- position, the primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘al’ indicates that an aldehyde is present at 1-position.
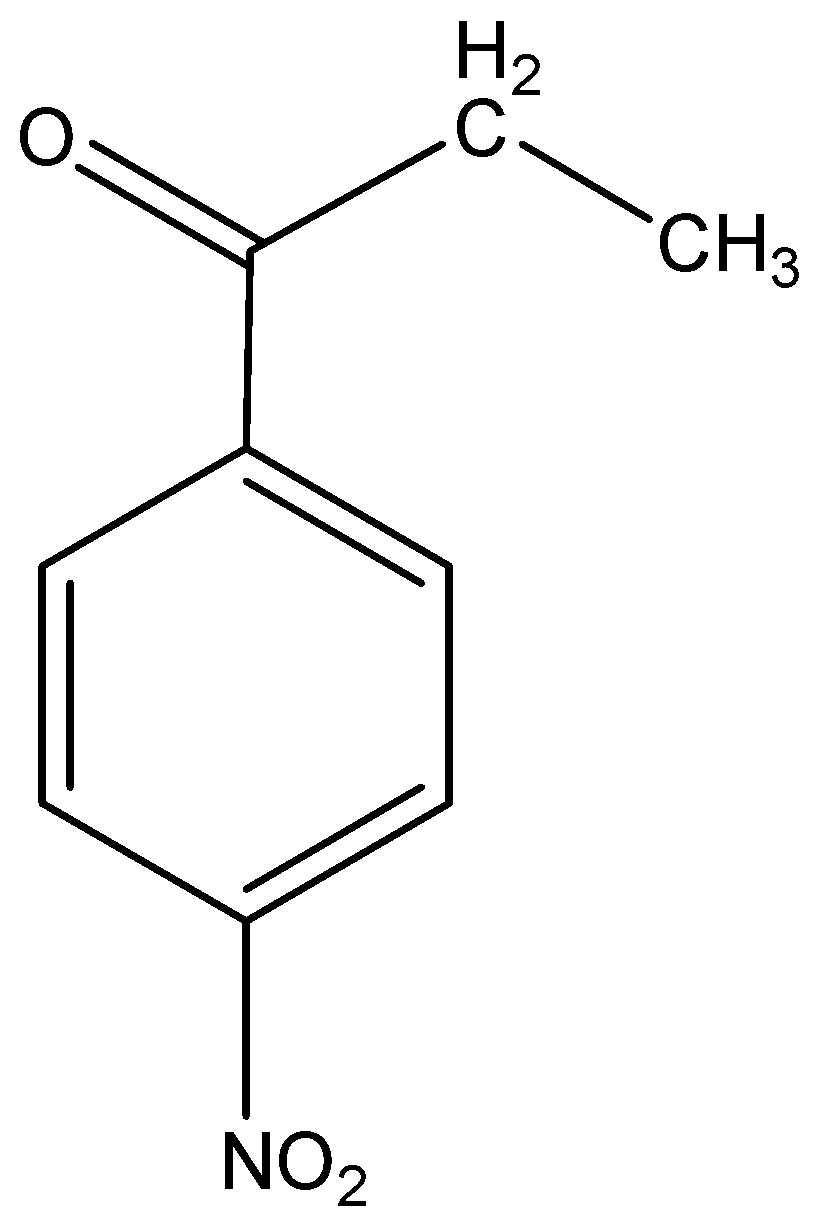
ii)p-Nitropropiophenone
The word root ‘prop’ suggest that there are 3 carbon atoms in the parent chain which contains the functional group ketone at 1-position, the suffix indicates that the functional group ketone is also attached to a phenyl group and the prefix indicates that a nitro group is present at para (p) position to the functional group.
