
Draw a line segment. Take any point C lying in between A and B. Measure the length of AB, BC and AC. Is AB=AC+CB?
[Note: If A,B,C are any three points on a line, such that AC+CB=AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B]
Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: Here in the given question, we need to draw a line segment of some length and put its name as A and B, now take any new point between this line segment, here we can see that the total length of the line segment will be equal to the sum of length of the starting point to the point taken and then point taken to the end point of line segment.
Complete step by step answer:
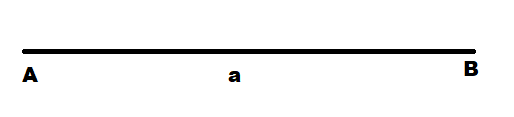
Here the given question is of straight line where to solve this question first we need to draw a line segment of some length say “a”, on solving we get:
Let's take any point between this line segment as “C”, which is midpoint of AB:
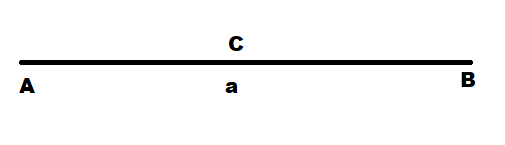
Here C is the midpoint of AB, and at a distance of half of total length of AB, now on solving we get:
\[
\Rightarrow length\,of\,AB = a \\
\Rightarrow length\,of\,AC = \dfrac{a}{2} \\
\Rightarrow length\,of\,CB = \dfrac{a}{2} \\
\Rightarrow AB = AC + CB \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{a}{2} + \dfrac{a}{2} = \dfrac{{a + a}}{2} = \dfrac{{2a}}{2} = a \\
\]
Here we can see that the asked result is here proven, similarly if we take any of the points as C in the same line segment then the summation will always be equal to the whole line segment.
Note: Here in the given question we first draw a line segment and then check for the result, asked by assuming the required values, whenever we need to solve coordinate geometry problems then we need to solve accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
Here the given question is of straight line where to solve this question first we need to draw a line segment of some length say “a”, on solving we get:

Let's take any point between this line segment as “C”, which is midpoint of AB:

Here C is the midpoint of AB, and at a distance of half of total length of AB, now on solving we get:
\[
\Rightarrow length\,of\,AB = a \\
\Rightarrow length\,of\,AC = \dfrac{a}{2} \\
\Rightarrow length\,of\,CB = \dfrac{a}{2} \\
\Rightarrow AB = AC + CB \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{a}{2} + \dfrac{a}{2} = \dfrac{{a + a}}{2} = \dfrac{{2a}}{2} = a \\
\]
Here we can see that the asked result is here proven, similarly if we take any of the points as C in the same line segment then the summation will always be equal to the whole line segment.
Note: Here in the given question we first draw a line segment and then check for the result, asked by assuming the required values, whenever we need to solve coordinate geometry problems then we need to solve accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE

What is the full form of pH?




