
Draw a circle with the help of a bangle. Take a point outside the circle. Construct the pair of tangents from this point to the circle.
Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, we need to find the center of the circle using non-parallel chords and then from that center we need to construct a perpendicular bisector outside the circle and then using it we will find two tangents at the circle.
Complete step by step solution:
As given in the question we have to draw a circle with the help of a bangle to make a circle of any arbitrary radius r. Now, we also know that the perpendicular of chords passes through the center of a circle, so using that method we will find the center of the circle.
Now, we will solve this problem step wise:
Step 1: First of all, to find the center of the circle we need to construct two non-parallel chords AB and CD as shown in figure below.
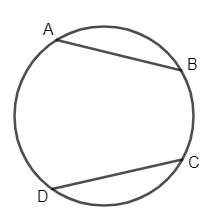
Step-2: Now, we will draw perpendicular bisectors of the chord AB and CD by making arcs of any arbitrary radius.
1. There are some points to be remembered while drawing a perpendicular bisector i.e., taking more than half of length AB as radius and with A as center draw arcs above and below the chords AB.
2. Then again with the same radius and B as center, we will draw arcs cutting the previous two arcs.
3. Then we will draw a line passing through the intersection of the arcs cut above and below the chords.
4. Similarly, we have to do this for chord DC. Thus, we will find one intersection point between the circle which will be our center.
Now, we will mark the point of intersection of two perpendicular bisectors as the center of circle O.
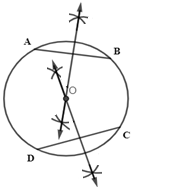
Now, we need to draw a tangent to the circle with center O.
For that the steps are:
Step 1: Draw a point P outside the circle as shown in the figure.
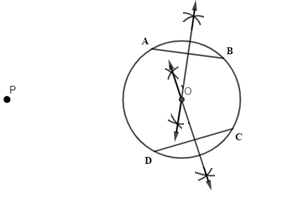
Step 2: Join P and O as PO line segment. Now, take the perpendicular bisector of PO and let M be the midpoint of PO as shown in figure.
1. Here, the perpendicular bisector for the PO line segment can be drawn the same as we did for the chord AB.
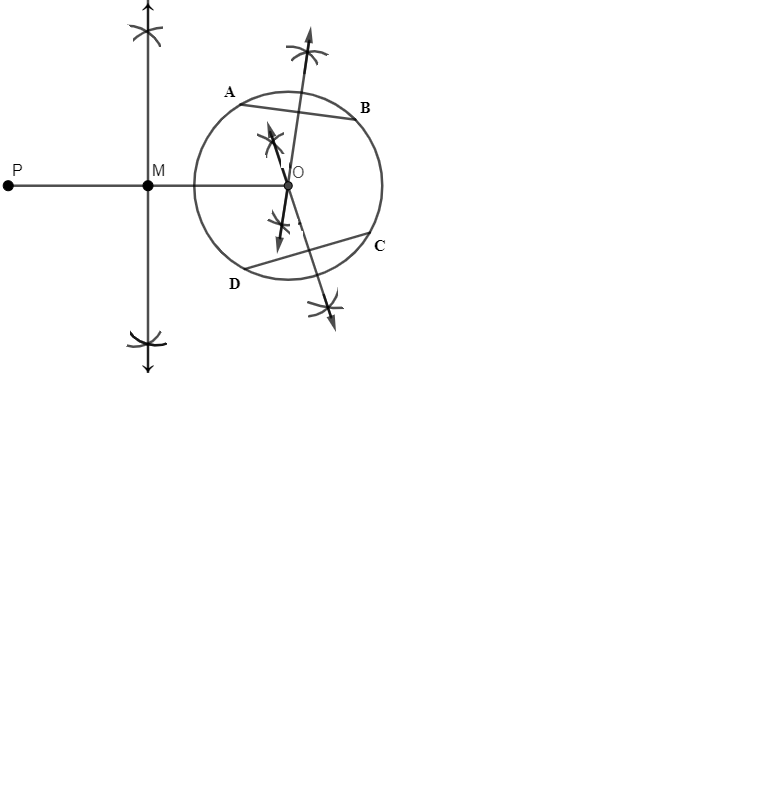
Step 3: Now, take M as center and MO as radius, draw a circle. Now mark the points where the new circle intersects the original circle as Q and R.
Step 4: Join PQ and PR as shown in the figure.
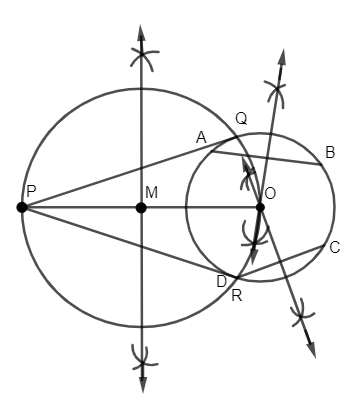
Thus, PQ and PR are the required tangents.
Note: While solving such questions students must take care in construction because if the point is marked wrongly then the required answer will not be obtained. The work should be neat and tidy so that each intersection point is visible easily and less time is consumed during construction. Also in construction, we have to draw a pair of tangents. Sometimes students draw only one tangent then also the diagram will be wrong. While drawing a perpendicular bisector, students should use proper construction, instead of drawing a line just using scale and pencil students should have a clear idea in mind how to approach and then start drawing.
Complete step by step solution:
As given in the question we have to draw a circle with the help of a bangle to make a circle of any arbitrary radius r. Now, we also know that the perpendicular of chords passes through the center of a circle, so using that method we will find the center of the circle.
Now, we will solve this problem step wise:
Step 1: First of all, to find the center of the circle we need to construct two non-parallel chords AB and CD as shown in figure below.

Step-2: Now, we will draw perpendicular bisectors of the chord AB and CD by making arcs of any arbitrary radius.
1. There are some points to be remembered while drawing a perpendicular bisector i.e., taking more than half of length AB as radius and with A as center draw arcs above and below the chords AB.
2. Then again with the same radius and B as center, we will draw arcs cutting the previous two arcs.
3. Then we will draw a line passing through the intersection of the arcs cut above and below the chords.
4. Similarly, we have to do this for chord DC. Thus, we will find one intersection point between the circle which will be our center.
Now, we will mark the point of intersection of two perpendicular bisectors as the center of circle O.

Now, we need to draw a tangent to the circle with center O.
For that the steps are:
Step 1: Draw a point P outside the circle as shown in the figure.

Step 2: Join P and O as PO line segment. Now, take the perpendicular bisector of PO and let M be the midpoint of PO as shown in figure.
1. Here, the perpendicular bisector for the PO line segment can be drawn the same as we did for the chord AB.

Step 3: Now, take M as center and MO as radius, draw a circle. Now mark the points where the new circle intersects the original circle as Q and R.
Step 4: Join PQ and PR as shown in the figure.

Thus, PQ and PR are the required tangents.
Note: While solving such questions students must take care in construction because if the point is marked wrongly then the required answer will not be obtained. The work should be neat and tidy so that each intersection point is visible easily and less time is consumed during construction. Also in construction, we have to draw a pair of tangents. Sometimes students draw only one tangent then also the diagram will be wrong. While drawing a perpendicular bisector, students should use proper construction, instead of drawing a line just using scale and pencil students should have a clear idea in mind how to approach and then start drawing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




