
What does sonar equipment measure?
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: We measure distance by taking two points (initial and final) and we measure the length span between them. Sometimes this method is not quite applicable so we sent a ray and let it bounce back to yourself then we find the distance by dividing the total length covered by the ray into half
Pythagoras Theorem.
$ {A^2} = {B^2} + {C^2} $ where $ A $ is the hypotenuse and $ B $ and $ C $ are the base and perpendicular.
$ d = v \times t $ where $ d $ is the distance covered, $ v $ is the speed and $ t $ is the time.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Sonar also called sound navigation and ranging is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.
In this process we send a sound ray in water by the transmitter, the ray then bounces back to the receiver.
We then note the time after which the ray has reached us.
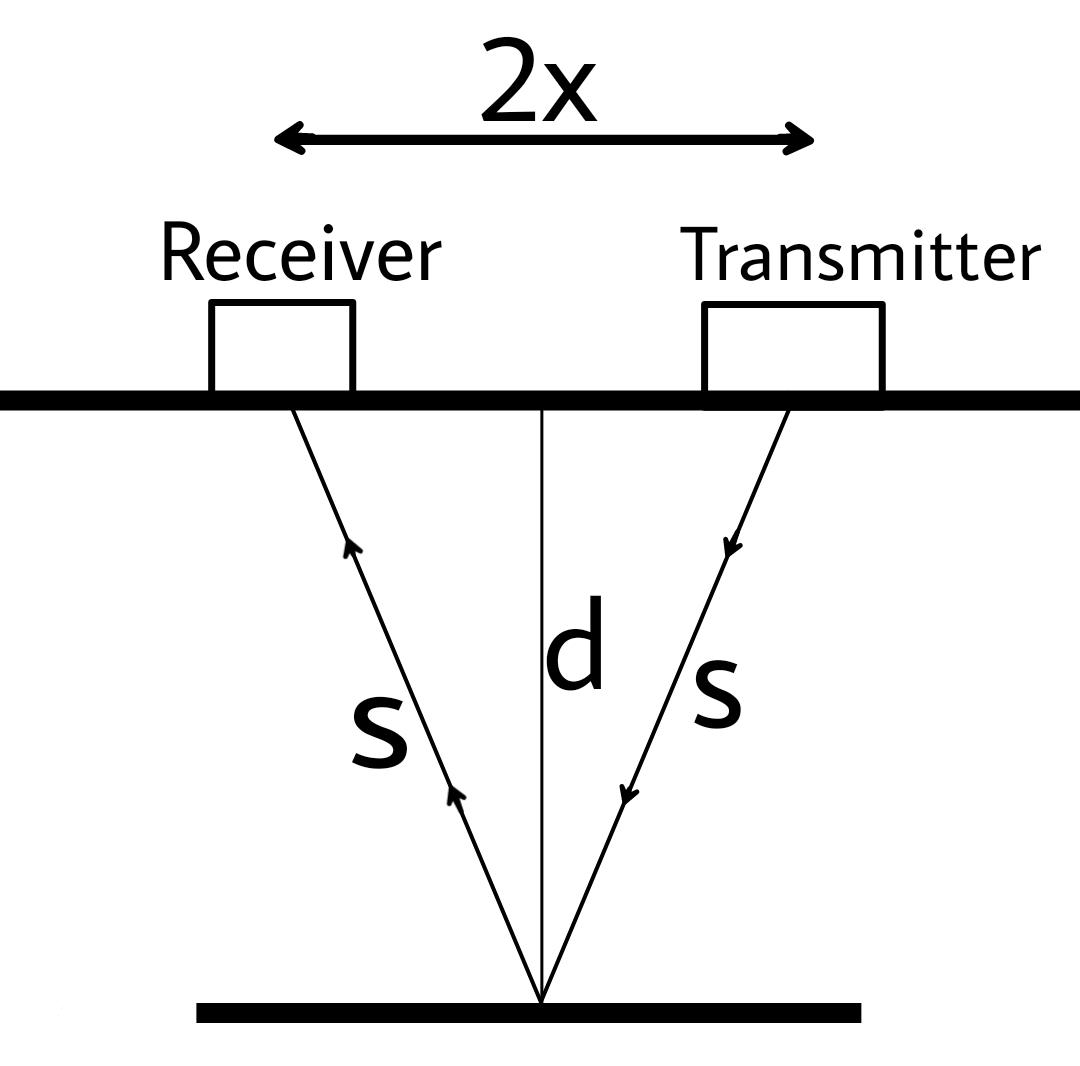
The above figure shows the propagation of the ray inside water. Where $ 2x $ is the distance between the transmitter and the receiver and depth is $ d $ .
Since, we know the time and the velocity of the sound ray we have the value of (hypotenuse).
$ s = vt $ where $ v $ is the speed of the sound wave and $ t $ is the time taken by the wave to reach the receiver.
