
Draw the structures of the following:
a. ${\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}$
b. ${\rm{Br}}{{\rm{F}}_5}$
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: The total number of bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom can be used to deduce the geometry of the molecules as per VSEPR theory.
Complete answer
a. We know that VSEPR theory is based on the repulsion between valence shell electrons. These electrons can be bonded or non-bonded thus it is the total number of valence shell electrons on the central atom in a molecule that would decide the structure of the molecule. This theory has given simple stable geometries for different types of molecules. For example, a molecule in which the central atom has only two bond pairs, will have a linear structure but in case it has two bond pairs and a lone pair, the structure would be bent. Now, let’s have a look at the given molecules one by one:
The first molecule given to us is ${\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}$. Here, xenon has a total eight valence electrons out of which four have been used in the bond formation with fluorine. So, we can say that there are four bond pairs around xenon and two lone pairs accounting for the remaining four valence electrons. Now, as per VSEPR theory, the structure for ${\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}$ would be square planar that can be drawn as follows:
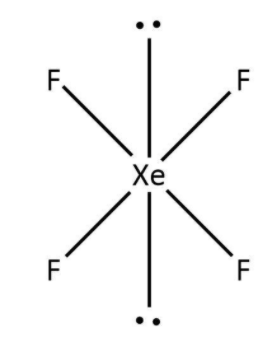
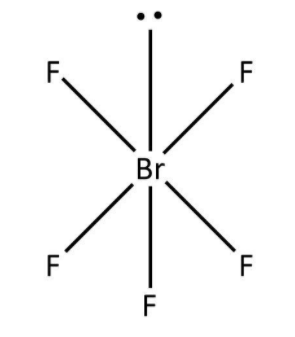
b. The second molecule given to us is ${\rm{Br}}{{\rm{F}}_5}$. Here, bromine has a total seven valence electrons out of which five have been used in the bond formation with fluorine. So, we can say that there are five bond pairs around bromine and one lone pair accounting for the remaining two valence electrons. Now, as per VSEPR theory, the structure for ${\rm{Br}}{{\rm{F}}_5}$ would be square pyramid that can be drawn as follows:
Note:
The arrangement of electron pairs in both the molecules is octahedral as there are a total six pairs but the shape is different as the number of bond pairs and lone pairs are not the same.
Complete answer
a. We know that VSEPR theory is based on the repulsion between valence shell electrons. These electrons can be bonded or non-bonded thus it is the total number of valence shell electrons on the central atom in a molecule that would decide the structure of the molecule. This theory has given simple stable geometries for different types of molecules. For example, a molecule in which the central atom has only two bond pairs, will have a linear structure but in case it has two bond pairs and a lone pair, the structure would be bent. Now, let’s have a look at the given molecules one by one:
The first molecule given to us is ${\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}$. Here, xenon has a total eight valence electrons out of which four have been used in the bond formation with fluorine. So, we can say that there are four bond pairs around xenon and two lone pairs accounting for the remaining four valence electrons. Now, as per VSEPR theory, the structure for ${\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}$ would be square planar that can be drawn as follows:

b. The second molecule given to us is ${\rm{Br}}{{\rm{F}}_5}$. Here, bromine has a total seven valence electrons out of which five have been used in the bond formation with fluorine. So, we can say that there are five bond pairs around bromine and one lone pair accounting for the remaining two valence electrons. Now, as per VSEPR theory, the structure for ${\rm{Br}}{{\rm{F}}_5}$ would be square pyramid that can be drawn as follows:

Note:
The arrangement of electron pairs in both the molecules is octahedral as there are a total six pairs but the shape is different as the number of bond pairs and lone pairs are not the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




