
Draw a labelled diagram of T.S. of spinal cord and describe its function.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The central nervous system integrates the received information and impulse and coordinates and it causes to influence the different activities of the organism. Along with the brain and the spinal cord together form the central nervous system.
Complete answer:
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure and is made up of nervous tissues. It extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The spinal cord encloses the central canal of the spinal cord and it contains the cerebrospinal fluid.
The spinal cord arises from the brainstem. It further passes through the foramen magnum and it continues through the conus medullaris and finally, it terminates in a fibrous extension which is known as the filum terminale. Thus, the spinal cord moves from the base of the skull to the first lumbar vertebra.
It is protected by three layers of tissues which is known as the meninges. The dura mater forms the outermost layer and it is protective in nature. The dura mater and vertebrae bones encloses a space that is known as the epidural space and contains adipose tissues and blood vessels. Arachnoid mater is the mid layer.
The transverse section of the peripheral region of the cord shows white matter which contains the sensory and motor axons. Towards the interior of this region, grey matter is present. The grey matter contains nerve cell bodies which are arranged in the three columns. The central part surrounds the central canal. It is the extension of the fourth ventricle and contains the cerebrospinal fluid.
The main function of the spinal cord involves the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex of the body and from afferent fibres of the sensory neurons to the sensory cortex. It forms the center for coordinating the different reflexes. It affects the control reflexes and the reflex arcs. The spinal cord is the location of spinal interneurons. The spinal interneurons are the groups that form the neural circuits and are known as the central pattern generators. These circuits function in the controlling of the motor instructions such as walking and other such rhythmic movements.
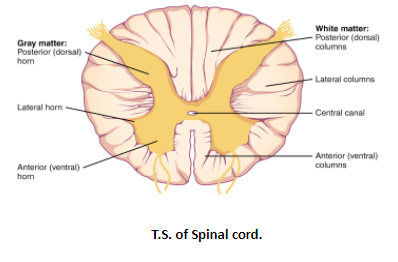
Note: The structure of the spinal cord appears as an elliptical structure. The T.S. of the spinal cord shows the areas of white matter and grey matter. The central canal forms the central portion and it is the extending part of the fourth ventricles. It forms a connection between the central nervous system and the brain and facilitates the movements of the body. It also provides to maintain the structural support of the body and plays an important role in the body reflexes.
Complete answer:
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure and is made up of nervous tissues. It extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The spinal cord encloses the central canal of the spinal cord and it contains the cerebrospinal fluid.
The spinal cord arises from the brainstem. It further passes through the foramen magnum and it continues through the conus medullaris and finally, it terminates in a fibrous extension which is known as the filum terminale. Thus, the spinal cord moves from the base of the skull to the first lumbar vertebra.
It is protected by three layers of tissues which is known as the meninges. The dura mater forms the outermost layer and it is protective in nature. The dura mater and vertebrae bones encloses a space that is known as the epidural space and contains adipose tissues and blood vessels. Arachnoid mater is the mid layer.
The transverse section of the peripheral region of the cord shows white matter which contains the sensory and motor axons. Towards the interior of this region, grey matter is present. The grey matter contains nerve cell bodies which are arranged in the three columns. The central part surrounds the central canal. It is the extension of the fourth ventricle and contains the cerebrospinal fluid.
The main function of the spinal cord involves the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex of the body and from afferent fibres of the sensory neurons to the sensory cortex. It forms the center for coordinating the different reflexes. It affects the control reflexes and the reflex arcs. The spinal cord is the location of spinal interneurons. The spinal interneurons are the groups that form the neural circuits and are known as the central pattern generators. These circuits function in the controlling of the motor instructions such as walking and other such rhythmic movements.

Note: The structure of the spinal cord appears as an elliptical structure. The T.S. of the spinal cord shows the areas of white matter and grey matter. The central canal forms the central portion and it is the extending part of the fourth ventricles. It forms a connection between the central nervous system and the brain and facilitates the movements of the body. It also provides to maintain the structural support of the body and plays an important role in the body reflexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




