
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of chloroplasts.
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: Plants form the base and are recognised as creators of all life on earth. In animal cells, plant cells contain structures known as plastids that are absent. These plastids are double-membraned organelles of cells which play a primary role in food production and storage.
Complete answer:
The three types of plastids are:
Chromoplasts-They are plastids of colour, present in all flowers and fruits and are primarily responsible for their distinctive colours.
Chloroplasts-They are green coloured plastids that are called chlorophyll, which contain green coloured pigments within the plant cell.
Leucoplasts-They are colourless plastids and are used primarily to store starch, lipids and proteins within the plant cells.
Chloroplasts are found in all green plants and algae. They are the food producers of plants. These are found in the guard cells that are located in the plants' leaves. They contain a high concentration of sunlight-trapping chlorophyll. In animal cells, this cell organelle is not present.
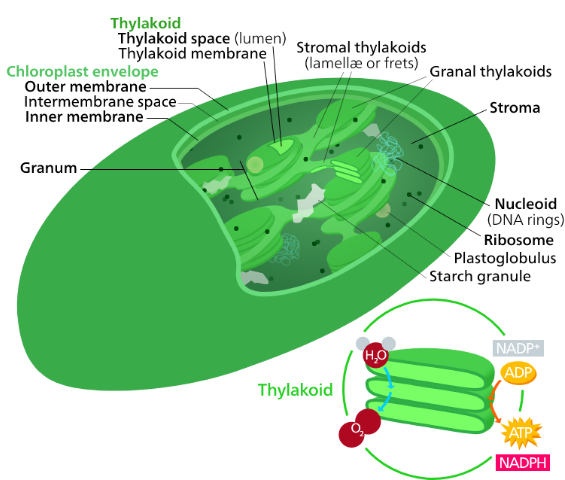
In all taller plants, chloroplasts are found. It is oval or biconvex, located inside the plant cell's mesophyll. The chloroplast size normally ranges between a diameter of 4-6 μm and a thickness of 1-3 μm. With the presence of external, inner and intermembrane space, they are double-membrane organelles. In a chloroplast known as the grana and stroma, there are two distinct regions present.
Stacks of disc-shaped structures known as thylakoids are made up of Grana. Chloroplast grana is composed of chlorophyll pigments and is the functional unit of chloroplasts.
Stroma is the grana-containing homogenous matrix that is identical to the cytoplasm in cells in which all the organelles are embedded. Various enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and other compounds are also found in Stroma. By linking the stacks of thylakoid sacs, stroma lamellae works.
Note: The chloroplast's most significant role is to synthesise food through the photosynthesis method.
absorbs and converts light energy into chemical energy.
Chloroplast has a structure called chlorophyll that works by trapping solar energy and in all green plants it is used for food synthesis.
The photosynthesis method generates ATP-Adenosine triphosphate.
Complete answer:
The three types of plastids are:
Chromoplasts-They are plastids of colour, present in all flowers and fruits and are primarily responsible for their distinctive colours.
Chloroplasts-They are green coloured plastids that are called chlorophyll, which contain green coloured pigments within the plant cell.
Leucoplasts-They are colourless plastids and are used primarily to store starch, lipids and proteins within the plant cells.
Chloroplasts are found in all green plants and algae. They are the food producers of plants. These are found in the guard cells that are located in the plants' leaves. They contain a high concentration of sunlight-trapping chlorophyll. In animal cells, this cell organelle is not present.
In all taller plants, chloroplasts are found. It is oval or biconvex, located inside the plant cell's mesophyll. The chloroplast size normally ranges between a diameter of 4-6 μm and a thickness of 1-3 μm. With the presence of external, inner and intermembrane space, they are double-membrane organelles. In a chloroplast known as the grana and stroma, there are two distinct regions present.
Stacks of disc-shaped structures known as thylakoids are made up of Grana. Chloroplast grana is composed of chlorophyll pigments and is the functional unit of chloroplasts.
Stroma is the grana-containing homogenous matrix that is identical to the cytoplasm in cells in which all the organelles are embedded. Various enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and other compounds are also found in Stroma. By linking the stacks of thylakoid sacs, stroma lamellae works.
| Structure | Function |
| Membrane Envelope | It contains bilayer membranes of inner and outer lipids. The inner membrane divides the intermembrane space from the stroma. |
| Intermembrane space | A void between the membranes inside and outside. |
| Thylakoid system | In the thylakoid membranes, the green coloured pigments called chlorophyll are found. It is the vision for the photosynthesis system of light-dependent reactions. In stacks known as grana, the thylakoids are organised and each granum contains approximately 10-20 thylakoids. |
| Stroma | It is a colourless, alkaline, aqueous, protein-rich fluid found in the grana-surrounding inner membrane of the chloroplast. |
| Grana | These are the sites of light energy conversion into chemical energy. |
| Chlorophyll | It is a photosynthetic green pigment that aids in the photosynthesis process. |

Note: The chloroplast's most significant role is to synthesise food through the photosynthesis method.
absorbs and converts light energy into chemical energy.
Chloroplast has a structure called chlorophyll that works by trapping solar energy and in all green plants it is used for food synthesis.
The photosynthesis method generates ATP-Adenosine triphosphate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




