
Draw the graph of the following pair of linear equations.
$x+3y=6$, $2x-3y=12$, hence find the area of the region bounded by lines $x=0,y=0$ and $2x-3y=12$ .
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: In order to plot the graphs, we need to find the two points where the line cuts both the axis. If the point lies on the x-axis that means the coordinate is zero and if the point lies on the y-axis that means the x coordinate is zero. To find the area of the triangle we need to know the formula for that. The area of the triangle is given by $\text{area = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ base }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ height}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The aim is to draw the two equations.
\[x+3y=6\] and $2x-3y=12$ .
Let’s start by plotting the first equation.
It is easier to plot the graph if we have two points where the line cuts.
So, for $x+3y=6$ ,
Let’s get the point it cuts the y-axis.
The point lies on the y-axis that means the x coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+3y=6 \\
& 0+3y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for y we get,
$y=\dfrac{6}{3}=2$
Therefore, let this point be A where $A\left( 0,2 \right)$ .
Let’s get the point: it cuts the x-axis.
The point lies on the x-axis that means the y coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+3y=6 \\
& x+3\left( 0 \right)=6 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for x we get,
$x=6$
Therefore, let this point be B where $B\left( 6,0 \right)$ .
Now following the same procedure for the second equation.
So, for $2x-3y=12$ ,
Let’s get the point it cuts the y-axis.
The point lies on the y-axis that means the x coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y=12 \\
& 2\left( 0 \right)-3y=12 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for y we get,
$y=\dfrac{12}{-3}=-4$
Therefore, let this point be C where $C\left( 0,-3 \right)$ .
Let’s get the point: it cuts the x-axis.
The point lies on the x-axis that means the y coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y=12 \\
& 2x-3\left( 0 \right)=12 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for x we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x=12 \\
& x=\dfrac{12}{2}=6 \\
\end{align}$
The coordinates are the same as that of B.
Therefore, at this point $B\left( 6,0 \right)$ , both the lines intersect.
Now drawing these lines, we get,
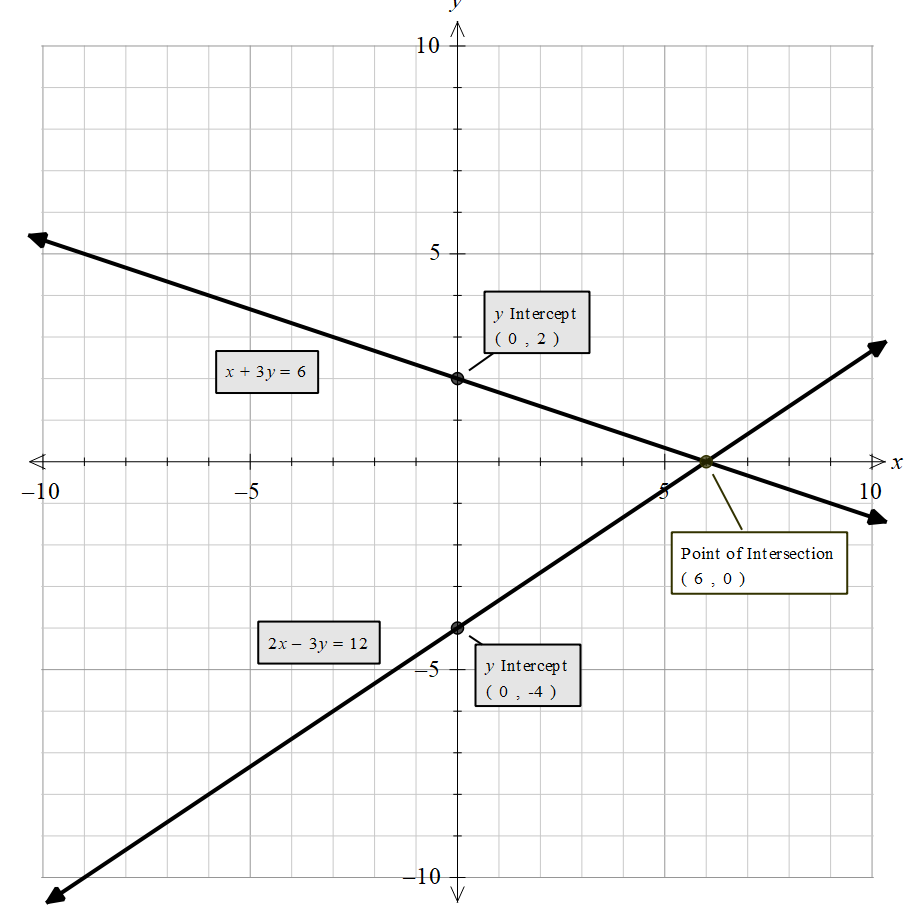
Now, we need to find the area of the region bounded by the lines $x=0,y=0$ and $2x-3y=12$ .
