
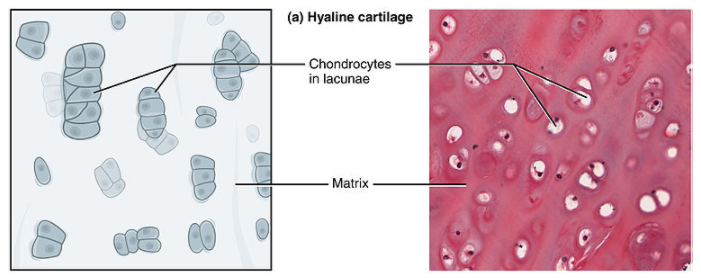
Draw a labelled diagram of the transverse section of the hyaline cartilage. Write a brief note on its function.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in organs such as the ears, nose, and trachea. The term hyaline means "glass-like" and it is a glossy, greyish-white tissue with a uniform appearance. It is one among the three types of cartilage present in the human body. The other two types are elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage. The most abundant type of cartilage in the body is of the hyaline cartilage type.
Complete answer:
Hyaline cartilage is rich in collagen, a protein that helps keep the body together and is not only present in connective tissues, but also in skin and bones. Hyaline cartilage provides protection and flexibility to various parts of the body. It is located in structures such as the nose, ears, and areas where the sternum is connected to the ends of the ribs, and in parts of the respiratory system such as the trachea and larynx, where it not only helps to form these parts but also allows them some flexibility as well. It is referred to as the articular cartilage when hyaline cartilage is on the articular surfaces of the bones (the surfaces of the joints). As a shock absorber, articular cartilage works to decrease the tension between bones where they meet at joints. This cartilage can begin to wear away as a person ages, resulting in joint pain and swelling that can be mitigated by surgery.
Note: The cartilage tissue does not include blood vessels or nerves. Instead, it has a basic structure that consists primarily of a group of cells enclosed in an intracellular matrix called the chondrocytes. The protoplasm is transparent, and there are one or two nuclei present in the cells. Lacunae are tiny cavities that surround the chondrocytes and the chondrocytes are found within these.
Complete answer:

Hyaline cartilage is rich in collagen, a protein that helps keep the body together and is not only present in connective tissues, but also in skin and bones. Hyaline cartilage provides protection and flexibility to various parts of the body. It is located in structures such as the nose, ears, and areas where the sternum is connected to the ends of the ribs, and in parts of the respiratory system such as the trachea and larynx, where it not only helps to form these parts but also allows them some flexibility as well. It is referred to as the articular cartilage when hyaline cartilage is on the articular surfaces of the bones (the surfaces of the joints). As a shock absorber, articular cartilage works to decrease the tension between bones where they meet at joints. This cartilage can begin to wear away as a person ages, resulting in joint pain and swelling that can be mitigated by surgery.
Note: The cartilage tissue does not include blood vessels or nerves. Instead, it has a basic structure that consists primarily of a group of cells enclosed in an intracellular matrix called the chondrocytes. The protoplasm is transparent, and there are one or two nuclei present in the cells. Lacunae are tiny cavities that surround the chondrocytes and the chondrocytes are found within these.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




