
Draw a ray diagram for a concave mirror when the object is placed between focus and centre of curvature. Also write position, nature and size of image.
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: Study about spherical mirrors. Understand the concepts of image formation in spherical mirrors. Draw a ray diagram to show the process for the given condition. Then try to show the position, magnification and nature of the image.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Concave mirror is a spherical mirror with its reflecting surface inside the curved area. The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part of is called the centre of curvature(c) of the mirror. Again, when light ray travelling parallel to the principal axis after reflecting passes through a point in the principal axis, which is called the focus(F) of the mirror.
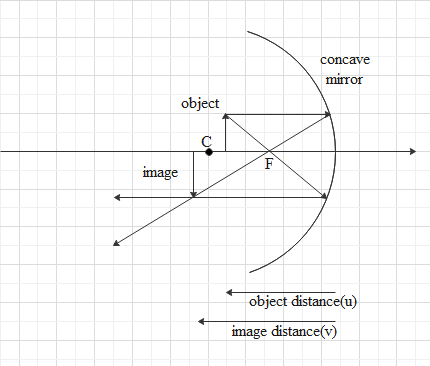
Here, the object is in front of the mirror at a point between the centre of curvature and the focus of the mirror. The light ray coming from the object parallel to the principal axis will reflect at the mirror and pass through the focus. Another light ray will go through the focus and will reflect parallel to the principal axis and will intersect with the first ray. This way we will get the image of the object.
The image will form outside the centre of curvature of the mirror.
The image will be inverted and is a real image in nature.
Image will be magnified because the distance of image from the centre of mirror is larger than the distance of object from mirror.
Note: If we consider different positions for the object in front of the mirror, the characteristics of the image will also be different. If we consider a convex mirror it will always produce a virtual and diminished image behind the mirror.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Concave mirror is a spherical mirror with its reflecting surface inside the curved area. The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part of is called the centre of curvature(c) of the mirror. Again, when light ray travelling parallel to the principal axis after reflecting passes through a point in the principal axis, which is called the focus(F) of the mirror.

Here, the object is in front of the mirror at a point between the centre of curvature and the focus of the mirror. The light ray coming from the object parallel to the principal axis will reflect at the mirror and pass through the focus. Another light ray will go through the focus and will reflect parallel to the principal axis and will intersect with the first ray. This way we will get the image of the object.
The image will form outside the centre of curvature of the mirror.
The image will be inverted and is a real image in nature.
Image will be magnified because the distance of image from the centre of mirror is larger than the distance of object from mirror.
Note: If we consider different positions for the object in front of the mirror, the characteristics of the image will also be different. If we consider a convex mirror it will always produce a virtual and diminished image behind the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




