
Draw a labelled diagram of the zone refining process. In which process is this useful?
Answer
527.4k+ views
Hint: Zone refining is a method to obtain metals which are highly purity for example, silicon and germanium. Zone melting, floating zone process, and travelling melting zone are different names for zone refining.
Complete answer:
Zone refining is a method that is used to purify a crystal where a small part of a crystal undergoes smelting. This zone is now moved across the crystal. The impurities that are present in the metal are melted at a forward edge by a molten zone and move through the block of metal, which leaves behind a solidified pure element. As we move through this block of metal, the impurities are concentrated in the melting process and are transported to one end of the metal block. This is shown in the following diagram;
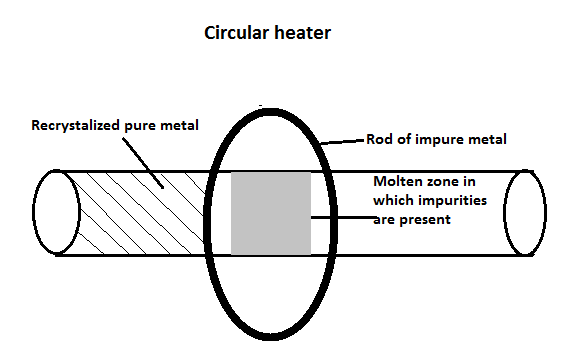
The semiconductors such as silicon and germanium are required in the highest form of purity. These can be extracted with the help of this process and is based on the principle that the impurities should be more soluble in molten form than solid form and when it is cooled, pure metal will crystallize out of the smelt while the impurities will remain in the form of smelt in the molten zone.
Note:
This process is highly useful to gain an ultra pure metal and non metals where $ 99.99\% $ of purity is achieved. This process is effective to remove impurities especially the semiconducting elements such as germanium, silicon, and gallium.
Complete answer:
Zone refining is a method that is used to purify a crystal where a small part of a crystal undergoes smelting. This zone is now moved across the crystal. The impurities that are present in the metal are melted at a forward edge by a molten zone and move through the block of metal, which leaves behind a solidified pure element. As we move through this block of metal, the impurities are concentrated in the melting process and are transported to one end of the metal block. This is shown in the following diagram;

The semiconductors such as silicon and germanium are required in the highest form of purity. These can be extracted with the help of this process and is based on the principle that the impurities should be more soluble in molten form than solid form and when it is cooled, pure metal will crystallize out of the smelt while the impurities will remain in the form of smelt in the molten zone.
Note:
This process is highly useful to gain an ultra pure metal and non metals where $ 99.99\% $ of purity is achieved. This process is effective to remove impurities especially the semiconducting elements such as germanium, silicon, and gallium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




