
How does the kinetic energy of the alpha particles affect the angle of deflection?
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: Alpha particles with a smaller amount of kinetic energy are deflected and conclude at greater angles than more energetic ones. Then \[E\] is always positive, we need to look at only the right hand side of the plot. We understand that as the kinetic energy \[E\] increases, the deflection angle \[\theta \] decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
Alpha particles with a lesser amount of kinetic energy are deflected through greater angles than added energetic ones.
While you calculate the scattering angle \[\theta \] as a purpose of the kinetic energy \[E\] of the \[\alpha \] particle, you change to the equation
\[\dfrac{{2bE}}{{{Z_1}{Z_2}{e^2}}} = cot\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right),\]where
b is the influence parameter — the distance of adjoining approach if the \[\alpha \] particle were not deflected \[{Z_1}\] and \[\;{Z_2}\;\] are the charges taking place the \[\alpha \] particle and the gold nucleus e is the electronic charge
For a stable value of b, the equation says that
\[\alpha \] \[E \propto cot\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)\]or
\[\theta \; \propto arccot(E)\]
A plot of \[y\; = arccot(x)or\;\theta \; = arccot(E)\]
Since \[\;E\;\] is permanently positive, we need to expression at only the right hand side of the plot.
We appreciate that as the kinetic energy E increases, the deflection angle \[\theta \] decreases. Likewise, as per the kinetic energy \[\;E\;\] decreases, the deflection angle \[\theta \] increases.
Additional information:
The Alpha Particle Scattering Experiment -
They acquired a thin gold foil having a thickness of \[2.1 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\] and to be found in the centre of a rotatable indicator made of zinc sulfide and a microscope. Then, they fixed a beam of \[5.5MeV\]alpha particles emitted from a radioactive basis at the foil. Lead bricks collimated these alpha particles as they passed and concluded them.
After defeating the foil, the scattering of these alpha particles could be studied by the brief flickers on the screen. Rutherford and his team are predictable to learn more about the structure of the atom from the consequences of this experiment.
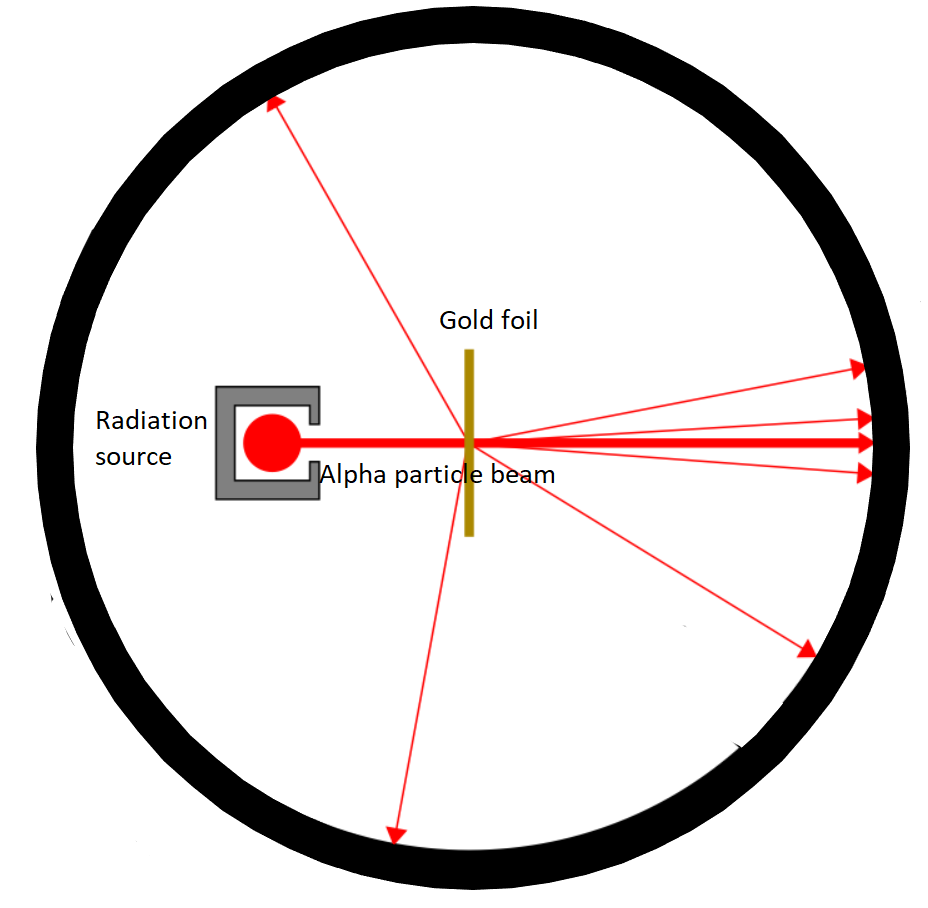
Observations:
Here is what they initiate:
Maximum of the alpha particles passed concluded the foil without suffering any collisions.
