
How do you draw the Lewis dot structure for KOH.
Answer
483.3k+ views
Hint: Electron Dot structures also known as the Lewis electron Dot structures, are diagrams that depict the bonding between different atoms and also show their valence electrons and lone pairs, if any exists. It mostly has two types of dots $ \times \& \circ $ that represent electrons from two different atoms.
Complete answer:
The inorganic compound given to us is Potassium Hydroxide with the chemical formula KOH. The central atom is Oxygen. It is attached to one potassium and one Hydrogen. Oxygen belongs to the group 16 of the periodic table and has 6 valence electrons. Potassium belongs to the group 1 of the periodic table and has 1 valence electron. Potassium donates the one electron in its valence shell to form a monocation, oxygen gains that one electron from Potassium and one from Hydrogen making a total of 8 electrons in the outermost orbital. It becomes stable as it attains the stable electronic configuration. It is easier for the oxygen to gain 2 electrons than to lose all the six electrons. Hence oxygen acts as a base.
The Lewis dot structure deals with only the valence electrons of an element, and shows the bonding precisely. The outermost electron count can be easily figured out.
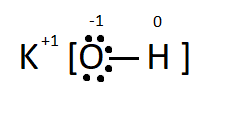
Here the $ \bullet $ represents the valence electrons present in the valence shell of the oxygen and the charge on each atom is shown as their valencies.
Note:
KOH is a very strong base and is commonly known as caustic soda. It is mainly used in the industries and has high reactivity towards acids. It is the important precursor for soft and liquid soaps as well as for numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is white solid and is dangerously corrosive.
Complete answer:
The inorganic compound given to us is Potassium Hydroxide with the chemical formula KOH. The central atom is Oxygen. It is attached to one potassium and one Hydrogen. Oxygen belongs to the group 16 of the periodic table and has 6 valence electrons. Potassium belongs to the group 1 of the periodic table and has 1 valence electron. Potassium donates the one electron in its valence shell to form a monocation, oxygen gains that one electron from Potassium and one from Hydrogen making a total of 8 electrons in the outermost orbital. It becomes stable as it attains the stable electronic configuration. It is easier for the oxygen to gain 2 electrons than to lose all the six electrons. Hence oxygen acts as a base.
The Lewis dot structure deals with only the valence electrons of an element, and shows the bonding precisely. The outermost electron count can be easily figured out.
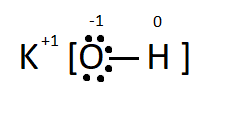
Here the $ \bullet $ represents the valence electrons present in the valence shell of the oxygen and the charge on each atom is shown as their valencies.
Note:
KOH is a very strong base and is commonly known as caustic soda. It is mainly used in the industries and has high reactivity towards acids. It is the important precursor for soft and liquid soaps as well as for numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is white solid and is dangerously corrosive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




