
Draw a labelled diagram of an electric generator.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to see what an electric generator is and how it works. The diagram is drawn for a generator taking all the parts and labelling them and then, by telling the function of each of the parts of the generator and telling how the current is generated.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
An electric generator is a device that converts the mechanical energy into the electrical energy for use in an electric circuit. The sources of the mechanical energy for this are the wind turbines, water turbines, steam turbines, etc.
Electromagnetic generators generally fall into the two categories, dynamos and alternators.
The electric generator works on the principle of Faraday’s law of EM induction.
The magnetic flux of an electric generator is given by
$ \phi = NBA\cos \omega t $
And the induced EMF is given by
$ \phi = NBA\omega \sin \omega t $
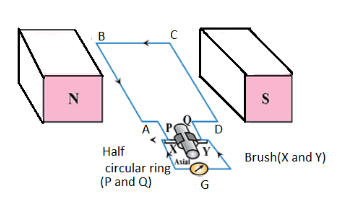
Working: On rotating a loop in a magnetic field, the side AB moves upward and the side CD moves downwards. Thus, magnetic flux linked with the loop changes and the current is induced in it whose direction can be determined by Fleming’s right hand rule. In the figure, the current is flowing through the path B-A-G-D-C.
After half rotation, the ring P comes in contact with brush Y and the ring Q, comes in contact with the brush X. Thus, the brush X is always in contact with the side moving upwards and the brush Y is always in contact with the side moving downwards.
Note :
The diagram for the generator that has been drawn shows the current which flows in single direction and is known as Direct current, it has half ring which generates the DC current and is known as a DC generator. Now, if there is a full ring in the circuit, the whole AC current is generated and it is called an AC generator.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
An electric generator is a device that converts the mechanical energy into the electrical energy for use in an electric circuit. The sources of the mechanical energy for this are the wind turbines, water turbines, steam turbines, etc.
Electromagnetic generators generally fall into the two categories, dynamos and alternators.
The electric generator works on the principle of Faraday’s law of EM induction.
The magnetic flux of an electric generator is given by
$ \phi = NBA\cos \omega t $
And the induced EMF is given by
$ \phi = NBA\omega \sin \omega t $

Working: On rotating a loop in a magnetic field, the side AB moves upward and the side CD moves downwards. Thus, magnetic flux linked with the loop changes and the current is induced in it whose direction can be determined by Fleming’s right hand rule. In the figure, the current is flowing through the path B-A-G-D-C.
After half rotation, the ring P comes in contact with brush Y and the ring Q, comes in contact with the brush X. Thus, the brush X is always in contact with the side moving upwards and the brush Y is always in contact with the side moving downwards.
Note :
The diagram for the generator that has been drawn shows the current which flows in single direction and is known as Direct current, it has half ring which generates the DC current and is known as a DC generator. Now, if there is a full ring in the circuit, the whole AC current is generated and it is called an AC generator.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