All over the place \[0.14\% \]of the occurrence alpha particles scattered by more than \[{1^o}\].
All over the place\[\;1\]in \[8000\] alpha particles deflected by more than \[{90^o}\].
These observations led to many influences and conclusion which laid downcast the structure of the nuclear model on an atom.
Note: The particles with a small influence parameter or the particles nearer to the nucleus, experience a large angle of scattering. On the additional hand, those with a large impact parameter are smart with no deflection or scattering at all. To end with, those particles having ~zero impact parameter or a dome-on collision with the nucleus reverberation back.
Complete step by step answer:
Alpha particles with a lesser amount of kinetic energy are deflected through greater angles than added energetic ones.
While you calculate the scattering angle \[\theta \] as a purpose of the kinetic energy \[E\] of the \[\alpha \] particle, you change to the equation
\[\dfrac{{2bE}}{{{Z_1}{Z_2}{e^2}}} = cot\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right),\]where
b is the influence parameter — the distance of adjoining approach if the \[\alpha \] particle were not deflected \[{Z_1}\] and \[\;{Z_2}\;\] are the charges taking place the \[\alpha \] particle and the gold nucleus e is the electronic charge
For a stable value of b, the equation says that
\[\alpha \] \[E \propto cot\left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)\]or
\[\theta \; \propto arccot(E)\]
A plot of \[y\; = arccot(x)or\;\theta \; = arccot(E)\]
Since \[\;E\;\] is permanently positive, we need to expression at only the right hand side of the plot.
We appreciate that as the kinetic energy E increases, the deflection angle \[\theta \] decreases. Likewise, as per the kinetic energy \[\;E\;\] decreases, the deflection angle \[\theta \] increases.
Additional information:
The Alpha Particle Scattering Experiment -
They acquired a thin gold foil having a thickness of \[2.1 \times {10^{ - 7}}m\] and to be found in the centre of a rotatable indicator made of zinc sulfide and a microscope. Then, they fixed a beam of \[5.5MeV\]alpha particles emitted from a radioactive basis at the foil. Lead bricks collimated these alpha particles as they passed and concluded them.
After defeating the foil, the scattering of these alpha particles could be studied by the brief flickers on the screen. Rutherford and his team are predictable to learn more about the structure of the atom from the consequences of this experiment.

Observations:
Here is what they initiate:
Maximum of the alpha particles passed concluded the foil without suffering any collisions.
All over the place \[0.14\% \]of the occurrence alpha particles scattered by more than \[{1^o}\].
All over the place\[\;1\]in \[8000\] alpha particles deflected by more than \[{90^o}\].
These observations led to many influences and conclusion which laid downcast the structure of the nuclear model on an atom.
Note: The particles with a small influence parameter or the particles nearer to the nucleus, experience a large angle of scattering. On the additional hand, those with a large impact parameter are smart with no deflection or scattering at all. To end with, those particles having ~zero impact parameter or a dome-on collision with the nucleus reverberation back.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




