
Draw a labelled diagram of stomata. Write two functions of stomata.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: The stomata in plants are enclosed by bean shaped cells called guard cells. Guard cells also contain chloroplasts.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, first we need to know about stomata. Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for exchange of gases. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems.
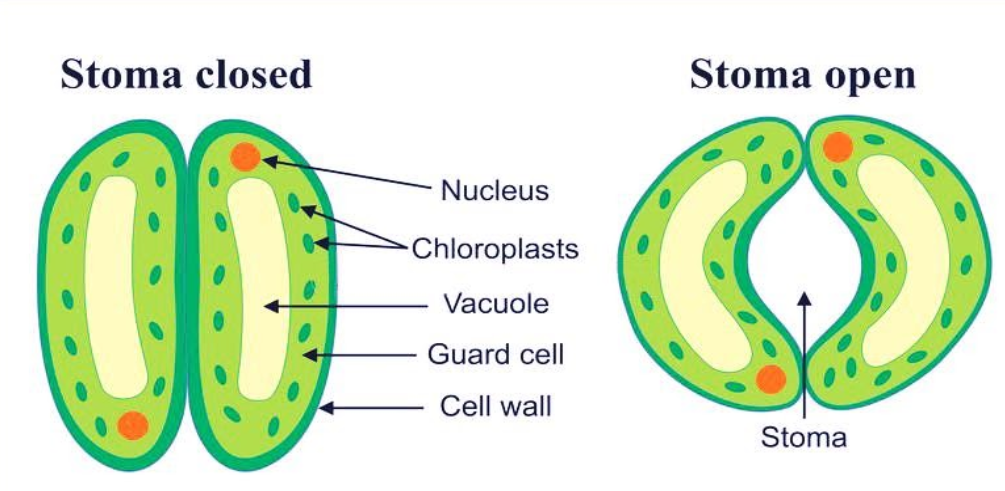
Fig- Labelled diagram of stomata.
Since large amounts of water can also be lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The opening and closing of the pore is regulated by the guard cells. As water flows through them, the guard cells swell allowing the stomatal pore to expand. The pore often closes as the guard cells shrink. Apart from water vapour loss in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through these stomata. Stomata are usually open in daytime and close at night.
Two functions of stomata are:
1. It controls the amount of water entering and leaving the plants.
2. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen for photosynthesis.
Factors including carbon dioxide levels, light, and environmental factors control the opening and closing of stomata. Humidity is an instance of an environmental condition that controls when stomata are open or close. Stomata are open when the humidity levels are maximum. When humidity levels drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Note: When humidity levels in the air around the plant drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, first we need to know about stomata. Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for exchange of gases. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems.

Fig- Labelled diagram of stomata.
Since large amounts of water can also be lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The opening and closing of the pore is regulated by the guard cells. As water flows through them, the guard cells swell allowing the stomatal pore to expand. The pore often closes as the guard cells shrink. Apart from water vapour loss in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through these stomata. Stomata are usually open in daytime and close at night.
Two functions of stomata are:
1. It controls the amount of water entering and leaving the plants.
2. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen for photosynthesis.
Factors including carbon dioxide levels, light, and environmental factors control the opening and closing of stomata. Humidity is an instance of an environmental condition that controls when stomata are open or close. Stomata are open when the humidity levels are maximum. When humidity levels drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Note: When humidity levels in the air around the plant drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE




