
What does the equation $9{{y}^{2}}-4{{x}^{2}}=36$ tell me about its hyperbola?
Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint: For solving this question you should know about the concept of hyperbola. And you should know about the equations of hyperbola and to find the axis of hyperbola, coordinate of foci, coordinate of vertices, eccentricity of a hyperbola and the latus rectum of the hyperbola. The equation of a hyperbola tells us everything about all of these elements of the hyperbola.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to our question the equation of a hyperbola is $9{{y}^{2}}-4{{x}^{2}}=36$. Simply we can say that a hyperbola is a symmetrical open curve which is formed by the intersection of a circular cone with a plane at any small angle with its axis than the sides of a cone. All the elements of a hyperbola are shown in the figure below.
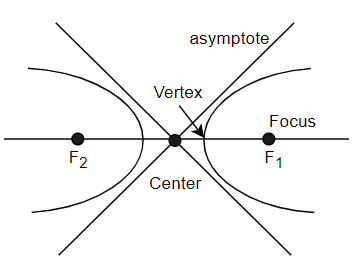
According to our equation, if we see that;
Then $9{{y}^{2}}-4{{x}^{2}}=36$
Divide the whole equation by 36,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9{{y}^{2}}}{36}-\dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{36}=\dfrac{36}{36} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}=1\ldots \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
So, the equation of the hyperbola is $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}=1$.
It will be the y-axis of this hyperbola.
For the coordinates of Foci,
$\begin{align}
& {{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=4+9=13 \\
& \Rightarrow c=\sqrt{13} \\
\end{align}$
So, the coordinate of Foci $=\left( 0,\pm c \right)=\left( 0,\pm \sqrt{13} \right)$.
So, the Foci are $\left( 0,\sqrt{13} \right)$ and $\left( 0,-\sqrt{13} \right)$.
Coordinates of the vertices $=\left( 0,\pm a \right)=\left( 0,\pm 2 \right)$.
So, the coordinates of the vertices are $\left( 0,2 \right)$ and $\left( 0,-2 \right)$.
Eccentricity of the hyperbola $=e=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{\sqrt{13}}{2}$.
And the latus rectum of the hyperbola $=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{2\times 9}{2}=2$.
Thus, the equation of the hyperbola shows everything like this.
Note: The equation of a hyperbola is always in $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ form if the axis of hyperbola is x-axis and it will be in the form of $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ if the axis of the hyperbola is y-axis and the coordinates of Foci and coordinates of vertex will also change respectively. And eccentricity and latus rectum will remain the same.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to our question the equation of a hyperbola is $9{{y}^{2}}-4{{x}^{2}}=36$. Simply we can say that a hyperbola is a symmetrical open curve which is formed by the intersection of a circular cone with a plane at any small angle with its axis than the sides of a cone. All the elements of a hyperbola are shown in the figure below.

According to our equation, if we see that;
Then $9{{y}^{2}}-4{{x}^{2}}=36$
Divide the whole equation by 36,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9{{y}^{2}}}{36}-\dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{36}=\dfrac{36}{36} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}=1\ldots \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
So, the equation of the hyperbola is $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{9}=1$.
It will be the y-axis of this hyperbola.
For the coordinates of Foci,
$\begin{align}
& {{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}={{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{c}^{2}}=4+9=13 \\
& \Rightarrow c=\sqrt{13} \\
\end{align}$
So, the coordinate of Foci $=\left( 0,\pm c \right)=\left( 0,\pm \sqrt{13} \right)$.
So, the Foci are $\left( 0,\sqrt{13} \right)$ and $\left( 0,-\sqrt{13} \right)$.
Coordinates of the vertices $=\left( 0,\pm a \right)=\left( 0,\pm 2 \right)$.
So, the coordinates of the vertices are $\left( 0,2 \right)$ and $\left( 0,-2 \right)$.
Eccentricity of the hyperbola $=e=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{\sqrt{13}}{2}$.
And the latus rectum of the hyperbola $=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{2\times 9}{2}=2$.
Thus, the equation of the hyperbola shows everything like this.
Note: The equation of a hyperbola is always in $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ form if the axis of hyperbola is x-axis and it will be in the form of $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ if the axis of the hyperbola is y-axis and the coordinates of Foci and coordinates of vertex will also change respectively. And eccentricity and latus rectum will remain the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




