
Draw the diagram and label any two parts mentioned below.
(a) Bowman’s capsule
(b) Glomerulus
(c) Loop of Henle
(d) Collecting duct
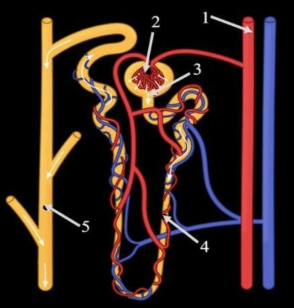

Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: In the urinary system, complex microscopic cells are present and known as nephrons. Their functions include urine production and removal of waste and excess of substance from the blood.
Complete answer:
A nephron is a structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its function is to convert blood into urine by filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion of useful and harmful substances which is present in the blood. In the mammalian kidney nephrons is a long tubular structure which consists of a bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus, Loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, collecting tubule.
1. Bowman’s capsule- It is a cup-shaped structure form where the renal tubule extents. In the Bowman’s capsule, ultrafiltration occurs.
2. Glomerulus- Glomerulus is small tufts of capillaries through which blood flows in the high pressure. These capillaries receive blood from afferent arterioles.
3. Loop of Henle- It is a hairpin-like structure and has a thin and thick ascending limb. Through the loop of Henle fluid which is filtered through the glomerulus reaches the collecting duct. In the Loop of Henle reabsorption of useful substances takes place.
4. Distal convoluted tubule- These tubules contain cell linings having mitochondria which produce energy which is needed for active transport. They reabsorb calcium ions.
5. Proximal convoluted tubule- It is a part of nephrons where saltwater, organic solutes, glucose, and amino acids are filtered.
6. Collecting tubule- This tubule is the final segment before entering the collecting duct. In this tubule reabsorption of water occurs.
In the given diagram: (a) Bowman’s capsule by 3, (b) Glomerulus is represented by 2, (c)Loop of Henle by 4, and (d) Collecting duct by 5.
Note:
Nephrons is a structural and functional unit of the kidney and it regulates water and other soluble substances in the blood, also it helps in maintaining homeostasis of blood volume, and blood pressure by excreting out harmful substances and reabsorbing useful substances.
Complete answer:
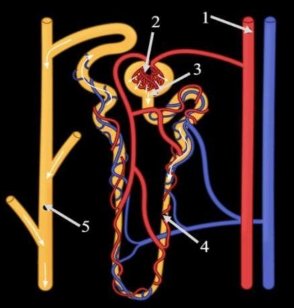
A nephron is a structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its function is to convert blood into urine by filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion of useful and harmful substances which is present in the blood. In the mammalian kidney nephrons is a long tubular structure which consists of a bowman’s capsule, Glomerulus, Loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, collecting tubule.
1. Bowman’s capsule- It is a cup-shaped structure form where the renal tubule extents. In the Bowman’s capsule, ultrafiltration occurs.
2. Glomerulus- Glomerulus is small tufts of capillaries through which blood flows in the high pressure. These capillaries receive blood from afferent arterioles.
3. Loop of Henle- It is a hairpin-like structure and has a thin and thick ascending limb. Through the loop of Henle fluid which is filtered through the glomerulus reaches the collecting duct. In the Loop of Henle reabsorption of useful substances takes place.
4. Distal convoluted tubule- These tubules contain cell linings having mitochondria which produce energy which is needed for active transport. They reabsorb calcium ions.
5. Proximal convoluted tubule- It is a part of nephrons where saltwater, organic solutes, glucose, and amino acids are filtered.
6. Collecting tubule- This tubule is the final segment before entering the collecting duct. In this tubule reabsorption of water occurs.

In the given diagram: (a) Bowman’s capsule by 3, (b) Glomerulus is represented by 2, (c)Loop of Henle by 4, and (d) Collecting duct by 5.
Note:
Nephrons is a structural and functional unit of the kidney and it regulates water and other soluble substances in the blood, also it helps in maintaining homeostasis of blood volume, and blood pressure by excreting out harmful substances and reabsorbing useful substances.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




