
Draw the graph of a knee voltage in forward and reverse region.
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: In order to draw a graph first we will understand the definition of knee voltage, then according to its property we will make a graph of knee voltage in forward and reverse region for better understanding of the term in both the regions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Knee voltage: The forward voltage at which the flow of the current during the PN Junction of the diode begins increasing very quickly is commonly known as knee voltage. This voltage is also known as cut-in voltage.
The PN junction diode V-I characteristics are simply a curve between the flow of current in the diode and the applied voltage across the two terminals of the diode. Diode characteristics split into two divisions, such as forwarding characteristics and reverse characteristics.
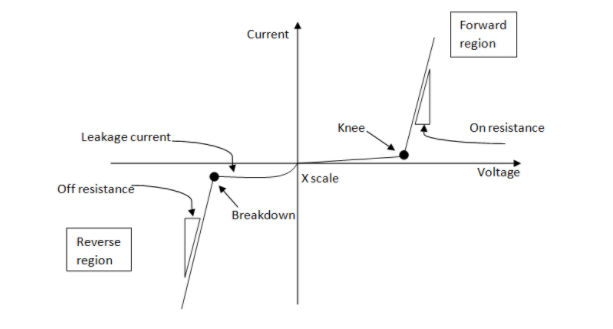
Breakdown voltage: It is the voltage in the reverse biased condition after which the PN Junction fails due to avalanche effect which causes the junction to short and maximum amount of current starts flowing through the junction. These are generally observed in Zener diodes.
Leakage current: It is a small amount of current which passes through the PN junction in reverse biased condition . It can be measured in micro-Ampere$(\mu A)$.
Note: Practically if we take the case of an LED, once the LED or light emitting diode is connected to an external voltage in the forward bias, the potential barrier height across the PN junction will be decreased. The exact voltage is referred to as the Lead knee voltage. When this voltage is reached, the current flow can increase but the voltage is not variable. The knee voltage is different from breakdown voltage, which can be seen in the figure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Knee voltage: The forward voltage at which the flow of the current during the PN Junction of the diode begins increasing very quickly is commonly known as knee voltage. This voltage is also known as cut-in voltage.
The PN junction diode V-I characteristics are simply a curve between the flow of current in the diode and the applied voltage across the two terminals of the diode. Diode characteristics split into two divisions, such as forwarding characteristics and reverse characteristics.

Breakdown voltage: It is the voltage in the reverse biased condition after which the PN Junction fails due to avalanche effect which causes the junction to short and maximum amount of current starts flowing through the junction. These are generally observed in Zener diodes.
Leakage current: It is a small amount of current which passes through the PN junction in reverse biased condition . It can be measured in micro-Ampere$(\mu A)$.
Note: Practically if we take the case of an LED, once the LED or light emitting diode is connected to an external voltage in the forward bias, the potential barrier height across the PN junction will be decreased. The exact voltage is referred to as the Lead knee voltage. When this voltage is reached, the current flow can increase but the voltage is not variable. The knee voltage is different from breakdown voltage, which can be seen in the figure.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




