
Draw chain and dot structure of first two alkanes
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Here the dot structure refers to the Lewis structure and the chain structures refers to show the chemical bonding in the structure. From this much information it is easy to draw the following.
Complete answer:
First let us look into Lewis structure.
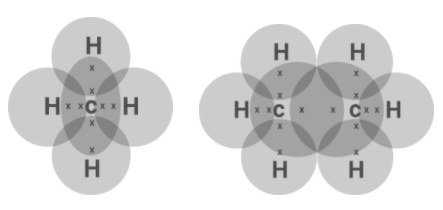
We know it is a simplified representation of valence shell electrons in a molecule. We are asked to draw the dot structure of the first two alkane. As we know the first two alkanes are methane $\left( {C{H_4}} \right)$ and ethane ${C_2}{H_6}$
Then the Lewis structure is obtained by drawing the valence electrons of carbons as dot around them. We know that carbon has four valence electrons. So, we can form 4 bonds with another atom since this is how they complete their octet of 8. When they share their electron with hydrogen which has one 1 electron, they have four electrons from hydrogens and the carbons complete their octet of 8. Also, hydrogen only needs 2 electrons in its shell therefore they also complete their shell. The shared electrons are presented in a circle.
Now for ethane the process is the same as we have two carbon atoms both of them have 3 hydrogen atoms to pair up with and the remaining one is shared among them the carbon atom to complete their octet.
Chain Structure:
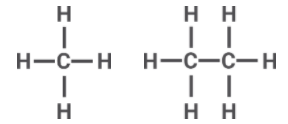
In chain structure we represent the shared electrons in a line, as they are the covalent bond formed in between them. The concept for obtaining the octet is the same as the Lewis structure, the only difference is that we just draw a line in place of the circle.
Note:
When there are two electrons sharing the same atom we obtain double and if three atoms are shared with the same atom we obtain triples bonds. In chained structure they will have double lines and triple lines respectively.
Complete answer:
First let us look into Lewis structure.
We know it is a simplified representation of valence shell electrons in a molecule. We are asked to draw the dot structure of the first two alkane. As we know the first two alkanes are methane $\left( {C{H_4}} \right)$ and ethane ${C_2}{H_6}$
Then the Lewis structure is obtained by drawing the valence electrons of carbons as dot around them. We know that carbon has four valence electrons. So, we can form 4 bonds with another atom since this is how they complete their octet of 8. When they share their electron with hydrogen which has one 1 electron, they have four electrons from hydrogens and the carbons complete their octet of 8. Also, hydrogen only needs 2 electrons in its shell therefore they also complete their shell. The shared electrons are presented in a circle.
Now for ethane the process is the same as we have two carbon atoms both of them have 3 hydrogen atoms to pair up with and the remaining one is shared among them the carbon atom to complete their octet.

Chain Structure:
In chain structure we represent the shared electrons in a line, as they are the covalent bond formed in between them. The concept for obtaining the octet is the same as the Lewis structure, the only difference is that we just draw a line in place of the circle.

Note:
When there are two electrons sharing the same atom we obtain double and if three atoms are shared with the same atom we obtain triples bonds. In chained structure they will have double lines and triple lines respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




