
Draw a simple sketch of a step-up transformer. Label the different parts in the diagram.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: A transformer is a device that can increase or decrease the voltage or current of an AC source as per our convenience. It consists of two coils called the primary and secondary coils. These coils are wounded across an iron core.
Complete answer:
A transformer is a device that can increase or decrease the voltage of the circuit as per requirement. It consists of a primary coil and secondary coil. The coil attached to the input source is called a primary coil and the coil attached to the output circuit is called a secondary coil as shown. Therefore, the primary coil acts as an input and the secondary coil acts as an output.
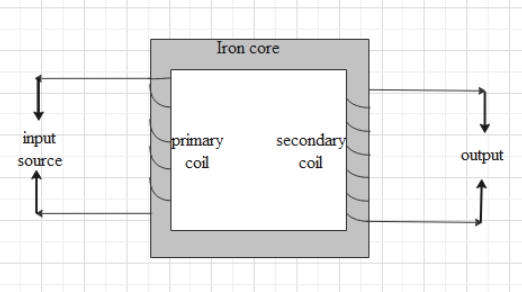
A transformer is used in two ways. One is to get a voltage greater than the voltage of the primary coil. This type of transformer is called a step-up transformer.
Another is get the voltage of the secondary coil smaller than the voltage of the primary coil. This type of transformer is called a step-down transformer.
A transformer works the principle of electro-magnetic induction. This means that the magnetic flux due to the current in the primary coil, an emf is induced in the secondary coil. The magnetic flux due to the primary coil is carried to the secondary coil with the help of an iron core. An iron core has a property of confining the magnetic field within itself.
The ratio of the voltages across the primary and secondary coils depends on the number of turns in both coils. i.e. $\dfrac{{{V}_{s}}}{{{V}_{p}}}=\dfrac{{{N}_{s}}}{{{N}_{p}}}$.
Here, ${{N}_{s}}$ and ${{N}_{p}}$ are the number of turns in the secondary and the primary coils respectively.
When ${{N}_{s}}$>${{N}_{p}}$, the transformer acts as a step-up transformer.
When ${{N}_{s}}$<${{N}_{p}}$, the transformer acts as a step-down transformer.
Note:
From the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, we know that only a changing magnetic flux through a coil induces an emf in the coil. Therefore, the input source and output voltage on a transformer are AC and not DC.
Complete answer:
A transformer is a device that can increase or decrease the voltage of the circuit as per requirement. It consists of a primary coil and secondary coil. The coil attached to the input source is called a primary coil and the coil attached to the output circuit is called a secondary coil as shown. Therefore, the primary coil acts as an input and the secondary coil acts as an output.

A transformer is used in two ways. One is to get a voltage greater than the voltage of the primary coil. This type of transformer is called a step-up transformer.
Another is get the voltage of the secondary coil smaller than the voltage of the primary coil. This type of transformer is called a step-down transformer.
A transformer works the principle of electro-magnetic induction. This means that the magnetic flux due to the current in the primary coil, an emf is induced in the secondary coil. The magnetic flux due to the primary coil is carried to the secondary coil with the help of an iron core. An iron core has a property of confining the magnetic field within itself.
The ratio of the voltages across the primary and secondary coils depends on the number of turns in both coils. i.e. $\dfrac{{{V}_{s}}}{{{V}_{p}}}=\dfrac{{{N}_{s}}}{{{N}_{p}}}$.
Here, ${{N}_{s}}$ and ${{N}_{p}}$ are the number of turns in the secondary and the primary coils respectively.
When ${{N}_{s}}$>${{N}_{p}}$, the transformer acts as a step-up transformer.
When ${{N}_{s}}$<${{N}_{p}}$, the transformer acts as a step-down transformer.
Note:
From the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, we know that only a changing magnetic flux through a coil induces an emf in the coil. Therefore, the input source and output voltage on a transformer are AC and not DC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




