
Draw a longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts:
A. The part that develops into a fruit
B. The part that produces pollen grain
C. The part that transfers male gametes.
D. The part that is Sticky part.
Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D in the diagram given below.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: A complete flower consists of four whorls, viz., Calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. The calyx is the outermost whorl and generally known as the sepals. The corolla or the petals forms the second whorl of the flower. Androecium and gynoecium the male and female reproductive organs respectively make up the third and fourth whorls.
Complete answer:
A. The part that develops into a fruit: The ovary develops into a fruit due to development. The ovary is a part of the gynoecium.
B. The part that produces pollen grain: The anther, a part of the androecium is where the pollens are produced and later carried to the gynoecium to fertilize the female gamete.
C. The part that transfers male gametes: The style present just beneath the stigma transfers pollen grains after being received at the stigma
D. The sticky part- The stigma in the topmost part of gynoecium is sticky. Due to pollination, cross-pollination or self-pollination, the pollen from the anther gets transferred to the stigma and attaches due to sticky effect. Then the pollens are carried downwards to the ovary by style.
b) Refer to the diagram:
A: Part that develops into a fruit: The ovary
B: Part that produces pollen grain: The style
C: Part that transfers male gametes: The anther
D: Sticky Part- The stigma
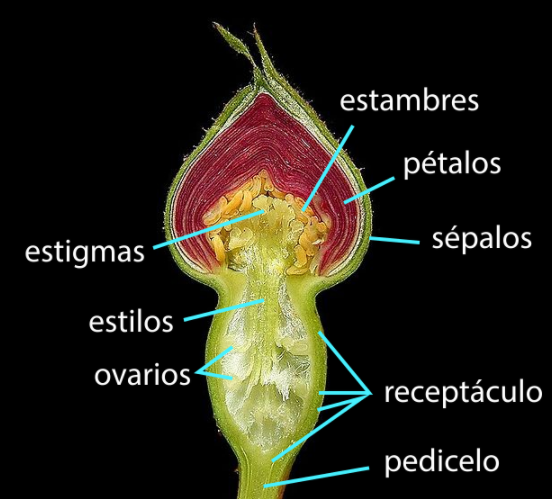
Note: The longitudinal section of a flower shown in the diagram represents the important parts of the androecium and gynoecium. The ovary develops into a fruit, the anther develops into the pollen grains. The style functions in transferring male gametes and stigma are the sticky part.
Complete answer:
A. The part that develops into a fruit: The ovary develops into a fruit due to development. The ovary is a part of the gynoecium.
B. The part that produces pollen grain: The anther, a part of the androecium is where the pollens are produced and later carried to the gynoecium to fertilize the female gamete.
C. The part that transfers male gametes: The style present just beneath the stigma transfers pollen grains after being received at the stigma
D. The sticky part- The stigma in the topmost part of gynoecium is sticky. Due to pollination, cross-pollination or self-pollination, the pollen from the anther gets transferred to the stigma and attaches due to sticky effect. Then the pollens are carried downwards to the ovary by style.
b) Refer to the diagram:
A: Part that develops into a fruit: The ovary
B: Part that produces pollen grain: The style
C: Part that transfers male gametes: The anther
D: Sticky Part- The stigma

Note: The longitudinal section of a flower shown in the diagram represents the important parts of the androecium and gynoecium. The ovary develops into a fruit, the anther develops into the pollen grains. The style functions in transferring male gametes and stigma are the sticky part.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




