
What is the domain and range of \[y = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\]?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Definition of a function:
Let \[A\,\,\& \,B\] be any two non-empty sets, a rule by which every elements in the set \[A\] is assigned to some unique elements in the set \[B\] and it is denoted as \[f:A \to B\]. Also we can define that \[f\] is a function from \[A\] into \[B\] and it is defined by \[f(x) = y\].
Definition of domain of the function:
Domain of the function is defined as \[{D_f} = \left\{ {x:x \in A} \right\}\], that is, all possible values of \[x \in A\].
There are some restrictions in the domain of the function in which few rules are listed below.
Rules for the domain of a function:
1. Non-zero denominator in the functions:
The function is of the form: \[f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\dfrac{{P\left( x \right)}}{{Q\left( x \right)}}:Q\left( x \right) \ne 0 = O\left( x \right)} \right\}\], where \[O\left( x \right) = \left\{ {O\left( x \right) = 0:x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\] is called a zero function.
2. Non-negative square root functions:
The function is of the form: \[f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\sqrt {G\left( x \right)} :G\left( x \right) \geqslant 0} \right\}\]
Definition of Range of a function:
Range of the function \[f(x)\] is the graph of \[f\] and is defined as \[{R_f} = \left\{ {f\left( x \right):f\left( x \right) \in B,\,x \in A} \right\}\], where range of \[f\] is always onto function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given function, we have \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\]
The domain of \[f(x)\] is \[x \in \mathbb{R} - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\] or in the interval notation \[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right) - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\]
And the range of \[f(x)\] is \[f\left( x \right) \in \mathbb{R} - \left( { - 13.633,\, - 0.367} \right)\] as seen in the below figure.
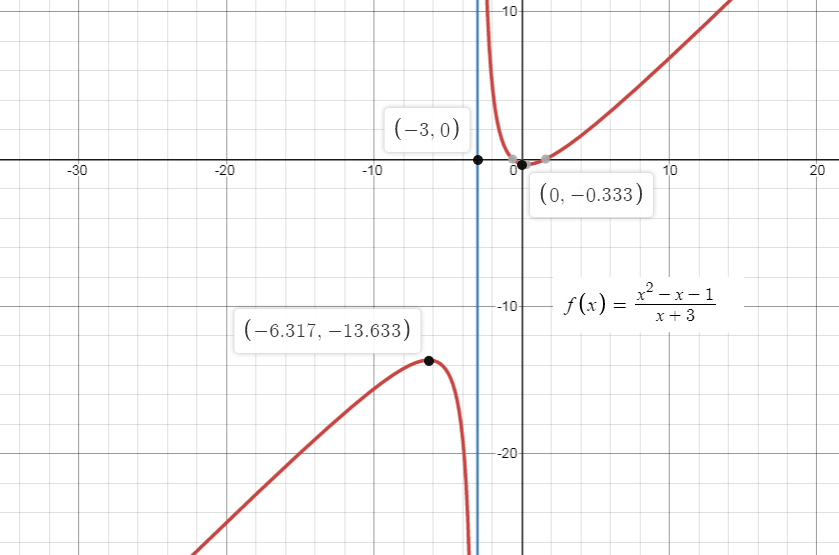
Therefore, the domain of a function \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\] is \[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right) - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\] and the range of the function is \[f\left( x \right) \in \mathbb{R} - \left( { - 13.633,\, - 0.367} \right)\].
Note: In the above graph of the function, \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\] has a vertical asymptotes at \[x = - 3\].
The domain of \[f(x)\] is except one point that covers all the real line and the range of \[f(x)\] is the graph of the function excluding the open intervals in which it has no pre-images.
Let \[A\,\,\& \,B\] be any two non-empty sets, a rule by which every elements in the set \[A\] is assigned to some unique elements in the set \[B\] and it is denoted as \[f:A \to B\]. Also we can define that \[f\] is a function from \[A\] into \[B\] and it is defined by \[f(x) = y\].
Definition of domain of the function:
Domain of the function is defined as \[{D_f} = \left\{ {x:x \in A} \right\}\], that is, all possible values of \[x \in A\].
There are some restrictions in the domain of the function in which few rules are listed below.
Rules for the domain of a function:
1. Non-zero denominator in the functions:
The function is of the form: \[f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\dfrac{{P\left( x \right)}}{{Q\left( x \right)}}:Q\left( x \right) \ne 0 = O\left( x \right)} \right\}\], where \[O\left( x \right) = \left\{ {O\left( x \right) = 0:x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\] is called a zero function.
2. Non-negative square root functions:
The function is of the form: \[f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\sqrt {G\left( x \right)} :G\left( x \right) \geqslant 0} \right\}\]
Definition of Range of a function:
Range of the function \[f(x)\] is the graph of \[f\] and is defined as \[{R_f} = \left\{ {f\left( x \right):f\left( x \right) \in B,\,x \in A} \right\}\], where range of \[f\] is always onto function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given function, we have \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\]
The domain of \[f(x)\] is \[x \in \mathbb{R} - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\] or in the interval notation \[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right) - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\]
And the range of \[f(x)\] is \[f\left( x \right) \in \mathbb{R} - \left( { - 13.633,\, - 0.367} \right)\] as seen in the below figure.

Therefore, the domain of a function \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\] is \[x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right) - \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\] and the range of the function is \[f\left( x \right) \in \mathbb{R} - \left( { - 13.633,\, - 0.367} \right)\].
Note: In the above graph of the function, \[y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - x - 1}}{{x + 3}}\] has a vertical asymptotes at \[x = - 3\].
The domain of \[f(x)\] is except one point that covers all the real line and the range of \[f(x)\] is the graph of the function excluding the open intervals in which it has no pre-images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




