
Draw the structures of the following:
(1) $HCl{{O}_{4}}$
(2) ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Perchloric acid is monobasic so there will be one $Cl-OH$ bond and Phosphorous acid is dibasic so there will be two $P-OH$ bonds. It has tetrahedral geometry just like methane with bond angle 109.8.
Complete Step by step Answer:
Perchloric acid
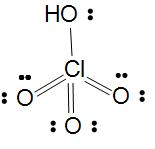
Basicity of oxoacids of Cl is equal to the number of $Cl-OH$ bonds in the molecule.
In Perchloric acid its basicity is 1 as there is one $Cl-OH$ bond in the molecule and three $Cl-O$ bonds due to which it is oxidizing power is less. Here Perchloric acid is monobasic and the halogen(chlorine) is $s{{p}_{3}}$ hybridized.
Halogens forms several oxyacids such as $HOX$, $HOXO$, $HOX{{O}_{2}}$, $HOX{{O}_{3}}$.
Order of acidic strength of oxoacids of the same halogen is
$HCl{{O}_{4}}$>$HCl{{O}_{3}}$>$HCl{{O}_{2}}$>$HCl{{O}_{{}}}$ it’s like this because acidic strength of oxoacids of same halogen increases when there oxidation state increases.
This following trend can also be seen from the stability of anion produced more stable is the conjugate base more is the acidic character.
Oxidizing power of the oxoacids of chlorine is
$HCl{{O}_{4}}$<$HCl{{O}_{3}}$<$HCl{{O}_{2}}$<$HCl{{O}_{{}}}$.
Phosphorous acid
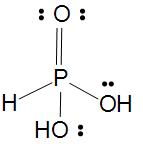
Basicity of oxoacids of P is equal to the number of $P-OH$ bonds in the molecule.
In Phosphorous acid its basicity is 2 as there is two $P-OH$ bond in the molecule which we can also say as dibasic and one $P=O$ bond and one $P-H$ bond which help to be as a strong reducing agents but Phosphorous acid is a weak reducing agent as we can see there is only one $P-H$ bond.
Oxidation state of phosphorus is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms.
Phosphorous acid is Dibasic due to the presence of two replaceable hydrogen.
On heating, ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ undergoes disproportionation reaction to form ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ and $P{{H}_{3}}$
$4{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }3{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}+P{{H}_{3}}$
Note:
- Phosphorous acid is triprotic as we can judge by the given formula ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$.
- Perchloric acid solids made up of perchlorate anion.
Complete Step by step Answer:
Perchloric acid

Basicity of oxoacids of Cl is equal to the number of $Cl-OH$ bonds in the molecule.
In Perchloric acid its basicity is 1 as there is one $Cl-OH$ bond in the molecule and three $Cl-O$ bonds due to which it is oxidizing power is less. Here Perchloric acid is monobasic and the halogen(chlorine) is $s{{p}_{3}}$ hybridized.
Halogens forms several oxyacids such as $HOX$, $HOXO$, $HOX{{O}_{2}}$, $HOX{{O}_{3}}$.
Order of acidic strength of oxoacids of the same halogen is
$HCl{{O}_{4}}$>$HCl{{O}_{3}}$>$HCl{{O}_{2}}$>$HCl{{O}_{{}}}$ it’s like this because acidic strength of oxoacids of same halogen increases when there oxidation state increases.
This following trend can also be seen from the stability of anion produced more stable is the conjugate base more is the acidic character.
Oxidizing power of the oxoacids of chlorine is
$HCl{{O}_{4}}$<$HCl{{O}_{3}}$<$HCl{{O}_{2}}$<$HCl{{O}_{{}}}$.
Phosphorous acid

Basicity of oxoacids of P is equal to the number of $P-OH$ bonds in the molecule.
In Phosphorous acid its basicity is 2 as there is two $P-OH$ bond in the molecule which we can also say as dibasic and one $P=O$ bond and one $P-H$ bond which help to be as a strong reducing agents but Phosphorous acid is a weak reducing agent as we can see there is only one $P-H$ bond.
Oxidation state of phosphorus is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms.
Phosphorous acid is Dibasic due to the presence of two replaceable hydrogen.
On heating, ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ undergoes disproportionation reaction to form ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ and $P{{H}_{3}}$
$4{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }3{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}+P{{H}_{3}}$
Note:
- Phosphorous acid is triprotic as we can judge by the given formula ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$.
- Perchloric acid solids made up of perchlorate anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