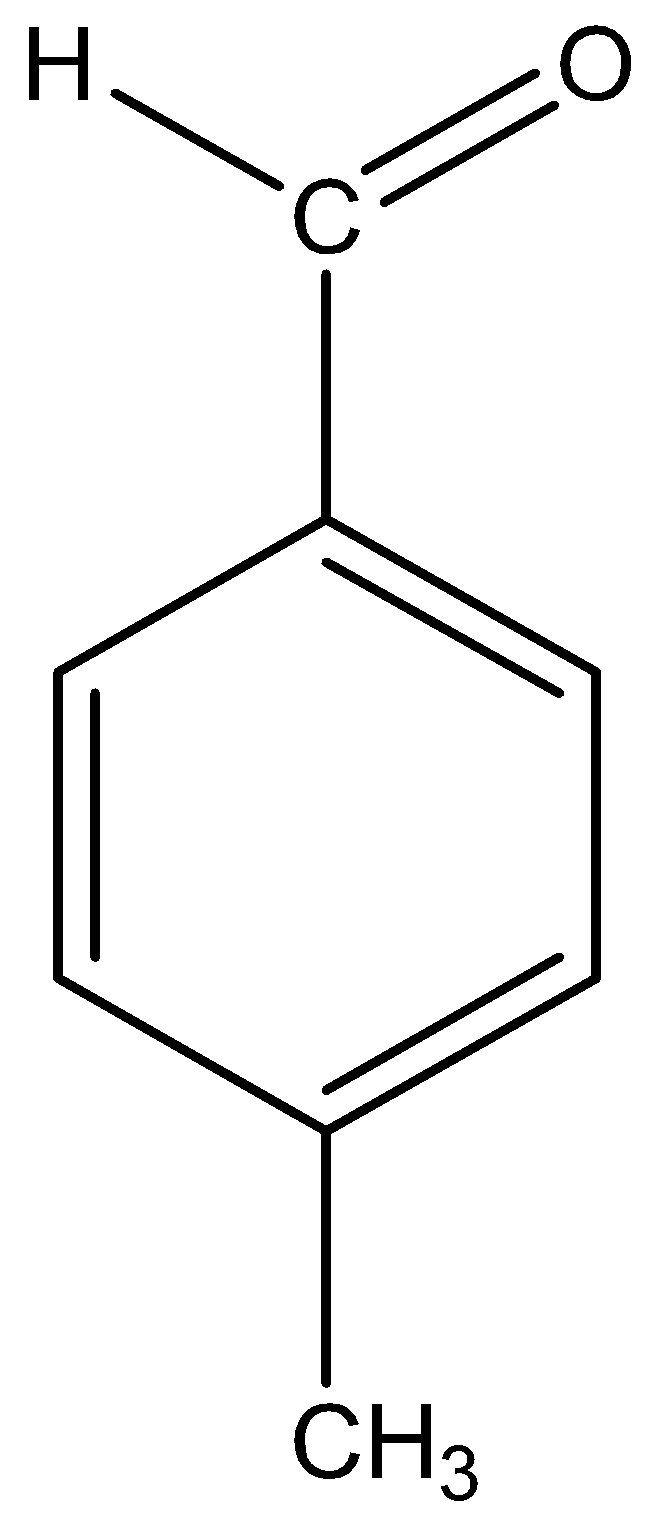
iii)p-Methylbenzaldehyde
The name suggests that a benzene ring is the parent chain, the suffix indicates that the functional group aldehyde is attached to the benzene ring and the prefix indicates that a methyl group is present at para (p) position to the functional group.
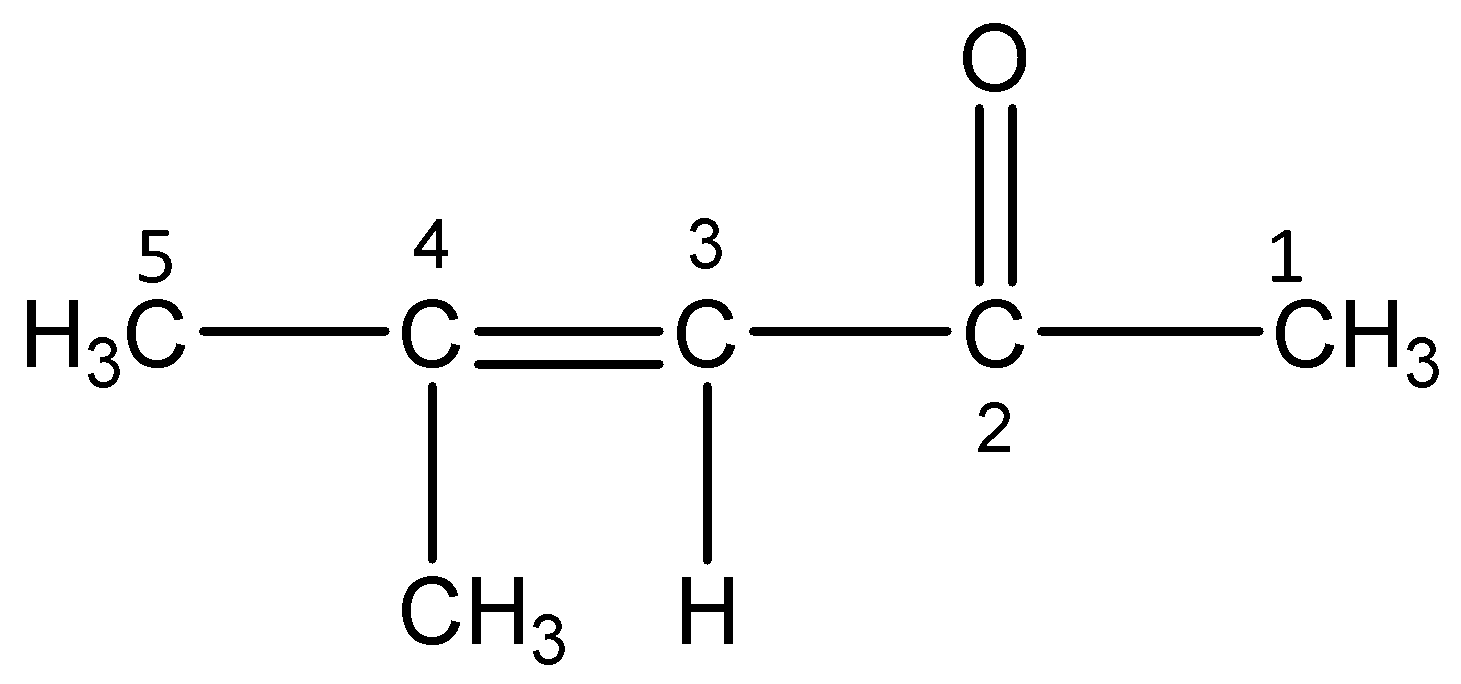
iv)4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
The word root ‘pent’ suggests that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a