
How can I draw dots-and-crosses diagrams (showing outer electrons only) for ammonia, $ N{{H}_{3}} $ ?
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that depict the bonding between atoms in a molecule, as well as any lone pairs of electrons that may be present. Any covalently bound molecule, as well as coordination compounds, can be represented by a Lewis structure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Ammonia is a nitrogen-hydrogen chemical with the formula $ N{{H}_{3}} $ . Ammonia is a colourless gas with a strong pungent odour. It is a stable binary hydride and the simplest pictogen hydride. It's a frequent nitrogenous waste, especially among aquatic creatures, and it helps terrestrial organisms meet their nutritional demands by acting as a precursor to food and fertilisers. Ammonia is also utilised in many commercial cleaning products and is a building block for the production of many medicinal drugs, either directly or indirectly. It is mostly gathered by air and water displacement downward.
With the dots and crosses at the intersections, you draw crossing circles.
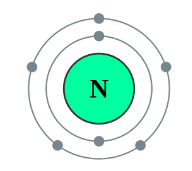
Nitrogen (N) belongs to Group 15, which means it contains five outer electrons. To complete its octet, it needs three additional electrons.
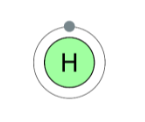
Hydrogen (H) belongs to Group 1, which means it only contains one electron. To complete its valence shell, it requires one additional electron.
Three H atoms sharing electrons and forming covalent connections with a N atom can provide each atom a full shell.
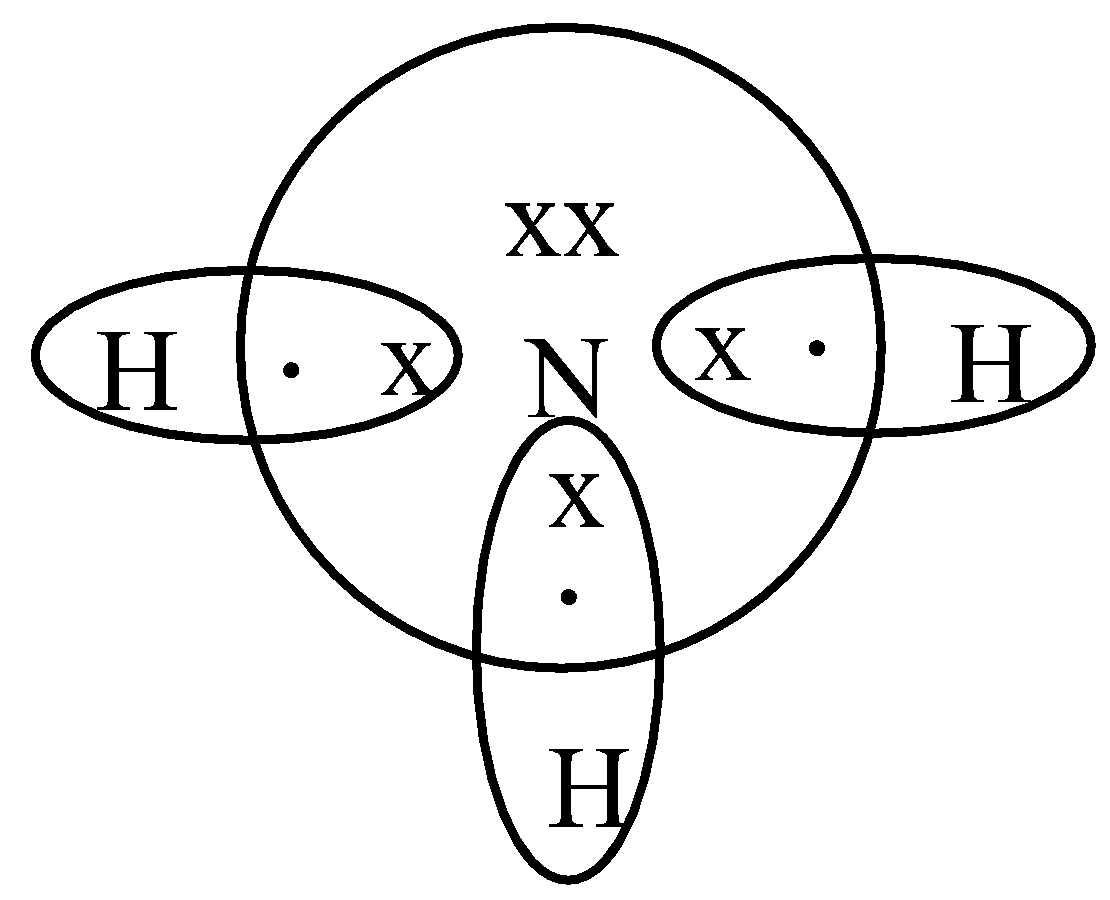
Hence this is the structure of Ammonia.
Note:
Because a particular mechanism exists to prevent ammonia build-up in the circulation, the toxicity of ammonia solutions seldom causes issues in humans and other mammals. The enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase converts ammonia to carbamoyl phosphate, which subsequently enters the urea cycle to be incorporated into amino acids or eliminated in the urine. This process is absent in fish and amphibians, who can generally remove ammonia from their bodies by direct excretion. Ammonia is very poisonous to aquatic creatures, even at low quantities, and is thus categorised as hazardous to the environment.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Ammonia is a nitrogen-hydrogen chemical with the formula $ N{{H}_{3}} $ . Ammonia is a colourless gas with a strong pungent odour. It is a stable binary hydride and the simplest pictogen hydride. It's a frequent nitrogenous waste, especially among aquatic creatures, and it helps terrestrial organisms meet their nutritional demands by acting as a precursor to food and fertilisers. Ammonia is also utilised in many commercial cleaning products and is a building block for the production of many medicinal drugs, either directly or indirectly. It is mostly gathered by air and water displacement downward.
With the dots and crosses at the intersections, you draw crossing circles.
Nitrogen (N) belongs to Group 15, which means it contains five outer electrons. To complete its octet, it needs three additional electrons.
Hydrogen (H) belongs to Group 1, which means it only contains one electron. To complete its valence shell, it requires one additional electron.
Three H atoms sharing electrons and forming covalent connections with a N atom can provide each atom a full shell.



Hence this is the structure of Ammonia.
Note:
Because a particular mechanism exists to prevent ammonia build-up in the circulation, the toxicity of ammonia solutions seldom causes issues in humans and other mammals. The enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase converts ammonia to carbamoyl phosphate, which subsequently enters the urea cycle to be incorporated into amino acids or eliminated in the urine. This process is absent in fish and amphibians, who can generally remove ammonia from their bodies by direct excretion. Ammonia is very poisonous to aquatic creatures, even at low quantities, and is thus categorised as hazardous to the environment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




