
Draw a rough sketch of the curves $y=\sin x\ and\ y=\cos x$, as x varies from \[0\ to\ \dfrac{\pi }{2}\], and find the area of the region enclosed between them and the x – axis.
Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: We will first start by drawing a graph for $y=\sin x\ and\ y=\cos x$. Then we will find the area between \[x=0\ to\ x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] by using the integral \[\int{\sin xdx}\ and\ \int{\cos xdx}\] for limits. We will refer to the graph and their point of intersection of all three curves.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we know that the graph of $y=\sin x,y=\cos x\ and\ x-axis$is,
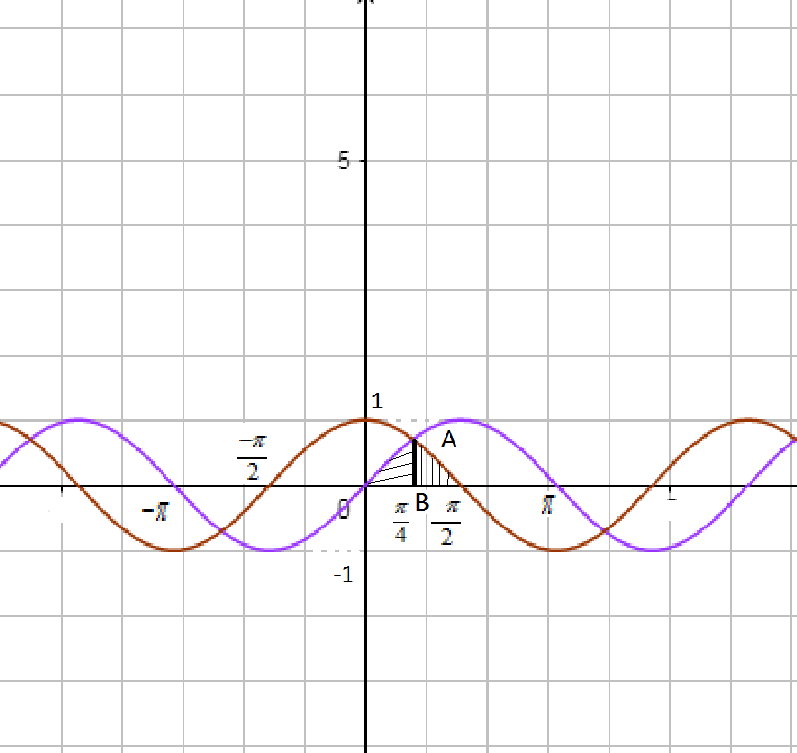
Now, we need to find the point of intersection of $y=\sin x\ and\ y=\cos x$. So we have,
$\begin{align}
& \sin x=\cos x \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that $\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}=\tan x$.
$\Rightarrow \tan x=1$
Now, we know $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}=1$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan x=\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, to find the area of the region bounded by three curves. We have,
ar of region OAE + ar of region AEB
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}{\sin xdx}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{\cos xdx}$
Now, we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \int{\sin \theta d\theta =-\cos \theta } \\
& \int{\cos \theta d\theta =\sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \left. -\cos x \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}+\left. \sin x \right|_{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)-\cos \left( 0 \right) \right)+\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}+\cos \left( 0 \right)+\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\cos \left( 0 \right)=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}}+1+1-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{2}}+2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2-\sqrt{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area bounded by the curves is \[2-\sqrt{2}sq\ units\].
Note: It is important to note that we have to find the point of intersection of $\sin x\ and\cos x$ before integrating as the same will be used as a limit while we integrate.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we know that the graph of $y=\sin x,y=\cos x\ and\ x-axis$is,

Now, we need to find the point of intersection of $y=\sin x\ and\ y=\cos x$. So we have,
$\begin{align}
& \sin x=\cos x \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that $\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}=\tan x$.
$\Rightarrow \tan x=1$
Now, we know $\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4}=1$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan x=\tan \dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, to find the area of the region bounded by three curves. We have,
ar of region OAE + ar of region AEB
$\Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}{\sin xdx}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{\cos xdx}$
Now, we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \int{\sin \theta d\theta =-\cos \theta } \\
& \int{\cos \theta d\theta =\sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \left. -\cos x \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}+\left. \sin x \right|_{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)-\cos \left( 0 \right) \right)+\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}+\cos \left( 0 \right)+\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that,
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\cos \left( 0 \right)=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}}+1+1-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{2}}+2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2-\sqrt{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area bounded by the curves is \[2-\sqrt{2}sq\ units\].
Note: It is important to note that we have to find the point of intersection of $\sin x\ and\cos x$ before integrating as the same will be used as a limit while we integrate.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




