
How can I draw Fischer projection from Haworth?
Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint :A Fischer projection is a way to represent a chemical compound in 2D structure without disturbing the stereochemistry of the molecule i.e., absolute configuration of the chiral carbons whereas Haworth projection is a way to represent cyclic compounds with a three-dimensional perspective.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
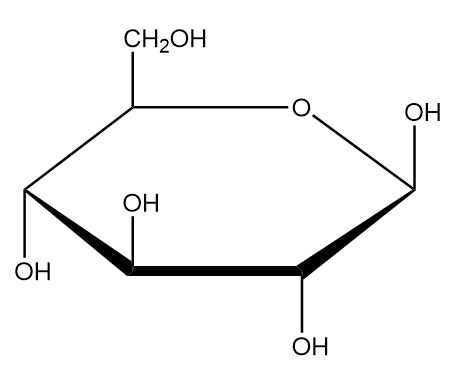
Let us consider an example of D-glucose, which we need to represent in Fisher projection. The Haworth projection of D-glucose is as follows:
The conversion of Haworth projection to Fischer projection undergoes in following steps:
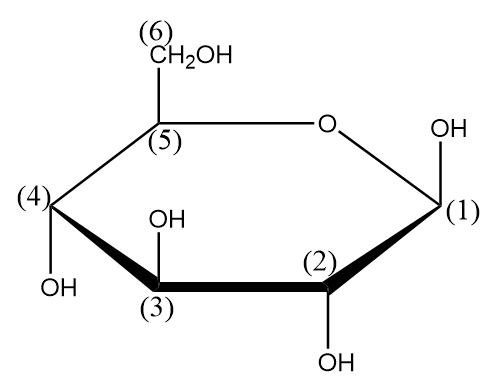
Step-1: The carbon atoms of the ring are numbered so that they can be easily identified from their positions. The numbering of ring is done as follows:
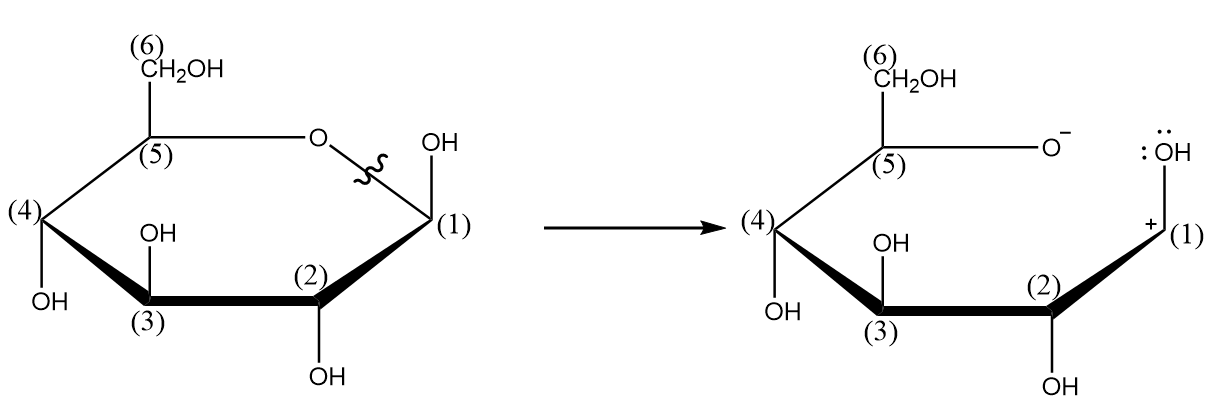
Step-2: Cleavage of the bond between oxygen and carbon-(1) takes place and a carbocation is formed. The process is shown as follows:
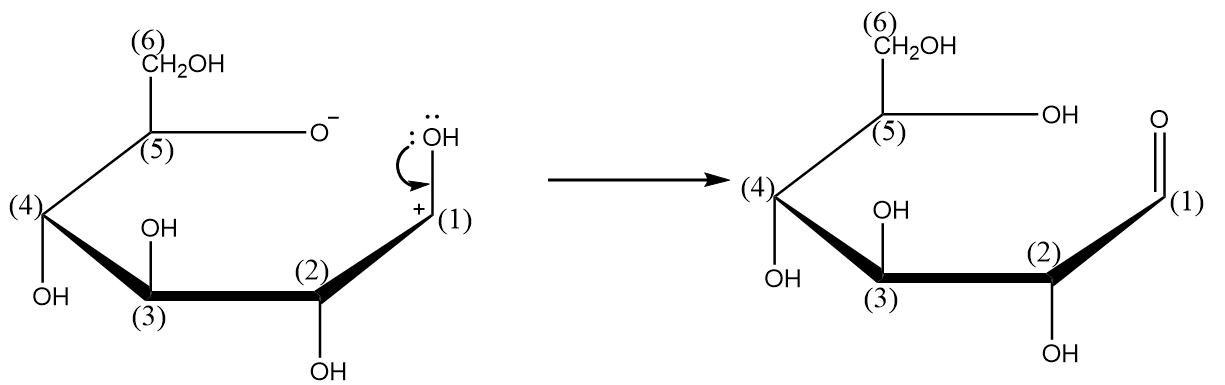
Step-3: The lone pair of electrons of oxygen atom will combine with the carbocation to form a double bond and hydrogen ion released will combine with the oxygen atom having negative charge. The process is shown as follows:
