
Draw the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ and hence solve $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ .
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint: Any year which has 366 days is called a leap year. Non-leap year contains 365 days. We have to find 80% of 365 days. We will write this mathematically as $80%\times 365$ . Then, we have to convert 80% into its number form by dividing 80 by 100 and simplify.
Complete step by step answer:
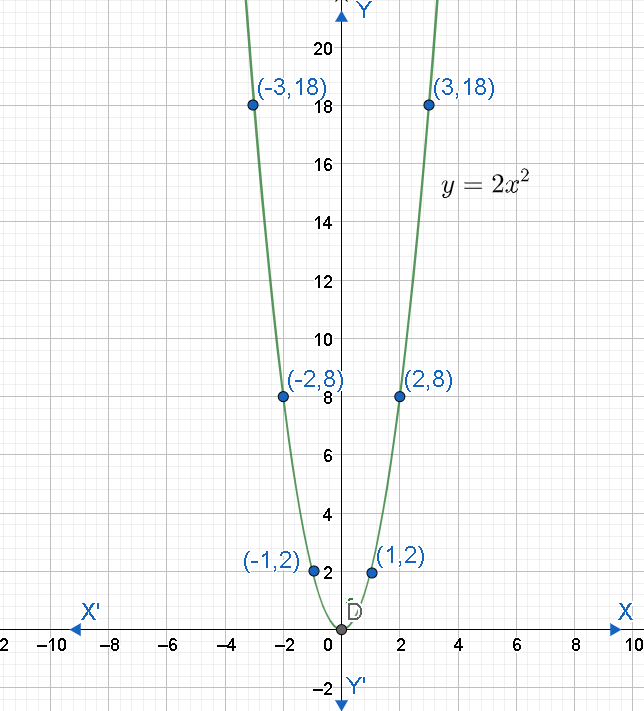
We have to draw the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ and hence solve $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ . Let us first draw the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ by substituting different values of x and find the corresponding values of y.
Let us consider when $x=-3,-2,1,0,1,2,3$ .
When $x=-3$ , we can find y as
$y=2\times {{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 9=18$
When $x=-2$ , we can find y as
$y=2\times {{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 4=8$
When $x=-1$ ,
$y=2\times {{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 1=2$
When $x=0$ ,
$y=2\times {{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}=0$
Similarly, we have to find the for $x=1,2,3$ .
We can tabulate the corresponding y values as follows.
Now, let us plot the points $\left( -3,18 \right),\left( -2,8 \right),\left( -1,2 \right),\left( 0,0 \right),\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 2,8 \right),\left( 3,18 \right)$ .
Now, let us consider the equation $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0...\left( i \right)$ .
We are given that $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ . Let us substitute this value in the equation (i).
$\Rightarrow y+x-6=0$
We have to take all the terms other than y to the RHS.
$\Rightarrow y=6-x$
We have to substitute different values of x and find the corresponding values of y.
Let us consider $x=-3$ .
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -3 \right)=6+3=9$
When $x=-2$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -2 \right)=6+2=8$
When $x=-1$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -1 \right)=6+1=7$
When $x=0$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( 0 \right)=6-0=6$
Similarly, we have to find the for $x=1,2,3$ .
We can tabulate the corresponding y values as follows.
