
Draw a graph of potential energy v/s reaction coordinate showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Potential energy of a reaction is the amount of energy required by a reaction to bring a chemical change. Several factors affect the rate of a reaction. Addition of catalyst affects the rate of a reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The kinetics of chemical reaction is dependent on the spontaneity of a reaction. According to thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy of a reaction must be negative for a reaction to take place smoothly.
The Gibbs free energy is denoted as $\Delta G$. The value of \[\Delta G < 0\], leads to a spontaneous reaction. The factors which lower the value of $\Delta G$, have a significant effect on the spontaneity of a reaction.
The activation energy is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to overcome the activation barrier and transform the reactants into products. It is dented as \[Ea\] and has units of \[KJ/mol\] .
A catalyst is a substance which helps in the reaction to proceed faster. The catalyst does not react with the starting material or the reactants to produce the product. It is not used in a stoichiometric amount in a reaction. It is not consumed in the process.
A catalyst only provides an alternate pathway for a reaction. A catalyst speeds up a reaction by reducing the activation energy required for the chemical reaction or changing the reaction mechanism.
Let us consider the transformation of A to B which requires the activation energy of \[Ea\] . The plot or graph of potential energy v/s reaction coordinate showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy is shown in figure \[1\] .
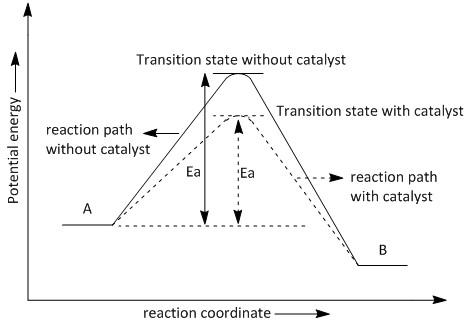
Figure\[1\] : The effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
Note: Enzymes are proteins which serve as catalysts for biochemical reactions inside the body. Several catalysts are used in laboratories to carry out chemical transformations. These include both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. The coupling reactions use palladium and copper catalysts (homogeneous catalyst) for giving excellent yields. Hydrogenation using \[10\% \] \[Pd\] on carbon is a heterogeneous catalyst.
Complete step by step answer:
The kinetics of chemical reaction is dependent on the spontaneity of a reaction. According to thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy of a reaction must be negative for a reaction to take place smoothly.
The Gibbs free energy is denoted as $\Delta G$. The value of \[\Delta G < 0\], leads to a spontaneous reaction. The factors which lower the value of $\Delta G$, have a significant effect on the spontaneity of a reaction.
The activation energy is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to overcome the activation barrier and transform the reactants into products. It is dented as \[Ea\] and has units of \[KJ/mol\] .
A catalyst is a substance which helps in the reaction to proceed faster. The catalyst does not react with the starting material or the reactants to produce the product. It is not used in a stoichiometric amount in a reaction. It is not consumed in the process.
A catalyst only provides an alternate pathway for a reaction. A catalyst speeds up a reaction by reducing the activation energy required for the chemical reaction or changing the reaction mechanism.
Let us consider the transformation of A to B which requires the activation energy of \[Ea\] . The plot or graph of potential energy v/s reaction coordinate showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy is shown in figure \[1\] .

Figure\[1\] : The effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
Note: Enzymes are proteins which serve as catalysts for biochemical reactions inside the body. Several catalysts are used in laboratories to carry out chemical transformations. These include both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. The coupling reactions use palladium and copper catalysts (homogeneous catalyst) for giving excellent yields. Hydrogenation using \[10\% \] \[Pd\] on carbon is a heterogeneous catalyst.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




