
Draw the complete structure of the given compound (using hydrogen- carbon bonds).
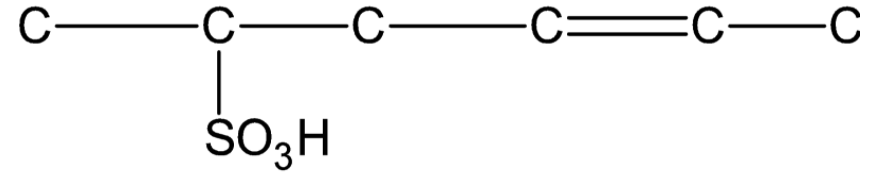

Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint:To answer this question, you must recall the valency of carbon atoms. The valency of an atom is equal to the number of electrons present in the valence shell of the atom. The valence electrons are the most loosely held electrons in the atom and thus they determine the properties of the element.
Complete answer:
We know that the atomic number of carbon is 6 and it carries four valence electrons. Thus, we can see that carbon has four electrons that can take place in bonding and it can easily form four covalent bonds. Thus, it has a valency of 4.
Now we number the carbon chain in the given compound in order to complete its structure.
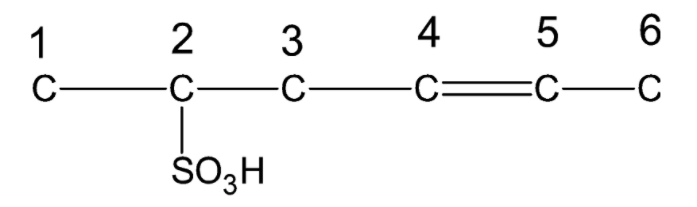
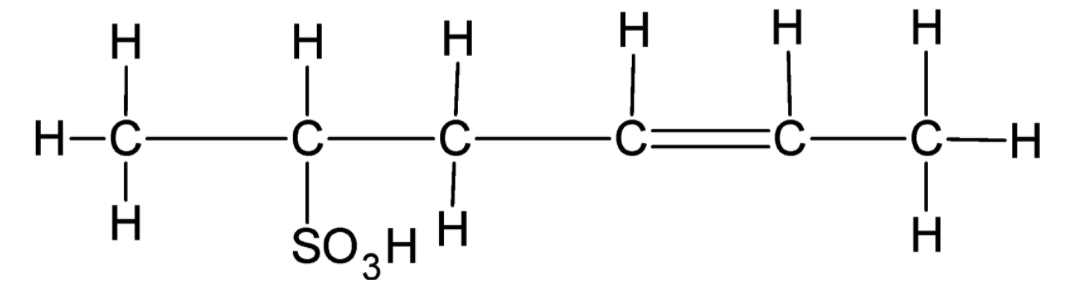
Carbon 1 has only one bond and can form 3 more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to three hydrogen atoms. Carbon 2 has three bonds and can form only one more bond. Thus, it must be bonded to one hydrogen atom. Carbon 3 has two bonds and can form two more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Both carbon 4 and Carbon 5 have three bonds and can form only one more bond. Thus, they must be bonded to one hydrogen atom each. Carbon 6 has only one bond and can form 3 more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
Note:
Each atom tends to attain a stable noble gas- like electronic configuration. This stable electronic configuration can be attained by either losing, gaining or sharing electrons. Valency of an element represents the combining capacity of that element. Valency is not always necessarily equal to the number of valence electrons. For number of valence electrons less than 4, the valency is equal to the number of valence electrons and for number of valence electrons more than 4, the valency is given by subtracting the number of electrons from 8.
Complete answer:
We know that the atomic number of carbon is 6 and it carries four valence electrons. Thus, we can see that carbon has four electrons that can take place in bonding and it can easily form four covalent bonds. Thus, it has a valency of 4.
Now we number the carbon chain in the given compound in order to complete its structure.

Carbon 1 has only one bond and can form 3 more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to three hydrogen atoms. Carbon 2 has three bonds and can form only one more bond. Thus, it must be bonded to one hydrogen atom. Carbon 3 has two bonds and can form two more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Both carbon 4 and Carbon 5 have three bonds and can form only one more bond. Thus, they must be bonded to one hydrogen atom each. Carbon 6 has only one bond and can form 3 more bonds. Thus, it must be bonded to three hydrogen atoms.

Note:
Each atom tends to attain a stable noble gas- like electronic configuration. This stable electronic configuration can be attained by either losing, gaining or sharing electrons. Valency of an element represents the combining capacity of that element. Valency is not always necessarily equal to the number of valence electrons. For number of valence electrons less than 4, the valency is equal to the number of valence electrons and for number of valence electrons more than 4, the valency is given by subtracting the number of electrons from 8.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