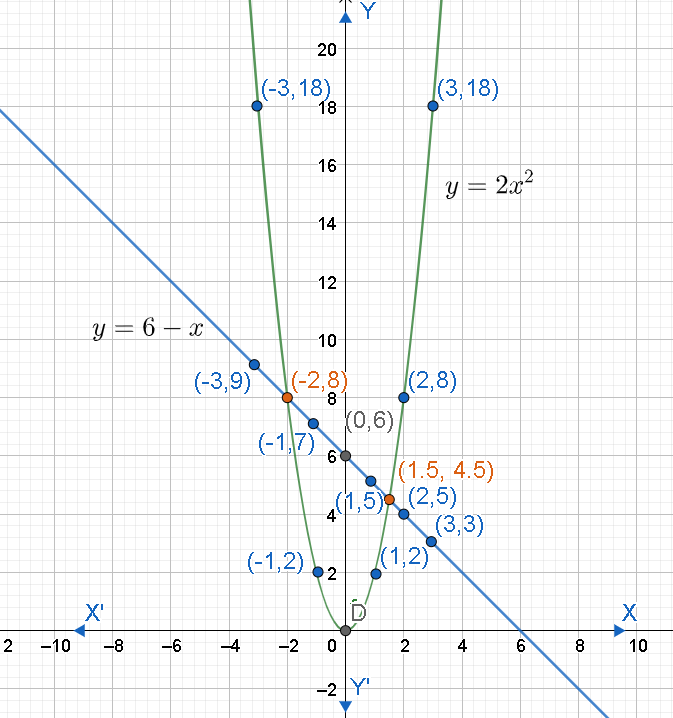
Now, let us plot the points $\left( -3,9 \right),\left( -2,8 \right),\left( -1,7 \right),\left( 0,6 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 2,4 \right),\left( 3,3 \right)$ .
From the graph, we have to look for the points of the intersection of equations $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ and $y=6-x$ .
We can see that both the equations intersect at $\left( -2,8 \right)$ and $\left( 1.5,4.5 \right)$ (shown as red colour in the graph). The solution of $y=6-x$ will be the set of x coordinates of the points of intersection.
Hence, the solution of $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ is $\left\{ -2,1.5 \right\}$ .
Note: Students must draw the graph of $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ in the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ . They must note that the solution set will be the set of x coordinates of the points of intersection not the y-coordinates. They must know to simplify an equation. Students must make the second equation in terms of y.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to draw the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ and hence solve $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ . Let us first draw the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ by substituting different values of x and find the corresponding values of y.
Let us consider when $x=-3,-2,1,0,1,2,3$ .
When $x=-3$ , we can find y as
$y=2\times {{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 9=18$
When $x=-2$ , we can find y as
$y=2\times {{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 4=8$
When $x=-1$ ,
$y=2\times {{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}=2\times 1=2$
When $x=0$ ,
$y=2\times {{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}=0$
Similarly, we have to find the for $x=1,2,3$ .
We can tabulate the corresponding y values as follows.
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ | 18 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 18 |
Now, let us plot the points $\left( -3,18 \right),\left( -2,8 \right),\left( -1,2 \right),\left( 0,0 \right),\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 2,8 \right),\left( 3,18 \right)$ .

Now, let us consider the equation $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0...\left( i \right)$ .
We are given that $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ . Let us substitute this value in the equation (i).
$\Rightarrow y+x-6=0$
We have to take all the terms other than y to the RHS.
$\Rightarrow y=6-x$
We have to substitute different values of x and find the corresponding values of y.
Let us consider $x=-3$ .
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -3 \right)=6+3=9$
When $x=-2$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -2 \right)=6+2=8$
When $x=-1$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( -1 \right)=6+1=7$
When $x=0$ ,
$\Rightarrow y=6-\left( 0 \right)=6-0=6$
Similarly, we have to find the for $x=1,2,3$ .
We can tabulate the corresponding y values as follows.
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| $y=6-x$ | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
Now, let us plot the points $\left( -3,9 \right),\left( -2,8 \right),\left( -1,7 \right),\left( 0,6 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 2,4 \right),\left( 3,3 \right)$ .
From the graph, we have to look for the points of the intersection of equations $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ and $y=6-x$ .
We can see that both the equations intersect at $\left( -2,8 \right)$ and $\left( 1.5,4.5 \right)$ (shown as red colour in the graph). The solution of $y=6-x$ will be the set of x coordinates of the points of intersection.
Hence, the solution of $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ is $\left\{ -2,1.5 \right\}$ .

Note: Students must draw the graph of $2{{x}^{2}}+x-6=0$ in the graph of $y=2{{x}^{2}}$ . They must note that the solution set will be the set of x coordinates of the points of intersection not the y-coordinates. They must know to simplify an equation. Students must make the second equation in terms of y.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




