
Draw a diagram to show a block and tackle pulley system having a velocity ratio of $3$ marking the direction of load $\left( L \right)$ , effort $\left( E \right)$ and tension $\left( T \right)$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Here we have to apply the concept of velocity lever and how load, effort and tension works in machines.
The velocity ratio indicates the distance travelled by the pulley.Tension levers are somewhat similar to flexible handles, allowing regular adjustment and quick clamping.
Complete Step by step answer: First let us see what a velocity ratio is since the diagram is totally dependent on the velocity ratio.
Velocity ratio is the ratio of the length of the out-lever to the in-lever (length of the resistance arm over stress arm). In order to increase the velocity ratio of the load being moved, we have to increase the resistance arm by bringing the fulcrum closer to the effort.
Since, the velocity ratio or ideal mechanical advantage is a basic ratio of two lengths, the velocity ratio does not have any units. There is no work of friction here.
The machine generates force and regulates the direction and motion of force but it cannot generate energy. The capacity of a machine to do work is calculated by two variables.
They are –mechanical advantages and efficiency.
The mechanical advantage of a lever is given by load over effort.
Less effort is needed to do a job if the effort lever is longer.
The work efficiency formula is efficiency equals output over input and we can multiply the outcome by $100$ to obtain work efficiency as a percentage. This is used in various ways of calculating energy and work, whether it is energy generation or machine efficiency.
Velocity ratio of the lever is 3 meaning the effort distance of the lever is 3 times the effort distance of the load.
So, the diagram is as below:
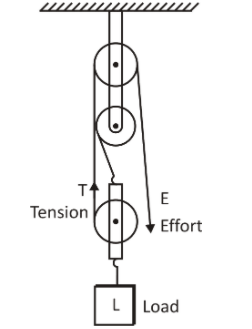
Note: Here three pulleys are drawn since the velocity ratio is three. So, we have to see what the number of the velocity ratio is given in the question. The proportion of the length of the out-lever to the in-lever (length of the resistance arm over the stress arm) is the velocity ratio. We have to boost the resistance arm by bringing the fulcrum closer to the effort in order to increase the velocity ratio of the load being moved.
The velocity ratio indicates the distance travelled by the pulley.Tension levers are somewhat similar to flexible handles, allowing regular adjustment and quick clamping.
Complete Step by step answer: First let us see what a velocity ratio is since the diagram is totally dependent on the velocity ratio.
Velocity ratio is the ratio of the length of the out-lever to the in-lever (length of the resistance arm over stress arm). In order to increase the velocity ratio of the load being moved, we have to increase the resistance arm by bringing the fulcrum closer to the effort.
Since, the velocity ratio or ideal mechanical advantage is a basic ratio of two lengths, the velocity ratio does not have any units. There is no work of friction here.
The machine generates force and regulates the direction and motion of force but it cannot generate energy. The capacity of a machine to do work is calculated by two variables.
They are –mechanical advantages and efficiency.
The mechanical advantage of a lever is given by load over effort.
Less effort is needed to do a job if the effort lever is longer.
The work efficiency formula is efficiency equals output over input and we can multiply the outcome by $100$ to obtain work efficiency as a percentage. This is used in various ways of calculating energy and work, whether it is energy generation or machine efficiency.
Velocity ratio of the lever is 3 meaning the effort distance of the lever is 3 times the effort distance of the load.
So, the diagram is as below:

Note: Here three pulleys are drawn since the velocity ratio is three. So, we have to see what the number of the velocity ratio is given in the question. The proportion of the length of the out-lever to the in-lever (length of the resistance arm over the stress arm) is the velocity ratio. We have to boost the resistance arm by bringing the fulcrum closer to the effort in order to increase the velocity ratio of the load being moved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