Step-4: Bonds connected with carbon-(5) are rotated in such a way that the $C{H_2}OH$ group aligns within the plane of the ring. The process is shown as follows:
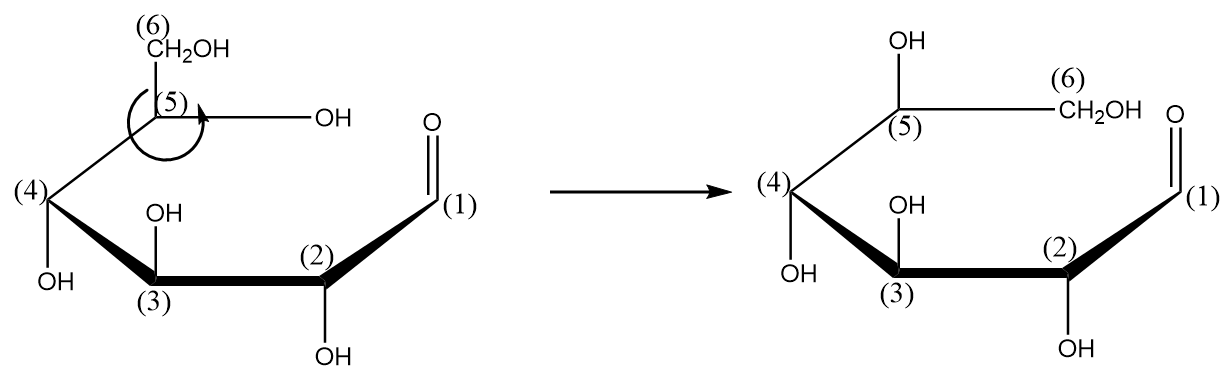
Step-5: Writing the structure of the compound in its complete expanded form as follows:
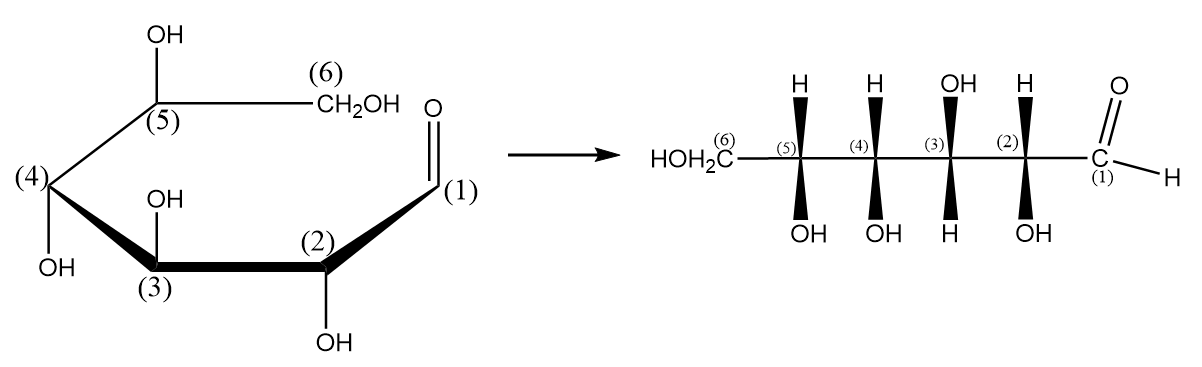
Step-6 Rotating the projection with an angle of ${90^o}$ as follows:
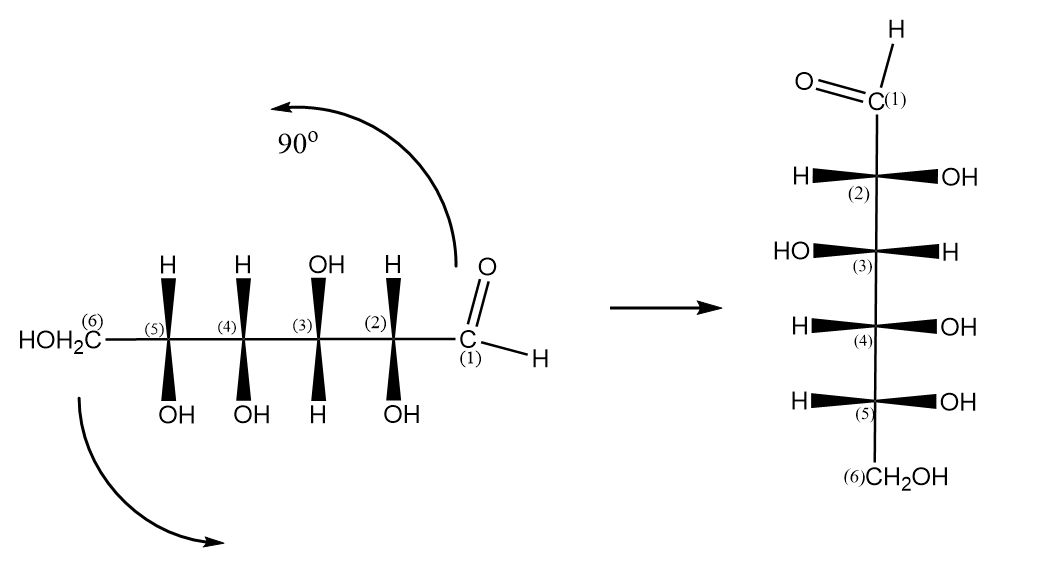
Hence, the equivalent Fischer projection for D-glucose is as follows:
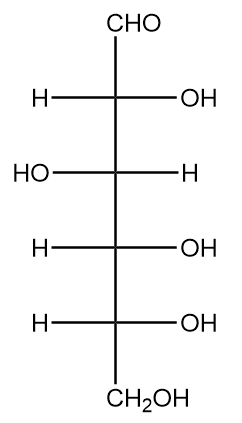
Therefore, by following these general steps we can easily convert Haworth projection into the Fischer projection.
Note :
It is important to know that we can convert the Fischer projection to the Haworth projection by following the steps in reverse order. The Haworth projection is the most convenient to represent a molecule with its stereochemistry.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider an example of D-glucose, which we need to represent in Fisher projection. The Haworth projection of D-glucose is as follows:

The conversion of Haworth projection to Fischer projection undergoes in following steps:
Step-1: The carbon atoms of the ring are numbered so that they can be easily identified from their positions. The numbering of ring is done as follows:

Step-2: Cleavage of the bond between oxygen and carbon-(1) takes place and a carbocation is formed. The process is shown as follows:

Step-3: The lone pair of electrons of oxygen atom will combine with the carbocation to form a double bond and hydrogen ion released will combine with the oxygen atom having negative charge. The process is shown as follows:

Step-4: Bonds connected with carbon-(5) are rotated in such a way that the $C{H_2}OH$ group aligns within the plane of the ring. The process is shown as follows:

Step-5: Writing the structure of the compound in its complete expanded form as follows:

Step-6 Rotating the projection with an angle of ${90^o}$ as follows:

Hence, the equivalent Fischer projection for D-glucose is as follows:

Therefore, by following these general steps we can easily convert Haworth projection into the Fischer projection.
Note :
It is important to know that we can convert the Fischer projection to the Haworth projection by following the steps in reverse order. The Haworth projection is the most convenient to represent a molecule with its stereochemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