methyl group is substituted at 4- position. The primary suffix ‘en’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a double bond (alkene) between 3 and 4 C-atoms. The secondary suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 2-position.
v)4-Chloropentan-2-one
The word root ‘pent’ suggest that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a chlorine atom is substituted at 4- position, the primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 2-position.
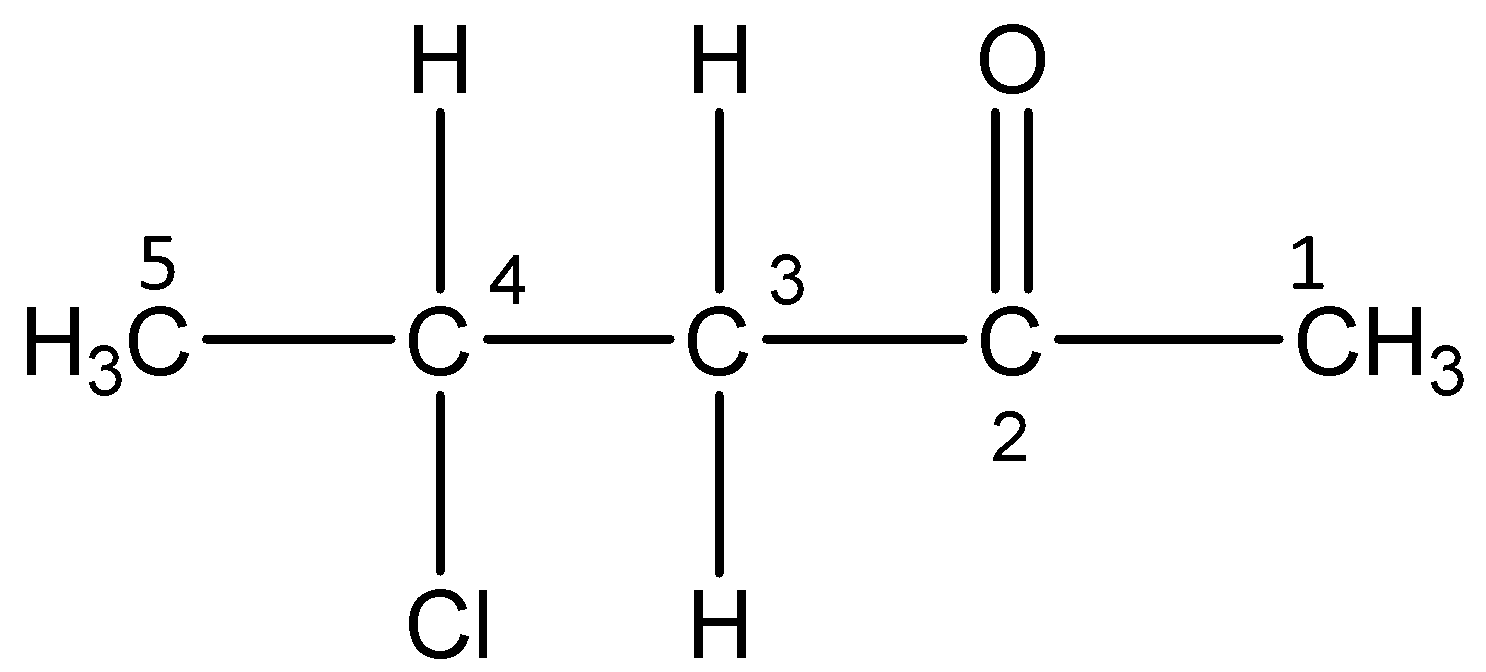
