
Draw a labelled diagram of a LS of an embryo of grass
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: The lateral section includes anterior-posterior axis. Hence drawing LS diagrams of grass embryo will include sections showing the anterior and posterior part of the developing embryo
Complete answer:
1.Grass is a monocotyledonous plant. Cotyledons give rise to the first leaves as a plant germinates. Monocots have a single cotyledon. The cotyledon in grass is made up of two parts known as scutellum and coleoptile. The scutellum is found in the lateral side of the embryonal axis. Scutellum assists movement of starch from the endosperm to the developing embryo in the adjacent endosperm.
2.Coleoptile is the protective sheath enclosing the shoots in monocots including grass. This is essentially a hollow structure enclosing the young shoot.
3.The shoot apex is the terminal meristem of the plants and is responsible for growth of plants.
4.Epiblast is a flap-like structure present opposite to the scutellum. Epiblast is continuous with coleorhiza. Epiblast is often considered as similar to the second cotyledon. It serves a storage purpose providing food to the embryo.
5.Epicotyl encloses the potential stem and shoots parts of the embryo and epicotyl lies above the embryonic axis. Within epicotyl a few leaf primordia are enclosed in coleoptile, a hollow structure
6.Protection of the developing root is carried out by coleorhiza. Coleorhiza encloses the potential root cap and developing root(radicle) of the plant. Roots develop from the radicle and root cap serves to protect the tip of developing root.
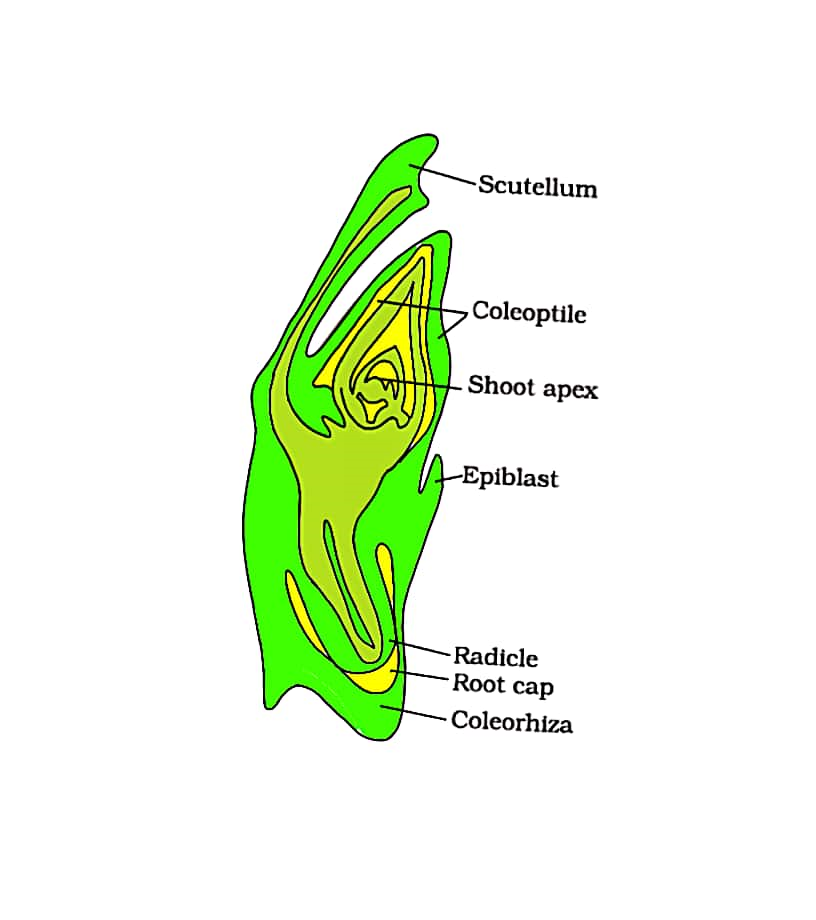
Note: It is important to label all the relevant parts. Coleorhiza, coleoptile, and scutellum are specific to monocots. Since grass is a monocot, the diagram of an embryo of grass must include these three parts.
Complete answer:
1.Grass is a monocotyledonous plant. Cotyledons give rise to the first leaves as a plant germinates. Monocots have a single cotyledon. The cotyledon in grass is made up of two parts known as scutellum and coleoptile. The scutellum is found in the lateral side of the embryonal axis. Scutellum assists movement of starch from the endosperm to the developing embryo in the adjacent endosperm.
2.Coleoptile is the protective sheath enclosing the shoots in monocots including grass. This is essentially a hollow structure enclosing the young shoot.
3.The shoot apex is the terminal meristem of the plants and is responsible for growth of plants.
4.Epiblast is a flap-like structure present opposite to the scutellum. Epiblast is continuous with coleorhiza. Epiblast is often considered as similar to the second cotyledon. It serves a storage purpose providing food to the embryo.
5.Epicotyl encloses the potential stem and shoots parts of the embryo and epicotyl lies above the embryonic axis. Within epicotyl a few leaf primordia are enclosed in coleoptile, a hollow structure
6.Protection of the developing root is carried out by coleorhiza. Coleorhiza encloses the potential root cap and developing root(radicle) of the plant. Roots develop from the radicle and root cap serves to protect the tip of developing root.

Note: It is important to label all the relevant parts. Coleorhiza, coleoptile, and scutellum are specific to monocots. Since grass is a monocot, the diagram of an embryo of grass must include these three parts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




