
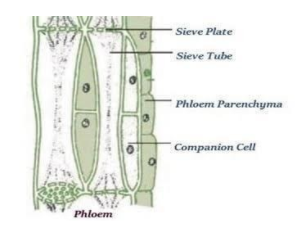
Draw and label the diagram of phloem?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Phloem is a living tissue of vascular plants. This companion cell in plants helps sieve elements in transport, the parenchyma cell in plants help in food storage within the plant, the sieve tubes transport sugars throughout the various parts of plants, and the sclerenchyma provides support to the plants.
Complete answer:
Phloem is a vascular tissue of plants. It plays an important role in the transportation of soluble organic photosynthesis (they are compounds made during the photosynthesis process) to the different plant parts. Phloem is composed of four types of cells, namely-
companion cells, parenchyma, sieve elements, and Sclerenchyma (or phloem fibers).
The structure of the phloem is made up of several different components. Each of these components works together as a team to provide CONDUCTION of sugars as well as amino acids, obtained from a source, and to sink tissues where they are consumed or stored by the leaves.
THE COMPANION CELLS
Each sieve element cell is closely associated with a ‘companion cell’ in angiosperms along with an aluminous cell or usually known as ‘Strasburg cell’ in gymnosperms
PARENCHYMA
The parenchyma is a collection of multiple cells, which together make a ‘filler’ of plant tissues. They have thin but very flexible walls made of cellulose. Within the phloem structure, the parenchyma’s main function is to store starch, fats as well as proteins along with tannins and resins in certain species of plants.
SIEVE PLATES
The place where sieve member cells connect with each other is known as sieve plates. These sieve plates can easily be modified by plasmodesmata.
SCLERENCHYMA
The sclerenchyma is the main support tissue of the phloem structure, which provides stiffness as well as strength to the plant. Sclerenchyma comes in two forms:
> fibers and
> sclerosis
Both are characterized by a thick secondary cell wall along with are usually dead upon reaching maturity.
Note: Phloem is the vascular tissue in charge of transportation along with the distribution of the organic nutrients around the body of plants. The phloem is also said to be a pathway to signaling molecules as well as has a structural function in the plant body.
Complete answer:
Phloem is a vascular tissue of plants. It plays an important role in the transportation of soluble organic photosynthesis (they are compounds made during the photosynthesis process) to the different plant parts. Phloem is composed of four types of cells, namely-
companion cells, parenchyma, sieve elements, and Sclerenchyma (or phloem fibers).
The structure of the phloem is made up of several different components. Each of these components works together as a team to provide CONDUCTION of sugars as well as amino acids, obtained from a source, and to sink tissues where they are consumed or stored by the leaves.
THE COMPANION CELLS
Each sieve element cell is closely associated with a ‘companion cell’ in angiosperms along with an aluminous cell or usually known as ‘Strasburg cell’ in gymnosperms
PARENCHYMA
The parenchyma is a collection of multiple cells, which together make a ‘filler’ of plant tissues. They have thin but very flexible walls made of cellulose. Within the phloem structure, the parenchyma’s main function is to store starch, fats as well as proteins along with tannins and resins in certain species of plants.
SIEVE PLATES
The place where sieve member cells connect with each other is known as sieve plates. These sieve plates can easily be modified by plasmodesmata.
SCLERENCHYMA
The sclerenchyma is the main support tissue of the phloem structure, which provides stiffness as well as strength to the plant. Sclerenchyma comes in two forms:
> fibers and
> sclerosis
Both are characterized by a thick secondary cell wall along with are usually dead upon reaching maturity.

Note: Phloem is the vascular tissue in charge of transportation along with the distribution of the organic nutrients around the body of plants. The phloem is also said to be a pathway to signaling molecules as well as has a structural function in the plant body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




