
Does the atomic volume rise with the increasing atomic mass?
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: Atomic mass of any element is the summation of mass of electrons, protons and neutrons present in the particular atom. Masses of all these fundamental particles are independent to each other and constant. Therefore, the mass of the atom is always constant with some exceptions.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that all the elements in a periodic table are arranged with their increasing atomic number not with their masses. But when we move from right to left along the period, the mass of the atom generally increases with increase of their atomic number because of the increase in fundamental particles associated with the atom. It means that with an increase in atomic number, the number of electrons and protons also increases and therefore atomic mass of the atom also increases.
Similarly, when we move down the periodic table, atomic number increases and along with-it atomic mass also increases.
But when we look for the trend of volume of atoms in the periodic table it varies from the atomic mass.
When we move from right to left, the atomic radius of the element decreases due to the increase in strength of force of attraction exerted by the nuclear charge due to the presence of protons and neutrons. As the atomic radius decreases, the volume of the atom also increases because we know that volume is a function of the radius of the atom.
When we move from top to bottom, atomic radius increases because with increase in atomic number, number of orbitals around the nucleus also increases and due to shielding effect of the nucleus atomic radius increases. Hence, atomic volume also increases when we move top to bottom.
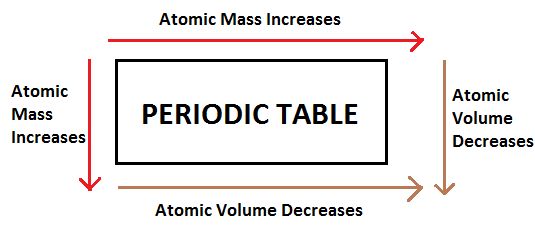
$ \Rightarrow $ Therefore, it is not necessary that with increase in atomic mass atomic volume also increases.
Note:
Atomic mass of the radioactive atom changes with time due to emission of radioactive particles from the nucleus which have some mass. Shielding effect is generally shown by electrons present in $d$ and $f$ orbitals. Size of the cation is always smaller than the atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that all the elements in a periodic table are arranged with their increasing atomic number not with their masses. But when we move from right to left along the period, the mass of the atom generally increases with increase of their atomic number because of the increase in fundamental particles associated with the atom. It means that with an increase in atomic number, the number of electrons and protons also increases and therefore atomic mass of the atom also increases.
Similarly, when we move down the periodic table, atomic number increases and along with-it atomic mass also increases.
But when we look for the trend of volume of atoms in the periodic table it varies from the atomic mass.
When we move from right to left, the atomic radius of the element decreases due to the increase in strength of force of attraction exerted by the nuclear charge due to the presence of protons and neutrons. As the atomic radius decreases, the volume of the atom also increases because we know that volume is a function of the radius of the atom.
When we move from top to bottom, atomic radius increases because with increase in atomic number, number of orbitals around the nucleus also increases and due to shielding effect of the nucleus atomic radius increases. Hence, atomic volume also increases when we move top to bottom.

$ \Rightarrow $ Therefore, it is not necessary that with increase in atomic mass atomic volume also increases.
Note:
Atomic mass of the radioactive atom changes with time due to emission of radioactive particles from the nucleus which have some mass. Shielding effect is generally shown by electrons present in $d$ and $f$ orbitals. Size of the cation is always smaller than the atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