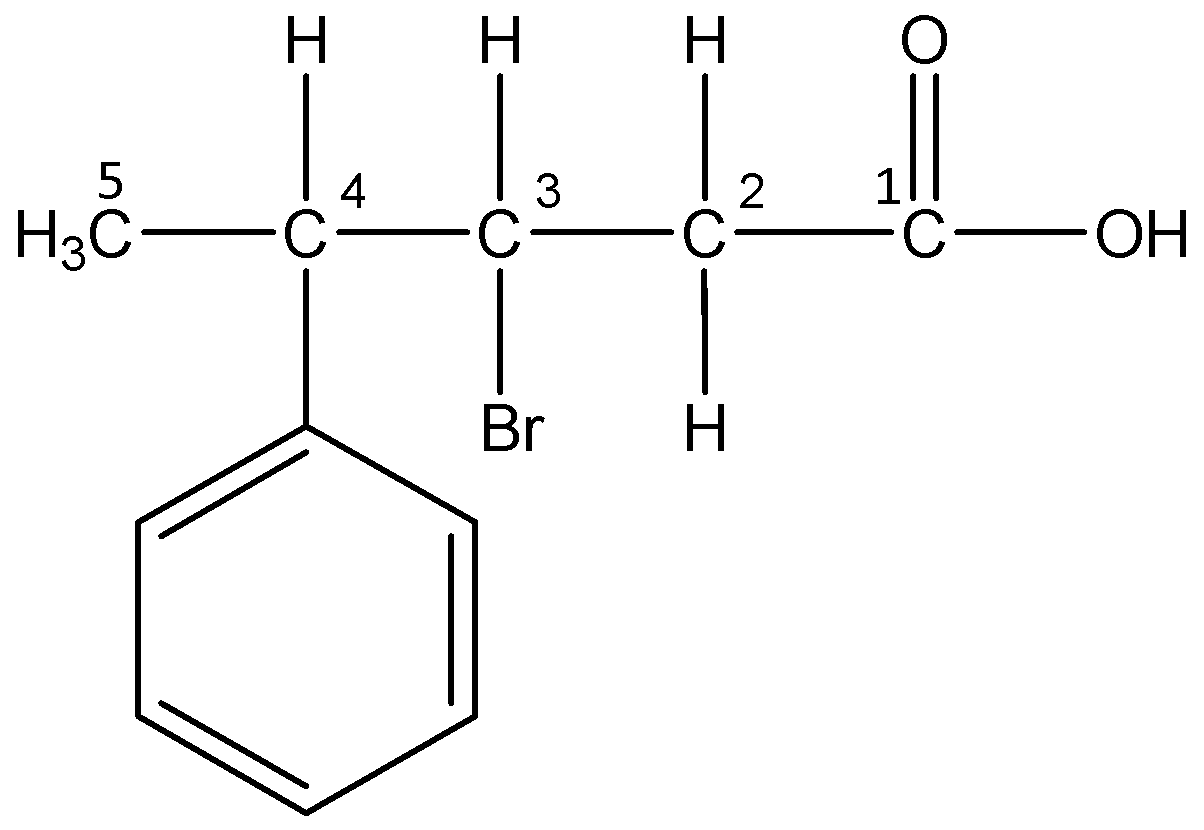
vi)3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
The word root ‘pent’ suggests that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain. The prefix ‘bromo’ indicates that a bromine atom is substituted at 3- position and the prefix ‘phenyl’ indicates that a phenyl group is present at 4- position. The primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘oic acid’ indicates that a carboxylic acid is present at 1-position.
