
Draw a labelled diagram of a candle flame and explain what happens in each zone.
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint: For light and heat, we use candles very frequently. A candle is mainly made by solidifying wax and putting a wick in it, which is used to light up the candle. Candles use wax as a form of fuel. Combustion takes place as a consequence of the production of heat and light. Further from the wick, more the chances of complete combustion occurring.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The below figure shows the basic zones in a flame
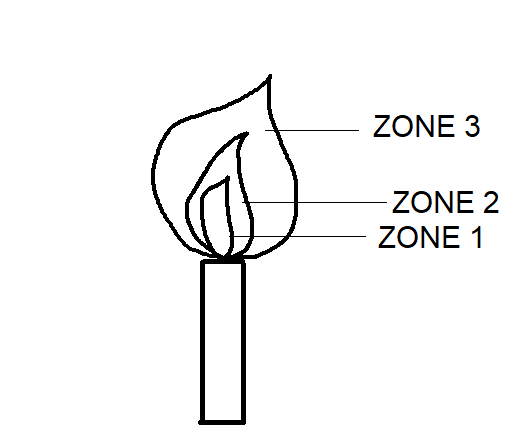
Now, let me explain all the zones of a flame one by one
ZONE $ 1 $ : It is a flame's innermost zone. In colour, it appears to be very dark blue or black. This part consists of the combustible fuel's warm, unburnt vapours. This part of the flame is the least hot. Or we can say it is the coldest part of the flame.
ZONE $ 2 $ : It is the flame's middle zone. This portion of the flame looks yellow in colour. It is luminous and very bright. Due to limited access to air, the fuel vapours partially burn in this zone. This partial burning causes carbon particles to be produced, which appear as smoke and soot. The temperature is not very hot nor too cool. It has moderate temperature. Or we can say that the temperature of this zone is between zone $ 1 $ and zone $ 3 $ .
ZONE $ 3 $ : It is the outermost zone of a flame. In colour, this part of the flame appears blue. In this zone, due to the complete access of air around it, complete combustion takes place. This is the hottest portion of the flame, so it has the highest temperature. This is the zone with the thinnest.
Note:
At a given point in the combustion process, called the ignition stage, flames are created. The flame is the exposed portion of the fire. Carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen are mainly composed of flames. The gases may become ionized if they are hot enough to produce plasma.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
The below figure shows the basic zones in a flame

Now, let me explain all the zones of a flame one by one
ZONE $ 1 $ : It is a flame's innermost zone. In colour, it appears to be very dark blue or black. This part consists of the combustible fuel's warm, unburnt vapours. This part of the flame is the least hot. Or we can say it is the coldest part of the flame.
ZONE $ 2 $ : It is the flame's middle zone. This portion of the flame looks yellow in colour. It is luminous and very bright. Due to limited access to air, the fuel vapours partially burn in this zone. This partial burning causes carbon particles to be produced, which appear as smoke and soot. The temperature is not very hot nor too cool. It has moderate temperature. Or we can say that the temperature of this zone is between zone $ 1 $ and zone $ 3 $ .
ZONE $ 3 $ : It is the outermost zone of a flame. In colour, this part of the flame appears blue. In this zone, due to the complete access of air around it, complete combustion takes place. This is the hottest portion of the flame, so it has the highest temperature. This is the zone with the thinnest.
Note:
At a given point in the combustion process, called the ignition stage, flames are created. The flame is the exposed portion of the fire. Carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen are mainly composed of flames. The gases may become ionized if they are hot enough to produce plasma.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




