
Draw the Newmann projection formula for different conformations of ethane.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Conformational isomerism is related to rotation about sigma bonds, and has no connection with the differences in the connectivity of the atoms or geometry of bonding.
Complete answer:
In ethane (HC-CH), the two carbon atoms are linked to each other by a single covalent bond. The remaining three valencies are satisfied by hydrogen atoms. If we keep the position of one carbon atom fixed and allow the other carbon to rotate about the covalent bond, an infinite number of relative arrangements (or conformations) of the hydrogen atoms attached to the two carbon atoms will be possible. Out of these, the two important conformations are staggered and eclipsed. These are described as follows:
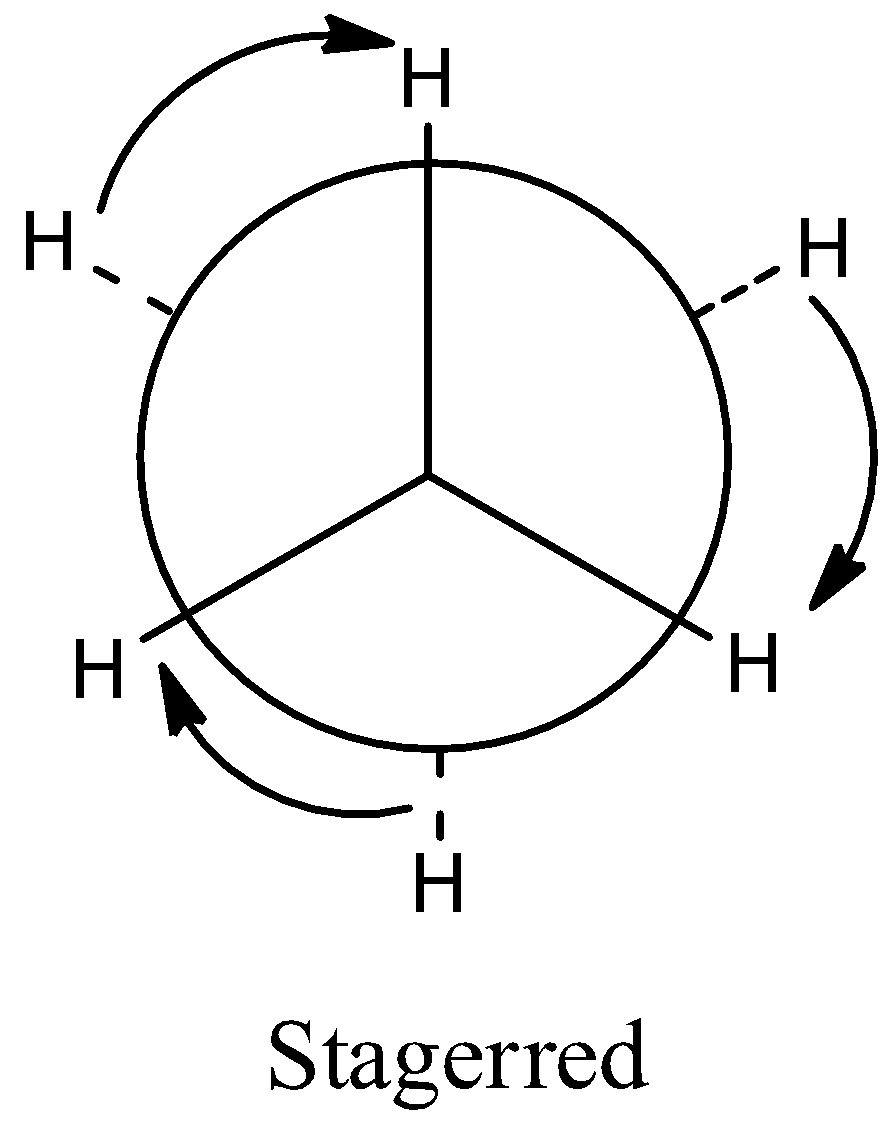
(a)Staggered conformation. In this conformation, the rotation about the C-C bond is such that the hydrogen atoms attached tetrahedrally to the two carbon atoms are completely staggered i.e. they are at maximum distance apart in space.