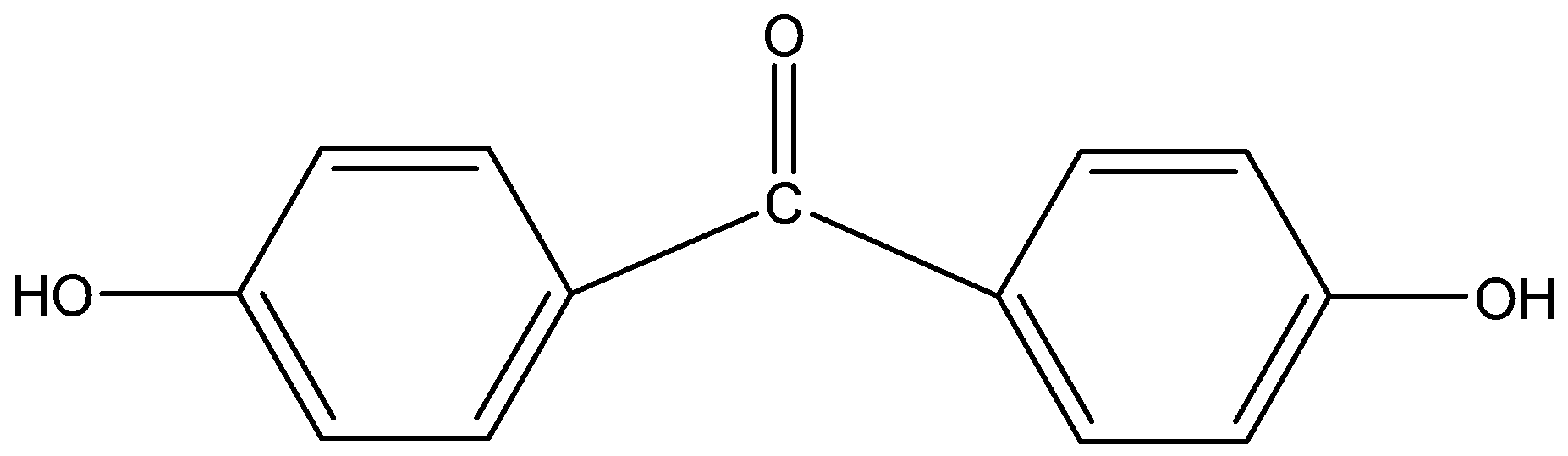
vii)p,p-Dihydroxybenzophenone
The word ‘benzo’ and ‘phen’ suggests that two benzene rings (phenyl group) are present in the compound. The suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 1- position to the phenyl group which is also attached to the other benzene ring at 1-position. The prefix ‘p,p-dihydroxy’ indicates that two alcohol groups are present at para position to each other.
