
How does $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized carbon differ from $s{{p}^{3}}$?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint:Hybridization is the process of intermixing of the orbitals of slightly different energies so as to redistribute their energies, resulting in the formation of new set of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape. $s{{p}^{2}}and\,s{{p}^{3}}$hybridization are types of hybridization.
Complete step-by-step answer:$s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization is a form of orbital hybridization in which $1$ s orbital overlaps with 2 p orbitals to form three new hybrid orbitals.
$s{{p}^{3}}$hybridization is a form of orbital hybridization in which 1 s orbital overlaps with 3 p orbitals to form four new hybrid orbitals.
If carbon in a carbon compound undergo $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization then it is referred to as $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized carbon atom and if the same carbon undergoes $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridization, then the carbon is called $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized carbon atom.
The differences between both the hybridized carbon atoms are mentioned below in tabular form.
Note:It should be noted that for explaining the characteristic shapes of the polyatomic molecule, Pauling- a great chemist, scientist introduced the concept of hybridization of the atomic orbitals. Always, draw structures while mentioning the types of hybridization for better reference.
Complete step-by-step answer:$s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization is a form of orbital hybridization in which $1$ s orbital overlaps with 2 p orbitals to form three new hybrid orbitals.
$s{{p}^{3}}$hybridization is a form of orbital hybridization in which 1 s orbital overlaps with 3 p orbitals to form four new hybrid orbitals.
If carbon in a carbon compound undergo $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridization then it is referred to as $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized carbon atom and if the same carbon undergoes $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridization, then the carbon is called $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized carbon atom.
The differences between both the hybridized carbon atoms are mentioned below in tabular form.
| FEATURE | $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized carbon | $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized carbon |
| Definition | A form of orbital hybridization in which one s-orbital of carbon overlaps with two p orbitals to form three new hybrid orbitals. | A form of orbital hybridization in which one s-orbital of carbon overlaps with three p orbitals to form four new hybrid orbitals. |
| s- characteristic | In such carbon the s character is $33%$ | In such carbon the s character is $25%$ |
| p- characteristic | In such hybridized carbon the p character is $66%$ | In such hybridized carbon the p character is $75%$ |
| Geometry | It has trigonal planar geometry | It has Tertrahedral geometry |
| Bond angle | $120\circ $ | ${{109.5}^{\circ }}$ |
| Unhybridized p orbital | One un-hybridized p orbital is present in such carbon | No un-hybridized p orbital is present in such carbon |
| Examples | Carbon in ethene is $s{{p}^{2}}$hybridized as shown below 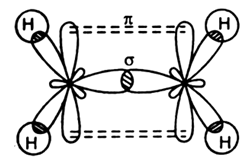
| Carbon in ethane is $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized as shown below. 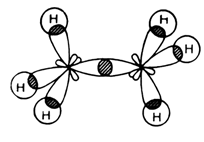
|
Note:It should be noted that for explaining the characteristic shapes of the polyatomic molecule, Pauling- a great chemist, scientist introduced the concept of hybridization of the atomic orbitals. Always, draw structures while mentioning the types of hybridization for better reference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




