
How do you draw a Newman projection for hexane while sighting down $ {C_2} - {C_3} $ ?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: For the given problem, we first need to figure out the normal structure of hexane which is a straight chain of six carbon atoms with all valances satisfied by the hydrogen atoms. Then figuring out the $ {C_2} - {C_3} $ and then fixing them in Newman projection template. After fixing the groups on the template, we have the Newman structure of hexane.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
1. Draw the structure of hexane.
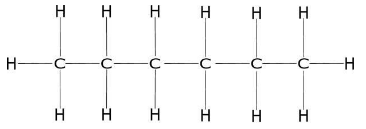
2. Convert the drawn structure from $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ to a wedge-dash structure.
3. Identifies the $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ groups.
The main chain of hexane is the horizontal zigzag line of carbon atoms. $ {C_1} $ is on the left.
The groups of $ {C_2} $ are $ H,H\& C{H_3} $ . At $ {C_3} $ are $ H,H,\& C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} $ .
4. Draw the Newman projection template.
5. Attach the group to the carbon in the template.
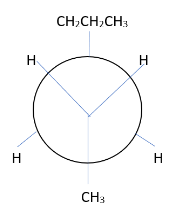
Shows the numerator from the left. The group of $ {C_2} $ is on the previous carbon atom. Place the $ C{H_3} $ group at the bottom. The two hydrogen atoms move to the other bond. The group of $ {C_3} $ moves to the rear carbon. The bulky $ C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} $ group is at the top and two hydrogen atoms are on the other bond.
This is the most stable conformer because it has displaced volumetric methyl and propyl groups.
Note:
The Newman projection, useful in alkane stereochemistry, visualizes the structure of a chemical bond from front to back, with the front atom represented as a point and the rear carbon as a circle. The carbon atom in front is called near, while the atom behind is called far.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
1. Draw the structure of hexane.

2. Convert the drawn structure from $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ to a wedge-dash structure.
3. Identifies the $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ groups.
The main chain of hexane is the horizontal zigzag line of carbon atoms. $ {C_1} $ is on the left.
The groups of $ {C_2} $ are $ H,H\& C{H_3} $ . At $ {C_3} $ are $ H,H,\& C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} $ .
4. Draw the Newman projection template.
5. Attach the group to the carbon in the template.

Shows the numerator from the left. The group of $ {C_2} $ is on the previous carbon atom. Place the $ C{H_3} $ group at the bottom. The two hydrogen atoms move to the other bond. The group of $ {C_3} $ moves to the rear carbon. The bulky $ C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3} $ group is at the top and two hydrogen atoms are on the other bond.
This is the most stable conformer because it has displaced volumetric methyl and propyl groups.
Note:
The Newman projection, useful in alkane stereochemistry, visualizes the structure of a chemical bond from front to back, with the front atom represented as a point and the rear carbon as a circle. The carbon atom in front is called near, while the atom behind is called far.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