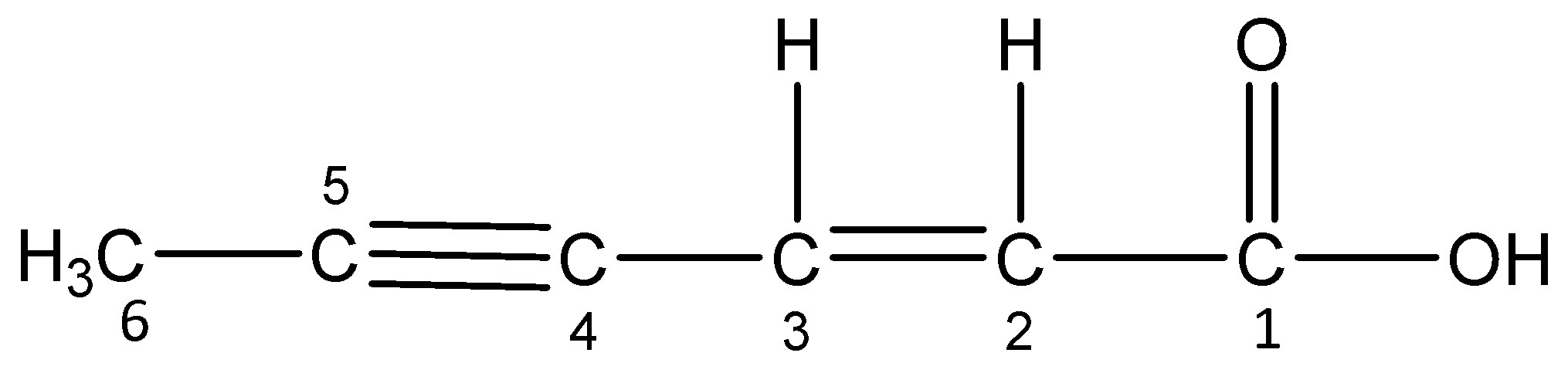
viii)Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid
The word root ‘hex’ suggests that there are 6 carbon atoms in the parent chain. The primary suffix ‘en’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a double bond (alkene) between 2 and 3 C-atom and ‘yne’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a triple bond (alkyne) between 4 and 5 C-atom. The secondary suffix ‘oic acid’ indicates that a carboxylic acid group is present at 1-position.
Note:
If two chains of equal lengths are possible, the one with the larger number of side chains will be the parent chain. The parent chain is numbered in such a way that the functional group gets the lowest locant. When a large and complex group is attached to a benzene ring it is common to name the molecule as an alkane, alkene, etc., and benzene as side chain derivative “phenyl”.
Complete step by step answer:
i)3-Methylbutanal:
The word root ‘but’ suggest that there are 4 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a methyl group is substituted at 3- position, the primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘al’ indicates that an aldehyde is present at 1-position.

ii)p-Nitropropiophenone
The word root ‘prop’ suggest that there are 3 carbon atoms in the parent chain which contains the functional group ketone at 1-position, the suffix indicates that the functional group ketone is also attached to a phenyl group and the prefix indicates that a nitro group is present at para (p) position to the functional group.

iii)p-Methylbenzaldehyde
The name suggests that a benzene ring is the parent chain, the suffix indicates that the functional group aldehyde is attached to the benzene ring and the prefix indicates that a methyl group is present at para (p) position to the functional group.

iv)4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
The word root ‘pent’ suggests that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a methyl group is substituted at 4- position. The primary suffix ‘en’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a double bond (alkene) between 3 and 4 C-atoms. The secondary suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 2-position.

v)4-Chloropentan-2-one
The word root ‘pent’ suggest that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a chlorine atom is substituted at 4- position, the primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 2-position.

vi)3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
The word root ‘pent’ suggests that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain. The prefix ‘bromo’ indicates that a bromine atom is substituted at 3- position and the prefix ‘phenyl’ indicates that a phenyl group is present at 4- position. The primary suffix ‘an’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and the secondary suffix ‘oic acid’ indicates that a carboxylic acid is present at 1-position.

vii)p,p-Dihydroxybenzophenone
The word ‘benzo’ and ‘phen’ suggests that two benzene rings (phenyl group) are present in the compound. The suffix ‘one’ indicates that a ketone is present at 1- position to the phenyl group which is also attached to the other benzene ring at 1-position. The prefix ‘p,p-dihydroxy’ indicates that two alcohol groups are present at para position to each other.

viii)Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid
The word root ‘hex’ suggests that there are 6 carbon atoms in the parent chain. The primary suffix ‘en’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a double bond (alkene) between 2 and 3 C-atom and ‘yne’ indicates that the parent chain is unsaturated and there is a triple bond (alkyne) between 4 and 5 C-atom. The secondary suffix ‘oic acid’ indicates that a carboxylic acid group is present at 1-position.

Note:
If two chains of equal lengths are possible, the one with the larger number of side chains will be the parent chain. The parent chain is numbered in such a way that the functional group gets the lowest locant. When a large and complex group is attached to a benzene ring it is common to name the molecule as an alkane, alkene, etc., and benzene as side chain derivative “phenyl”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