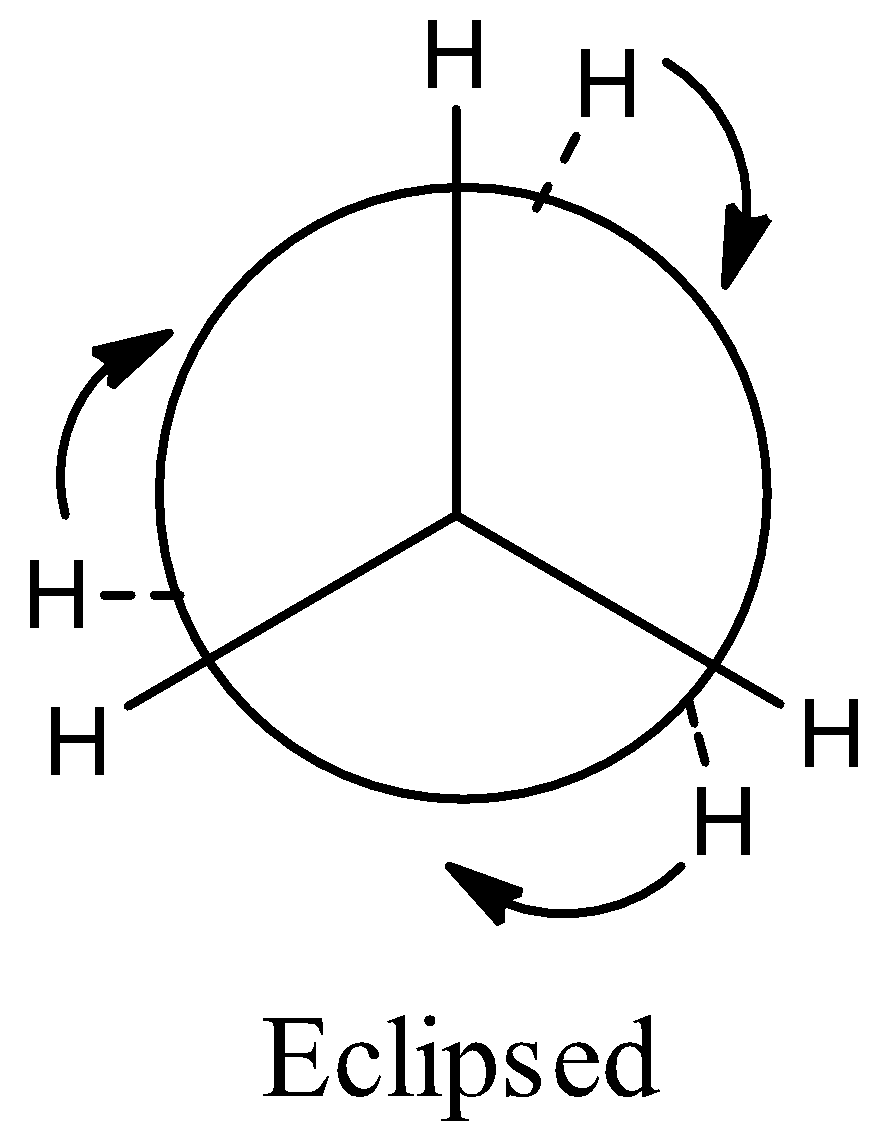
(b) Eclipsed conformation. In this case, the rotation about the C-C bond is such that the hydrogen atoms attached tetrahedrally to one carbon atom completely cover or eclipse the hydrogen atoms attached to the other carbon atom. The staggered and eclipsed conformations of ethane are represented with the help of space models (3D or three dimensional representations) called saw horse models.
Note: We know that a sigma bond between the two carbon atoms is formed as a result of the axial overlap of the two sp. hybrid orbitals. The electron distribution in the molecular orbital thus formed is cylindrically symmetrical around the internuclear axis. As a result, free rotation of the atoms or groups attached tetrahedrally to the carbon atoms is possible. This will lead to a number of different relative arrangements of the atoms or groups in space. These different relative spatial arrangements which arise because of rotation around the single bond are called conformations or rotational isomers or rotamers.
Complete answer:
In ethane (HC-CH), the two carbon atoms are linked to each other by a single covalent bond. The remaining three valencies are satisfied by hydrogen atoms. If we keep the position of one carbon atom fixed and allow the other carbon to rotate about the covalent bond, an infinite number of relative arrangements (or conformations) of the hydrogen atoms attached to the two carbon atoms will be possible. Out of these, the two important conformations are staggered and eclipsed. These are described as follows:
(a)Staggered conformation. In this conformation, the rotation about the C-C bond is such that the hydrogen atoms attached tetrahedrally to the two carbon atoms are completely staggered i.e. they are at maximum distance apart in space.

(b) Eclipsed conformation. In this case, the rotation about the C-C bond is such that the hydrogen atoms attached tetrahedrally to one carbon atom completely cover or eclipse the hydrogen atoms attached to the other carbon atom. The staggered and eclipsed conformations of ethane are represented with the help of space models (3D or three dimensional representations) called saw horse models.

Note: We know that a sigma bond between the two carbon atoms is formed as a result of the axial overlap of the two sp. hybrid orbitals. The electron distribution in the molecular orbital thus formed is cylindrically symmetrical around the internuclear axis. As a result, free rotation of the atoms or groups attached tetrahedrally to the carbon atoms is possible. This will lead to a number of different relative arrangements of the atoms or groups in space. These different relative spatial arrangements which arise because of rotation around the single bond are called conformations or rotational isomers or rotamers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




