
Draw a well-labelled diagram of a plant cell.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that change in several fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus alongside similar organelles. One among the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane.
Complete step by step answer:
Plant cell structure includes various components referred to as cell organelles that perform different functions to sustain itself. These organelles include,
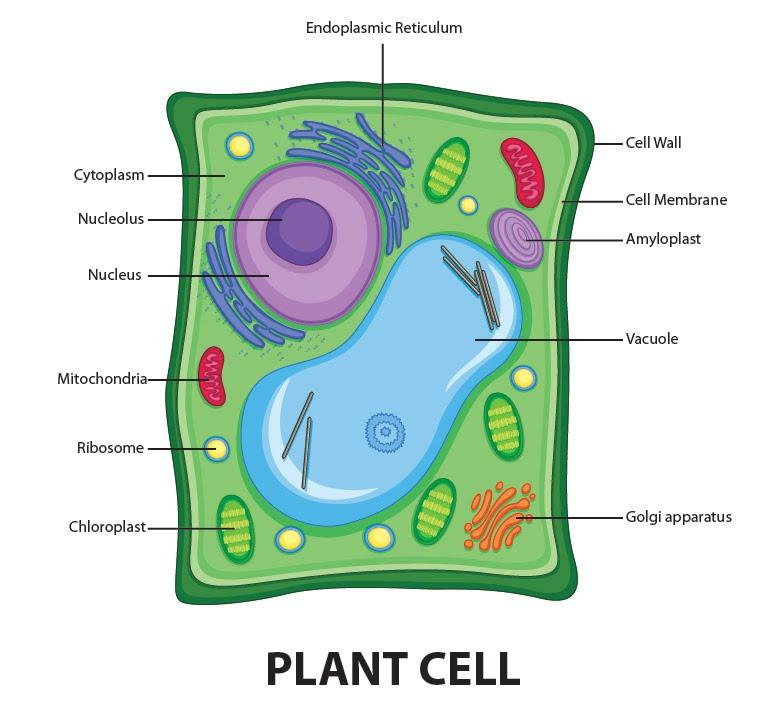
Cell Wall: It's a rigid layer which consists of cellulose, glycoproteins, lignin, pectin and hemicellulose. It’s located outside the cell wall. It comprises proteins, polysaccharides and cellulose.
Cell membrane: It's the semi-permeable membrane that's present within the cell wall. It’s composed of a skinny layer of protein and fat. The cell wall plays a crucial role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells. The vital function of a nucleus is to store DNA or hereditary information required for cellular division, metabolism and growth.
Central Vacuole: It occupies around 30 percent of the cell’s volume during a mature plant cell. The vital function of central vacuole aside from storage is to sustain turgor pressure against the cell membrane. The central vacuole consists of cell sap. It’s a mix of salts, enzymes and other substances.
Golgi apparatus: they're found altogether in eukaryotic cells which are involved in distributing synthesized macromolecules to varied parts of the cell.
Ribosomes: they're the littlest membrane-bound organelles which comprise RNA and protein. They’re the sites for protein synthesis, hence, also mentioned because of the protein factories of the cell.
Mitochondria: they're the double-membrane organelles found within the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. They supply energy by breaking down carbohydrate and sugar molecules, hence they're also mentioned because of the “Powerhouse of the cell.”
Lysosome: Lysosomes are called suicidal bags as they hold digestive enzymes in an indoor membrane. They perform the function of cellular waste disposal by digesting worn-out organelles, food particles and foreign bodies within the cell.
Note: Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. Photosynthesis is the major purpose performed by plant cells. Photosynthesis occurs within the chloroplasts of the plant cell. It’s the method of preparing food by the plants, by utilizing sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. Energy is produced within the sort of ATP within the process. A couple of plant cells help within the transport of water and nutrients from the roots and leaves to different parts of the plants.
Complete step by step answer:
Plant cell structure includes various components referred to as cell organelles that perform different functions to sustain itself. These organelles include,

Cell Wall: It's a rigid layer which consists of cellulose, glycoproteins, lignin, pectin and hemicellulose. It’s located outside the cell wall. It comprises proteins, polysaccharides and cellulose.
Cell membrane: It's the semi-permeable membrane that's present within the cell wall. It’s composed of a skinny layer of protein and fat. The cell wall plays a crucial role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells. The vital function of a nucleus is to store DNA or hereditary information required for cellular division, metabolism and growth.
Central Vacuole: It occupies around 30 percent of the cell’s volume during a mature plant cell. The vital function of central vacuole aside from storage is to sustain turgor pressure against the cell membrane. The central vacuole consists of cell sap. It’s a mix of salts, enzymes and other substances.
Golgi apparatus: they're found altogether in eukaryotic cells which are involved in distributing synthesized macromolecules to varied parts of the cell.
Ribosomes: they're the littlest membrane-bound organelles which comprise RNA and protein. They’re the sites for protein synthesis, hence, also mentioned because of the protein factories of the cell.
Mitochondria: they're the double-membrane organelles found within the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. They supply energy by breaking down carbohydrate and sugar molecules, hence they're also mentioned because of the “Powerhouse of the cell.”
Lysosome: Lysosomes are called suicidal bags as they hold digestive enzymes in an indoor membrane. They perform the function of cellular waste disposal by digesting worn-out organelles, food particles and foreign bodies within the cell.
Note: Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. Photosynthesis is the major purpose performed by plant cells. Photosynthesis occurs within the chloroplasts of the plant cell. It’s the method of preparing food by the plants, by utilizing sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. Energy is produced within the sort of ATP within the process. A couple of plant cells help within the transport of water and nutrients from the roots and leaves to different parts of the plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




