
Draw a diagram showing the refraction of light from water to glass. Lebel on it the incident ray, the angle of incidence$(i)$ , and the angle of refraction $(r)$.
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint: The definition of the refraction has to be known to draw the given diagram. Refraction is a phenomenon of the light ray when it tries to go from one medium to another medium. The normal on the separation plane of the two mediums is very important to draw. Because the angle of incident and the angle of refraction can be noted by showing the normal on the plane.
Complete answer:
Let us consider, \[CD\] is the separation plane of the water medium and the glass medium. The surface is called the refracting surface. $AO$ ray comes through the water and incident obliquely on the point $O$ of the plane \[CD\]. At this surface, the ray changes it’s direction and goes along the straight line$OB$ . Then we draw$NON'$ , a normal on the point $O$ of the plane \[CD\].
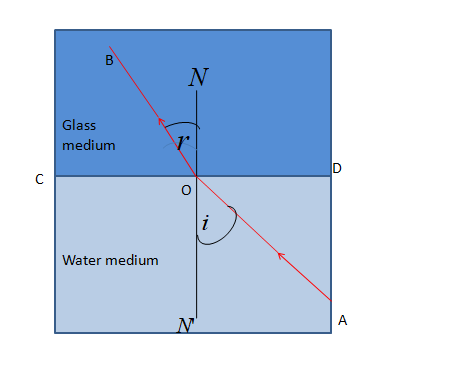
$AO$ is incident ray and $OB$ is the refracted ray.
The angle between the ray $AO$ and the normal $ON'$ is called the angle of incidence i.e. $\angle i = \angle AON'$
And, The angle between the ray $OB$the normal \[NO\] is called the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle r = \angle BON$
Note:
The light ray when entered obliquely from the rarer medium to the denser medium i.e. from water to glass, the refracting ray moves to the normal I.e to the \[NN'\] . In this case, the angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle i > \angle r$
The light ray when enters obliquely from the denser medium to the rarer medium i.e. from glass to water, the refracting ray moves away from the normal. In this case, the angle of incidence is less than the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle i < \angle r$.
Complete answer:
Let us consider, \[CD\] is the separation plane of the water medium and the glass medium. The surface is called the refracting surface. $AO$ ray comes through the water and incident obliquely on the point $O$ of the plane \[CD\]. At this surface, the ray changes it’s direction and goes along the straight line$OB$ . Then we draw$NON'$ , a normal on the point $O$ of the plane \[CD\].

$AO$ is incident ray and $OB$ is the refracted ray.
The angle between the ray $AO$ and the normal $ON'$ is called the angle of incidence i.e. $\angle i = \angle AON'$
And, The angle between the ray $OB$the normal \[NO\] is called the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle r = \angle BON$
Note:
The light ray when entered obliquely from the rarer medium to the denser medium i.e. from water to glass, the refracting ray moves to the normal I.e to the \[NN'\] . In this case, the angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle i > \angle r$
The light ray when enters obliquely from the denser medium to the rarer medium i.e. from glass to water, the refracting ray moves away from the normal. In this case, the angle of incidence is less than the angle of refraction i.e. $\angle i < \angle r$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




