
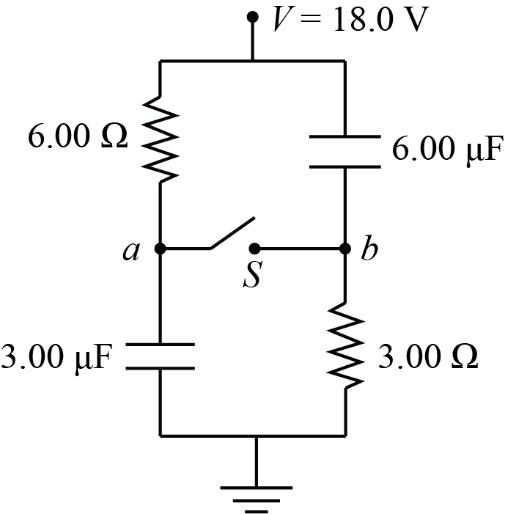
How much does the charge on each capacitor change when $S$ is closed?

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The voltage across capacitors will be different when the switch is closed and not closed. We will use the equation connecting charge, voltage and capacitance to find the charge on capacitors.
Complete step by step answer:
For a better understanding, first let us define the values given in the circuit.
Let the given resistances ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $, ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $,
Capacitance of capacitors,${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$, ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$
Voltage supplied, $V = 18\;{\rm{V}}$
First let us find the current flowing through the resistors ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$. The current is given by,
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{6\;\Omega }} + {R_{3\;\Omega }}}}$
Substituting the values of $V$, ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$ in the above equation, we ge
$\begin{array}{c}
I = \dfrac{{18}}{{6 + 3}}\\
= 2\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}$
When the switch $S$ is not closed, the voltage ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ across ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and the voltage ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ across ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ is $18\;{\rm{V}}$ itself. Hence,
${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 18\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, we can express the charge across the $6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor as
${Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting the values for ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6 \times 18\\
= 108\,{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
We can express the charge across the $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor as
${Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting the values for ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3 \times 18\\
= 54\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
When the switch $S$ is closed, the voltage drop across $6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor will be equal to the voltage drop across ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $.
${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{6\Omega }}$
Now, the voltage drop across ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $ can be written as
${V_{6\Omega }} = I{R_{6\Omega }}$
Substituting the values of $I$ and ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{V_{6\Omega }} = 2 \times 6\\
= 12\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Hence, ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 12\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, the new charge across ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ can be written as
${q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}}$
Substituting the values of ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6 \times 12\\
= 72\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Similarly, when the switch $S$ is closed, the voltage drop across $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor will be equal to the voltage drop across ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $.
${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{3\Omega }}$
Now, the voltage drop across ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $ can be written as
${V_{3\Omega }} = I{R_{3\Omega }}$
Substituting the values of $I$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{V_{3\Omega }} = 2 \times 3\\
= 6\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Hence, ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, the new charge across ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ can be written as
\[{q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{{\rm{3}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}\]
Substituting the values of ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3 \times 6\\
= 18\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Now, the change in the charge of ${\rm{16}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor after the switch is closed can be written as
$\Delta {Q_{{\rm{6}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} - {Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting ${\rm{78}}\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and $108\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
\Delta {Q_{{\rm{6}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 78 - 108\\
= - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Again, the change in the charge of $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor after the switch is closed can be written as
$\Delta {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} - {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting $18\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and $54\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
\Delta {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 18 - 54\\
= - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the change in charge on both the capacitors is $ - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}$.
Note:
It should be noted that one end of the circuit is connected to the ground. Since the potential of the ground is always zero, we took the potential difference as $18\;{\rm{V}}$ itself in calculations when the switch is not closed.
Complete step by step answer:
For a better understanding, first let us define the values given in the circuit.
Let the given resistances ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $, ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $,
Capacitance of capacitors,${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$, ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$
Voltage supplied, $V = 18\;{\rm{V}}$
First let us find the current flowing through the resistors ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$. The current is given by,
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{6\;\Omega }} + {R_{3\;\Omega }}}}$
Substituting the values of $V$, ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$ in the above equation, we ge
$\begin{array}{c}
I = \dfrac{{18}}{{6 + 3}}\\
= 2\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}$
When the switch $S$ is not closed, the voltage ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ across ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and the voltage ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ across ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ is $18\;{\rm{V}}$ itself. Hence,
${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 18\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, we can express the charge across the $6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor as
${Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting the values for ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6 \times 18\\
= 108\,{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
We can express the charge across the $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor as
${Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting the values for ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3 \times 18\\
= 54\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
When the switch $S$ is closed, the voltage drop across $6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor will be equal to the voltage drop across ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $.
${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{6\Omega }}$
Now, the voltage drop across ${R_{6\;\Omega }} = 6\;\Omega $ can be written as
${V_{6\Omega }} = I{R_{6\Omega }}$
Substituting the values of $I$ and ${R_{6\;\Omega }}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{V_{6\Omega }} = 2 \times 6\\
= 12\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Hence, ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 12\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, the new charge across ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ can be written as
${q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}}$
Substituting the values of ${C_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6 \times 12\\
= 72\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Similarly, when the switch $S$ is closed, the voltage drop across $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor will be equal to the voltage drop across ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $.
${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {V_{3\Omega }}$
Now, the voltage drop across ${R_{3\;\Omega }} = 3\;\Omega $ can be written as
${V_{3\Omega }} = I{R_{3\Omega }}$
Substituting the values of $I$ and ${R_{3\;\Omega }}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{V_{3\Omega }} = 2 \times 3\\
= 6\;{\rm{V}}
\end{array}$
Hence, ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 6\;{\rm{V}}$
Now, the new charge across ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ can be written as
\[{q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}{V_{{\rm{3}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}\]
Substituting the values of ${C_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and ${V_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
{q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 3 \times 6\\
= 18\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Now, the change in the charge of ${\rm{16}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor after the switch is closed can be written as
$\Delta {Q_{{\rm{6}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} - {Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting ${\rm{78}}\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and $108\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${Q_{6\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
\Delta {Q_{{\rm{6}}\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 78 - 108\\
= - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Again, the change in the charge of $3\;{\rm{\mu F}}$ capacitor after the switch is closed can be written as
$\Delta {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = {q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} - {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$
Substituting $18\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$ and $54\;{\rm{\mu C}}$ for ${Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}}$, we get
$\begin{array}{c}
\Delta {Q_{3\;{\rm{\mu F}}}} = 18 - 54\\
= - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}
\end{array}$
Therefore, the change in charge on both the capacitors is $ - 36\;{\rm{\mu C}}$.
Note:
It should be noted that one end of the circuit is connected to the ground. Since the potential of the ground is always zero, we took the potential difference as $18\;{\rm{V}}$ itself in calculations when the switch is not closed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




