
How do you draw the graph of the equation $y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$.
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: The above given equation is a quadratic equation. So, to plot the graph of the equation$y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$ we will at first find the vertex of the graph and for the general quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ vertex of the graph is equal to $\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},-\dfrac{D}{4a} \right)$ and here D is the discriminant of that quadratic equation and $D={{b}^{2}}-4ac$. Then, we will find the roots of the equation if it exists and also two or more points and then we will join all these points with smooth and free handed to get the required curve.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can see that the given equation is a quadratic equation as when we can see that x is multiplied two times. We know that the shape of the graph of the quadratic polynomial is a parabola. So, to plot the graph of the equation $y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$we will at first find the vertex of the graph and for the general quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ we know that vertex is given by $\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},-\dfrac{D}{4a} \right)$ where, D is the Discriminant of the quadratic equation and $D={{b}^{2}}-4ac$.
Now, we will multiply the terms of the given quadratic equation and convert it into a standard quadratic equation.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=x\left( x-3 \right)+\left( x-3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-3x+x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3 \\
\end{align}$
So, vertex of the quadratic equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$is $\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},\dfrac{-\left( {{b}^{2}}-4ac \right)}{4a} \right)$, where a =1, b = -2, and c = -3.
So, vertex is $\left( \dfrac{-\left( -2 \right)}{2\times 1},\dfrac{-\left( {{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-4\times \left( 1 \right)\times \left( -3 \right) \right)}{4\times 1} \right)$ = $\left( 1,-4 \right)$
Now, we will solve the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3=0$to get the root of the equation.
Since, we know that $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3=0=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\therefore x=-1,3$
So, the point $\left( -1,0 \right)$ and $\left( 3,0 \right)$ will lie on the graph $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ as they both are the root of this equation.
Also, when we will put $x=\infty $ in the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$, then we will get $y=\infty $.
So, we will first plot the points $\left( 1,-4 \right)$, $\left( -1,0 \right)$, $\left( 3,0 \right)$ on the graph, then we will join all of them with free hand to get the required curve and the graph will goes till $y=\infty $ as it is the maximum point of the graph.
Since, we know that we have got equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$on solving the equation $y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$. So, the graphs of both the equations are the same.
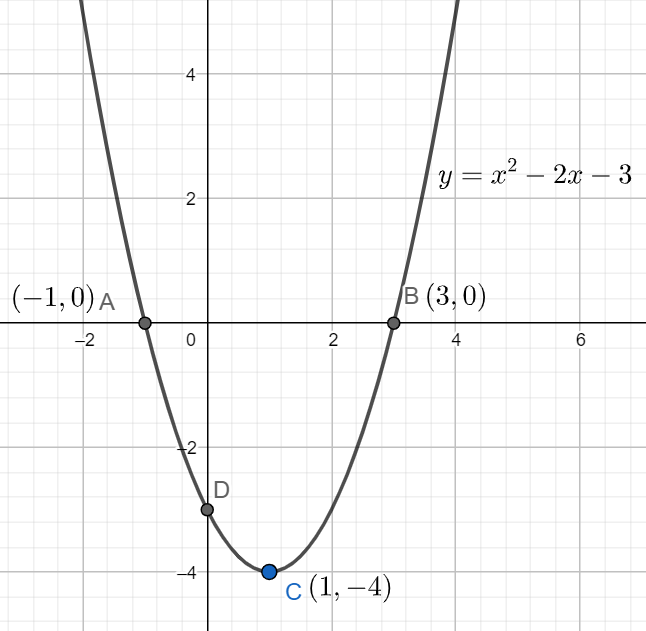
This is our required graph.
Note: We can also find the x- coordinate of the vertex directly by equating the first derivative of the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ to 0 as we know that tangent at vertex for the equation $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ has slope zero. And, then we will put the value of x in the equation to get y-coordinate of the point.
For example: Let us the equation is$y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$:
So, first derivative of the equation is:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2$
Now, when we equate $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ with zero we will get the x- coordinate of the vertex of the given parabola. So,
$\Rightarrow 2x-2=0$
$\Rightarrow x=1$
Now, we will put $x=1$ in the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ to get the y-coordinate of the vertex.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can see that the given equation is a quadratic equation as when we can see that x is multiplied two times. We know that the shape of the graph of the quadratic polynomial is a parabola. So, to plot the graph of the equation $y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$we will at first find the vertex of the graph and for the general quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ we know that vertex is given by $\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},-\dfrac{D}{4a} \right)$ where, D is the Discriminant of the quadratic equation and $D={{b}^{2}}-4ac$.
Now, we will multiply the terms of the given quadratic equation and convert it into a standard quadratic equation.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=x\left( x-3 \right)+\left( x-3 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-3x+x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3 \\
\end{align}$
So, vertex of the quadratic equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$is $\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},\dfrac{-\left( {{b}^{2}}-4ac \right)}{4a} \right)$, where a =1, b = -2, and c = -3.
So, vertex is $\left( \dfrac{-\left( -2 \right)}{2\times 1},\dfrac{-\left( {{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-4\times \left( 1 \right)\times \left( -3 \right) \right)}{4\times 1} \right)$ = $\left( 1,-4 \right)$
Now, we will solve the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3=0$to get the root of the equation.
Since, we know that $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3=0=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\therefore x=-1,3$
So, the point $\left( -1,0 \right)$ and $\left( 3,0 \right)$ will lie on the graph $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ as they both are the root of this equation.
Also, when we will put $x=\infty $ in the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$, then we will get $y=\infty $.
So, we will first plot the points $\left( 1,-4 \right)$, $\left( -1,0 \right)$, $\left( 3,0 \right)$ on the graph, then we will join all of them with free hand to get the required curve and the graph will goes till $y=\infty $ as it is the maximum point of the graph.
Since, we know that we have got equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$on solving the equation $y=\left( x+1 \right)\left( x-3 \right)$. So, the graphs of both the equations are the same.

This is our required graph.
Note: We can also find the x- coordinate of the vertex directly by equating the first derivative of the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ to 0 as we know that tangent at vertex for the equation $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$ has slope zero. And, then we will put the value of x in the equation to get y-coordinate of the point.
For example: Let us the equation is$y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$:
So, first derivative of the equation is:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2$
Now, when we equate $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ with zero we will get the x- coordinate of the vertex of the given parabola. So,
$\Rightarrow 2x-2=0$
$\Rightarrow x=1$
Now, we will put $x=1$ in the equation $y={{x}^{2}}-2x-3$ to get the y-coordinate of the vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




