
Draw a circle of radius 5cm. From a point 13cm away from the centre, construct a pair of tangents to the circle and measure their length. Also verify the measurement by actual calculation.
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: We need to construct a pair of tangents to a circle and find their length. We start to solve the given question by constructing a circle of radius 5cm with centre O and draw a line segment OP of length 13cm. Then, we need to find the length of the tangent of the circle. Lastly, we verify the length of the tangent to a circle by actual calculation.
Complete step by step solution:
We are asked to draw a circle of radius 5 cm and need to construct tangents for the same. We will be solving the given question by constructing a circle of radius 5 cm and then finding the length of tangents to the circle.
The tangent to the circle is defined as the straight line that touches a circle at exactly one point. The point of contact where a tangent meets the circle is called tangency or point of contact. There can be only one tangent to a circle at a given point.
The pair of tangents to a circle can be constructed as follows,
1. We need to draw a circle of radius 5cm with centre O using a compass and pencil. So, we can take 5 cm on the compass and draw the circle as below,
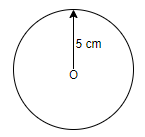
2.Draw a line segment OP of length 13 cm from the centre of the circle to P.
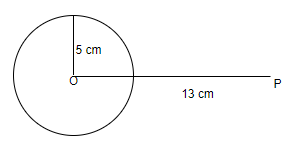
3. Join point P to any point Q on the circle such that PQ touches the circle.
After the steps, we find that the length of PQ is 12 cm with the help of a ruler.
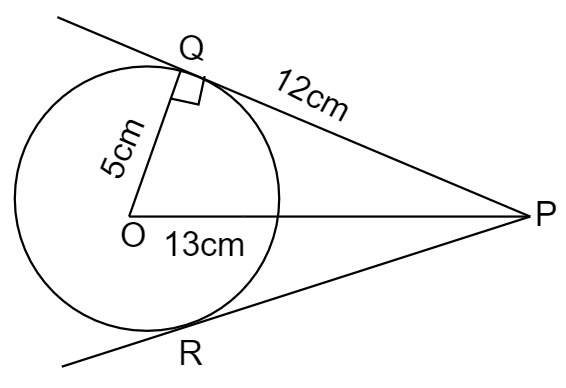
Actual calculation:
The above steps can be diagrammatically represented as follows,
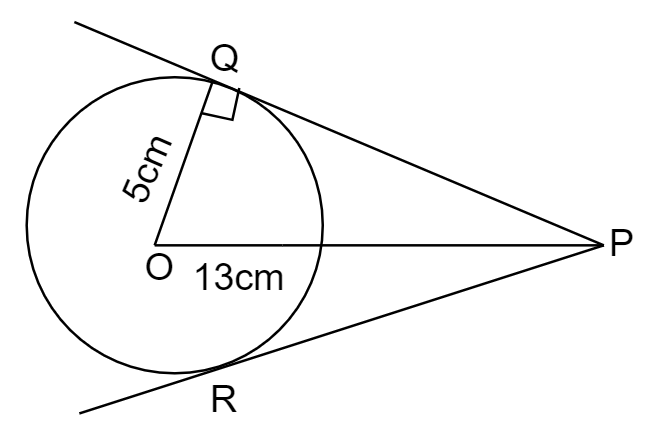
In the above figure,
PQ and PR are the pair of tangents to a circle.
We need to find the length of tangents PQ, PR.
From the figure,
We know that a triangle $OQP$ is a right-angled triangle.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem to the triangle, we get,
$\Rightarrow O{{P}^{2}}=O{{Q}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}$
Here,
$OP=13cm$ ;
$OQ=5cm$
Substituting the same, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{13}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}$
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow 169=25+P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 169-25=P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 144=P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{144}$
$\Rightarrow PQ=\pm 12$
The length of a tangent cannot be negative.
$\therefore PQ=12$
$\therefore$ The length of tangents in both cases is the same.
Note: We need to precisely measure the length of the sides with the ruler. We must remember that the value of $\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}}=\pm a$ and not $+a$ . Pythagoras Theorem defines the relationship between the three sides of a triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides of a triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
We are asked to draw a circle of radius 5 cm and need to construct tangents for the same. We will be solving the given question by constructing a circle of radius 5 cm and then finding the length of tangents to the circle.
The tangent to the circle is defined as the straight line that touches a circle at exactly one point. The point of contact where a tangent meets the circle is called tangency or point of contact. There can be only one tangent to a circle at a given point.
The pair of tangents to a circle can be constructed as follows,
1. We need to draw a circle of radius 5cm with centre O using a compass and pencil. So, we can take 5 cm on the compass and draw the circle as below,

2.Draw a line segment OP of length 13 cm from the centre of the circle to P.

3. Join point P to any point Q on the circle such that PQ touches the circle.
After the steps, we find that the length of PQ is 12 cm with the help of a ruler.

Actual calculation:
The above steps can be diagrammatically represented as follows,

In the above figure,
PQ and PR are the pair of tangents to a circle.
We need to find the length of tangents PQ, PR.
From the figure,
We know that a triangle $OQP$ is a right-angled triangle.
Applying the Pythagoras theorem to the triangle, we get,
$\Rightarrow O{{P}^{2}}=O{{Q}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}$
Here,
$OP=13cm$ ;
$OQ=5cm$
Substituting the same, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{13}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}$
Simplifying the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow 169=25+P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 169-25=P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 144=P{{Q}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow PQ=\sqrt{144}$
$\Rightarrow PQ=\pm 12$
The length of a tangent cannot be negative.
$\therefore PQ=12$
$\therefore$ The length of tangents in both cases is the same.
Note: We need to precisely measure the length of the sides with the ruler. We must remember that the value of $\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}}=\pm a$ and not $+a$ . Pythagoras Theorem defines the relationship between the three sides of a triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides of a triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