Let’s draw the lines of $x=0,y=0$ . we get,
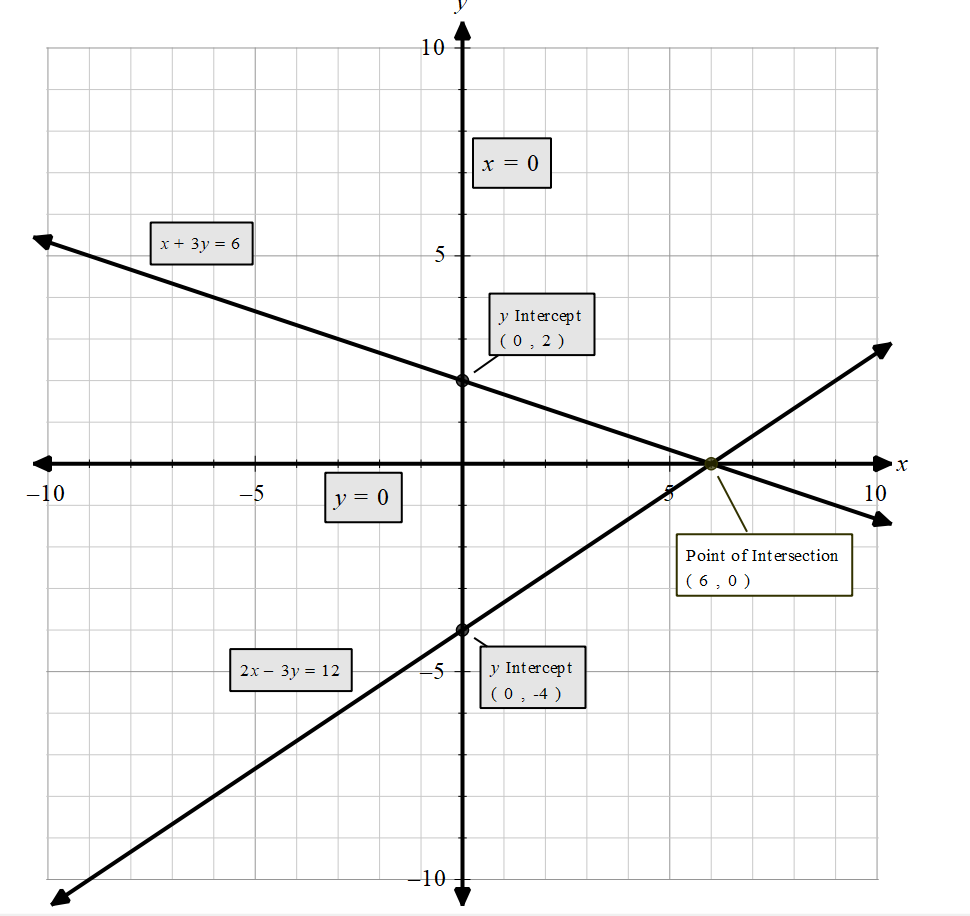
Now, we can mark the shaded region as follows,
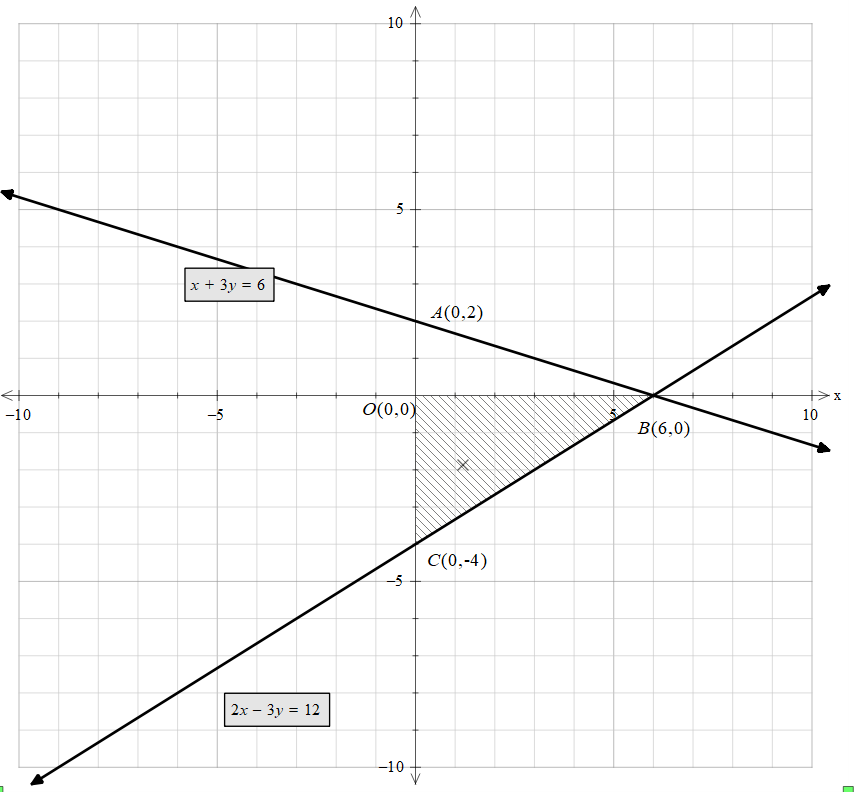
In this diagram, we can see that the shape formed is a triangle.
