
Draw Sawhorse projection for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, we must first understand the concept of Sawhorse projection. Then we need to assess the points leading to the stability of these conformations and then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts about Sawhorse Projection:
Sawhorse Projection is a view of a molecule down a particular carbon-carbon bond, and groups connected to both the front and back carbons are drawn using sticks at ${120^ \circ }$ angles. Sawhorse Projections can also be drawn so that the groups on the front carbon are staggered ( ${60^ \circ }$ apart) or eclipsed (directly overlapping) with the groups on the back carbon. Below are two Sawhorse Projections of ethane.
The structure on the left is staggered, and the structure on the right is eclipsed. These are the simplest Sawhorse Projections because they have only two carbons, and all of the groups on the front and back carbons are identical.
Step 1: The sawhorse projection is:
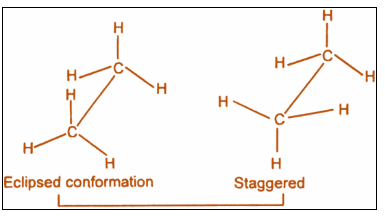
Step 2: The stability of conformations can be understood by:
Clearly we can observe that, In staggered form of ethane, the electron clouds of carbon-hydrogen bonds are as far apart as possible. Thus, there are minimum repulsive forces, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule.
Whereas on the other hand, when the staggered form changes into the eclipsed form, the electron clouds of the carbon-hydrogen bonds come closer to each other resulting in increase in electron cloud repulsion.
And in order to check the increased repulsive forces, molecules will have to possess more energy and thus have less stability.
Hence, Staggered form is more stable.
Note:Sawhorse projections are useful for determining if two molecules are enantiomers or diastereomers. They make it easier to see if the structures are mirror images or superimposable.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts about Sawhorse Projection:
Sawhorse Projection is a view of a molecule down a particular carbon-carbon bond, and groups connected to both the front and back carbons are drawn using sticks at ${120^ \circ }$ angles. Sawhorse Projections can also be drawn so that the groups on the front carbon are staggered ( ${60^ \circ }$ apart) or eclipsed (directly overlapping) with the groups on the back carbon. Below are two Sawhorse Projections of ethane.
The structure on the left is staggered, and the structure on the right is eclipsed. These are the simplest Sawhorse Projections because they have only two carbons, and all of the groups on the front and back carbons are identical.
Step 1: The sawhorse projection is:

Step 2: The stability of conformations can be understood by:
Clearly we can observe that, In staggered form of ethane, the electron clouds of carbon-hydrogen bonds are as far apart as possible. Thus, there are minimum repulsive forces, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule.
Whereas on the other hand, when the staggered form changes into the eclipsed form, the electron clouds of the carbon-hydrogen bonds come closer to each other resulting in increase in electron cloud repulsion.
And in order to check the increased repulsive forces, molecules will have to possess more energy and thus have less stability.
Hence, Staggered form is more stable.
Note:Sawhorse projections are useful for determining if two molecules are enantiomers or diastereomers. They make it easier to see if the structures are mirror images or superimposable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




