
Draw a labelled diagram of L.S. of human teeth.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: L.S is the longitudinal section and in this question, we have to draw a longitudinal section of human teeth along with labels.
Complete answer:
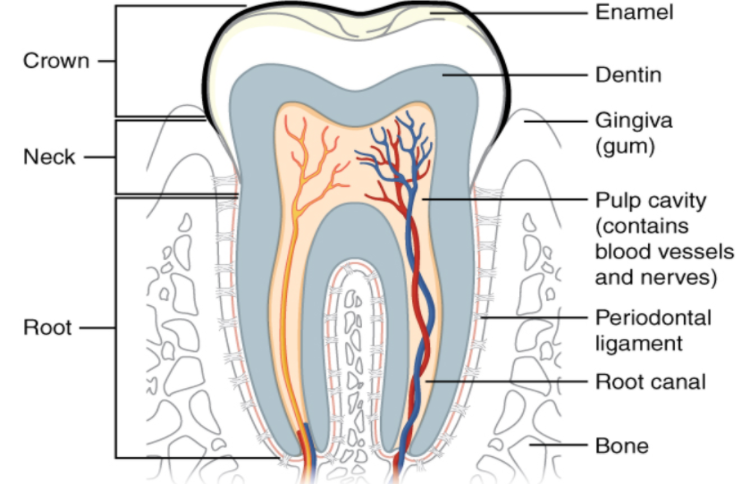
Basically a tooth has three parts, crown, neck and root. In a longitudinal section of a tooth, it contains enamel, dentin, pulp cavity, root canals and supporting structures like ligaments and bone. Enamel is one of the major tissues which make up the tooth. It is a visible region and is supported by underlying dentin. Most part of enamel consists of minerals, the rest is composed of water and organic material. It is semitransluscent, the colour of the enamel can appear from light yellow to greyish white depending on the structure present beneath it. At the edges of teeth, it can sometimes appear in a slightly blue tone due to absence of dentin beneath it. Dentin is present between enamel and the pulp chamber, it is secreted by the cells of dental pulp. It is a protective layer that supports the enamel. Dentin is a yellow-hued porous material, major part of which is made up of inorganic materials, some part formed of organic materials, and water constitutes the rest. It decays more rapidly because it is softer than enamel, severe cavities can be formed if it is not treated properly. The central part of a tooth filled with soft connective tissue is called the dental pulp, it contains blood vessels and nerves which enter the tooth from the apex of the root via a hole. The teeth are covered by a specialised bone like substance called cementum. Periodontal ligaments provide mechanical support to the teeth.
Note:The components in different types of teeth are similar but their proportion may vary. The teeth of males and females differ as the jaw of males is larger than that of females. Also, the amount of dentin is higher in males while in females, the amount of enamel is greater than that present in males.
Complete answer:

Basically a tooth has three parts, crown, neck and root. In a longitudinal section of a tooth, it contains enamel, dentin, pulp cavity, root canals and supporting structures like ligaments and bone. Enamel is one of the major tissues which make up the tooth. It is a visible region and is supported by underlying dentin. Most part of enamel consists of minerals, the rest is composed of water and organic material. It is semitransluscent, the colour of the enamel can appear from light yellow to greyish white depending on the structure present beneath it. At the edges of teeth, it can sometimes appear in a slightly blue tone due to absence of dentin beneath it. Dentin is present between enamel and the pulp chamber, it is secreted by the cells of dental pulp. It is a protective layer that supports the enamel. Dentin is a yellow-hued porous material, major part of which is made up of inorganic materials, some part formed of organic materials, and water constitutes the rest. It decays more rapidly because it is softer than enamel, severe cavities can be formed if it is not treated properly. The central part of a tooth filled with soft connective tissue is called the dental pulp, it contains blood vessels and nerves which enter the tooth from the apex of the root via a hole. The teeth are covered by a specialised bone like substance called cementum. Periodontal ligaments provide mechanical support to the teeth.
Note:The components in different types of teeth are similar but their proportion may vary. The teeth of males and females differ as the jaw of males is larger than that of females. Also, the amount of dentin is higher in males while in females, the amount of enamel is greater than that present in males.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