The area of the triangle is given by $\text{Area = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ base }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ height}$
Here, the base is OB and the height is OC.
To find the distance of OB, we can see that as the y coordinate is the same, we can get by just taking the difference between x coordinates.
Therefore, OB = 6 - 0 = 6 units.
To find the distance of OC, we can see that as the x coordinate is the same, we can get by just taking the difference between y coordinates.
Therefore, OC = 0 – (-4) = 4 units.
Substituting the value in the formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Area = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4} \\
& \text{=3}\times 4=12
\end{align}$
Hence, the area of the triangle is 12 sq. units.
Note: In this problem, we can directly subtract the coordinates because the line was either parallel to the x-axis or parallel to the y-axis. Also, we should not worry about the sign because the sign is always taken as positive as the distance can never be negative.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The aim is to draw the two equations.
\[x+3y=6\] and $2x-3y=12$ .
Let’s start by plotting the first equation.
It is easier to plot the graph if we have two points where the line cuts.
So, for $x+3y=6$ ,
Let’s get the point it cuts the y-axis.
The point lies on the y-axis that means the x coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+3y=6 \\
& 0+3y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for y we get,
$y=\dfrac{6}{3}=2$
Therefore, let this point be A where $A\left( 0,2 \right)$ .
Let’s get the point: it cuts the x-axis.
The point lies on the x-axis that means the y coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+3y=6 \\
& x+3\left( 0 \right)=6 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for x we get,
$x=6$
Therefore, let this point be B where $B\left( 6,0 \right)$ .
Now following the same procedure for the second equation.
So, for $2x-3y=12$ ,
Let’s get the point it cuts the y-axis.
The point lies on the y-axis that means the x coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y=12 \\
& 2\left( 0 \right)-3y=12 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for y we get,
$y=\dfrac{12}{-3}=-4$
Therefore, let this point be C where $C\left( 0,-3 \right)$ .
Let’s get the point: it cuts the x-axis.
The point lies on the x-axis that means the y coordinate is zero.
Hence, substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-3y=12 \\
& 2x-3\left( 0 \right)=12 \\
\end{align}$
Solving for x we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x=12 \\
& x=\dfrac{12}{2}=6 \\
\end{align}$
The coordinates are the same as that of B.
Therefore, at this point $B\left( 6,0 \right)$ , both the lines intersect.
Now drawing these lines, we get,

Now, we need to find the area of the region bounded by the lines $x=0,y=0$ and $2x-3y=12$ .
Let’s draw the lines of $x=0,y=0$ . we get,

Now, we can mark the shaded region as follows,

In this diagram, we can see that the shape formed is a triangle.
The area of the triangle is given by $\text{Area = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ base }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ height}$
Here, the base is OB and the height is OC.
To find the distance of OB, we can see that as the y coordinate is the same, we can get by just taking the difference between x coordinates.
Therefore, OB = 6 - 0 = 6 units.
To find the distance of OC, we can see that as the x coordinate is the same, we can get by just taking the difference between y coordinates.
Therefore, OC = 0 – (-4) = 4 units.
Substituting the value in the formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Area = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4} \\
& \text{=3}\times 4=12
\end{align}$
Hence, the area of the triangle is 12 sq. units.
Note: In this problem, we can directly subtract the coordinates because the line was either parallel to the x-axis or parallel to the y-axis. Also, we should not worry about the sign because the sign is always taken as positive as the distance can never be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




