
How does the blood absorb oxygen in the lungs?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Respiration is the process in which the gases such as carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged between the blood and external environment. During respiration, the complex substances (such as carbohydrates) are broken down to form simpler substances like water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen is utilized during this process. The synthesis of ATP takes place with the help of energy produced during this process.
Complete answer:
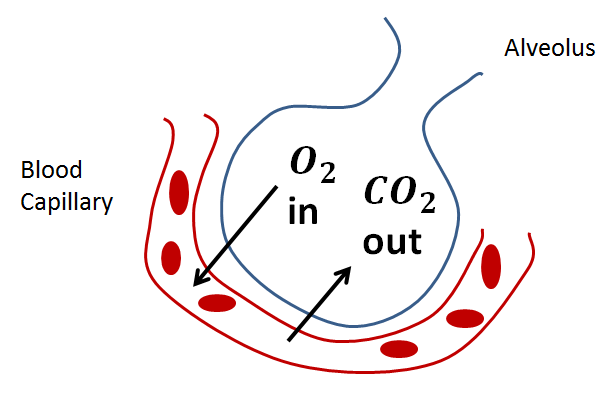
The respiratory system helps in respiration. It involves the exchange of gases between the lungs and body tissues. The alveoli of the lungs are responsible for the exchange of gases between the blood and surroundings. The following steps help the blood to absorb oxygen in the lungs:
When we breathe air, it reaches the alveoli of the lungs to supply oxygen. At the alveolar site, the partial pressure of oxygen is higher than the partial pressure of carbon dioxide. Hence when the impure blood reaches the alveolar capillaries, the oxygen binds with haemoglobin and forms oxyhaemoglobin in the capillary blood.
The oxyhaemoglobin is acidic in nature and thus it helps in the breakdown of sodium bicarbonate ($NaHCO_3$) present in blood. The carbon dioxide is released due to the breakdown of $NaHCO_3$.
Hence due to the high concentration of oxygen at the alveoli, the oxygen leaves the alveolar site and enters the red blood cells and binds with the haemoglobin. After that the pure blood which carries oxygen reaches to all cells and tissues of the body to supply oxygen there for various cellular activities. At the tissue level, the carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood and reaches the alveoli of the lungs from where it is exhaled out (released outside the body) through the nose.
Note:
The partial pressure gradient helps in the movement of gases i.e. from high partial pressure to low partial pressure. In the alveolar site, the gas exchange between the alveoli and the blood capillaries takes place by simple diffusion.
Complete answer:
The respiratory system helps in respiration. It involves the exchange of gases between the lungs and body tissues. The alveoli of the lungs are responsible for the exchange of gases between the blood and surroundings. The following steps help the blood to absorb oxygen in the lungs:
When we breathe air, it reaches the alveoli of the lungs to supply oxygen. At the alveolar site, the partial pressure of oxygen is higher than the partial pressure of carbon dioxide. Hence when the impure blood reaches the alveolar capillaries, the oxygen binds with haemoglobin and forms oxyhaemoglobin in the capillary blood.
The oxyhaemoglobin is acidic in nature and thus it helps in the breakdown of sodium bicarbonate ($NaHCO_3$) present in blood. The carbon dioxide is released due to the breakdown of $NaHCO_3$.
Hence due to the high concentration of oxygen at the alveoli, the oxygen leaves the alveolar site and enters the red blood cells and binds with the haemoglobin. After that the pure blood which carries oxygen reaches to all cells and tissues of the body to supply oxygen there for various cellular activities. At the tissue level, the carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood and reaches the alveoli of the lungs from where it is exhaled out (released outside the body) through the nose.

Note:
The partial pressure gradient helps in the movement of gases i.e. from high partial pressure to low partial pressure. In the alveolar site, the gas exchange between the alveoli and the blood capillaries takes place by simple diffusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




