
How do you draw $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ in standard position and find one positive and one negative angle that is coterminal to the given angle?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: We discuss the basic rules for representing a given angle. Then we discuss the coterminal angles and how to find them. We add or subtract ${{360}^{\circ }}$ or $2\pi $ to each angle to find the solutions.
Complete step by step solution:
The cartesian coordinates are divided into four parts. Every part is called quadrant. The count of angle is done on both sides. But the difference is positive and negative angles. If we count in a clockwise way then the angle goes negative and If we count in an anticlockwise way then the angle goes positive.
Every quadrant is of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ angles.
Now we have to find the $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ in standard position.
The angle is negative. Therefore, we go clockwise.
We first try to form the angle $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ in the form of multiples of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So, $-{{330}^{\circ }}=-\left( 3\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+{{60}^{\circ }} \right)$. So, there are three quadrants to cover.
As we are going clockwise, we cross fourth, then third and lastly second quadrant competently. We are at the first quadrant and have to go ${{60}^{\circ }}$ in that direction.
The representation will be
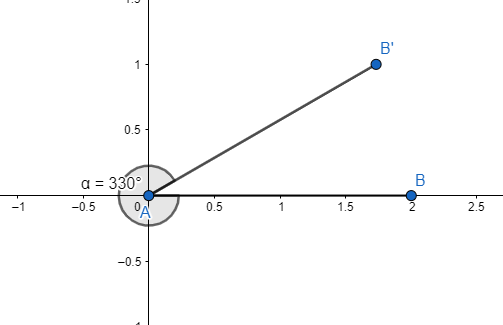
Finding coterminal angles is as simple as adding or subtracting ${{360}^{\circ }}$ or $2\pi $ to each angle, depending on whether the given angle is in degrees or radians.
So, one positive coterminal angle to $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ is $-{{330}^{\circ }}+{{360}^{\circ }}={{30}^{\circ }}$ and one negative coterminal angle to $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ is $-{{330}^{\circ }}-{{360}^{\circ }}={{690}^{\circ }}$.
Note: Now we know that coterminal angles are angles in standard position (angles with the initial side on the positive x-axis) that have a common terminal side. Two angles are coterminal when the angles themselves are different, but their sides and vertices are identical.
Complete step by step solution:
The cartesian coordinates are divided into four parts. Every part is called quadrant. The count of angle is done on both sides. But the difference is positive and negative angles. If we count in a clockwise way then the angle goes negative and If we count in an anticlockwise way then the angle goes positive.
Every quadrant is of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ angles.
Now we have to find the $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ in standard position.
The angle is negative. Therefore, we go clockwise.
We first try to form the angle $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ in the form of multiples of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So, $-{{330}^{\circ }}=-\left( 3\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+{{60}^{\circ }} \right)$. So, there are three quadrants to cover.
As we are going clockwise, we cross fourth, then third and lastly second quadrant competently. We are at the first quadrant and have to go ${{60}^{\circ }}$ in that direction.
The representation will be

Finding coterminal angles is as simple as adding or subtracting ${{360}^{\circ }}$ or $2\pi $ to each angle, depending on whether the given angle is in degrees or radians.
So, one positive coterminal angle to $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ is $-{{330}^{\circ }}+{{360}^{\circ }}={{30}^{\circ }}$ and one negative coterminal angle to $-{{330}^{\circ }}$ is $-{{330}^{\circ }}-{{360}^{\circ }}={{690}^{\circ }}$.
Note: Now we know that coterminal angles are angles in standard position (angles with the initial side on the positive x-axis) that have a common terminal side. Two angles are coterminal when the angles themselves are different, but their sides and vertices are identical.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