Now we use the Pythagoras theorem to find the value of the depth.
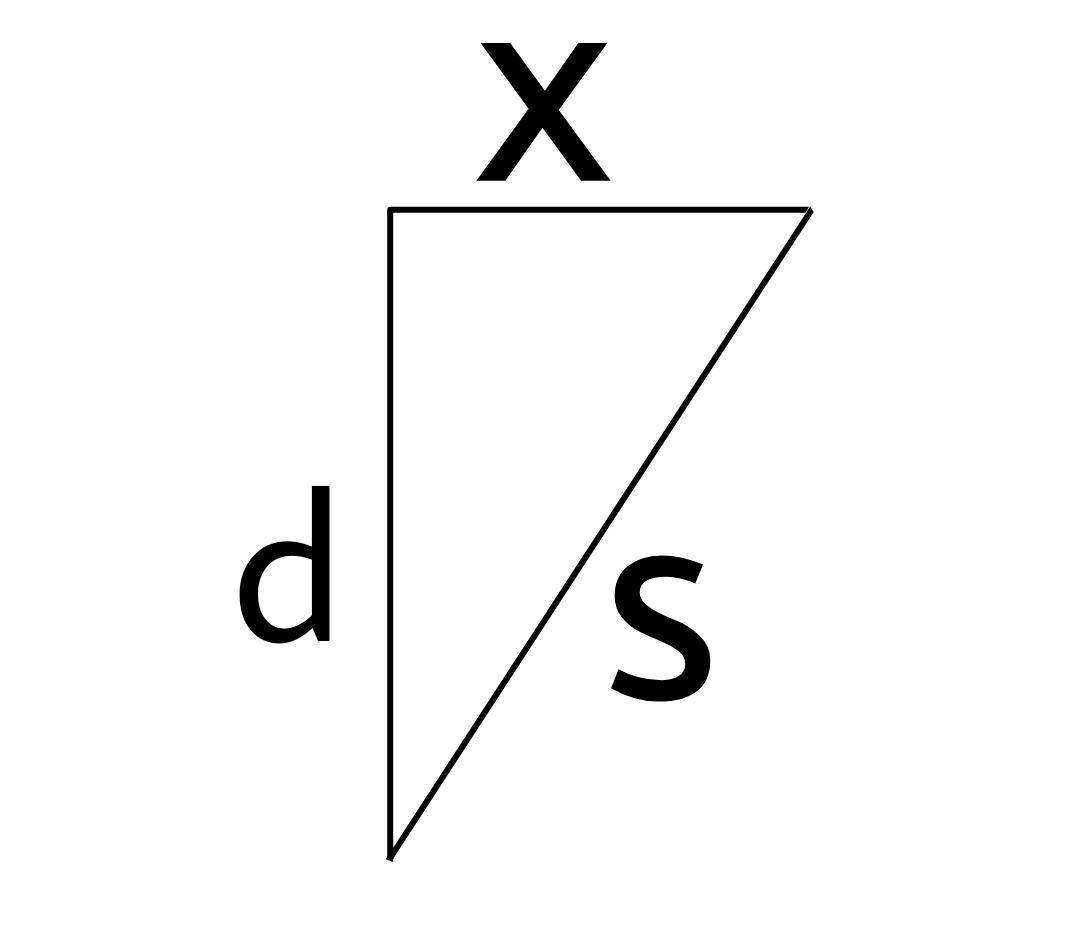
Now,
$ {s^2} = {x^2} + {d^2} $
$ {d^2} = {s^2} - {x^2} $
$ d = \sqrt {{s^2} - {x^2}} $
$ d = \sqrt {{{\left( {vt} \right)}^2} - {x^2}} $ substituting $ s = vt $
Thus, with the above formula we can find the depth of the sea.
Note:
Sometimes there can be rocks which can't give us the actual measurement of the depth so we send many rays in a particular large area in order to confirm the actual depth of the sea bed. And also at times If we know that the depth is too high and the distance between the transmitter and the receiver is very low we can neglect this distance as it the depth almost becomes equal to the distance the rays travelled $ \left( {s \cong d} \right) $ .
Pythagoras Theorem.
$ {A^2} = {B^2} + {C^2} $ where $ A $ is the hypotenuse and $ B $ and $ C $ are the base and perpendicular.
$ d = v \times t $ where $ d $ is the distance covered, $ v $ is the speed and $ t $ is the time.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Sonar also called sound navigation and ranging is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.
In this process we send a sound ray in water by the transmitter, the ray then bounces back to the receiver.
We then note the time after which the ray has reached us.

The above figure shows the propagation of the ray inside water. Where $ 2x $ is the distance between the transmitter and the receiver and depth is $ d $ .
Since, we know the time and the velocity of the sound ray we have the value of (hypotenuse).
$ s = vt $ where $ v $ is the speed of the sound wave and $ t $ is the time taken by the wave to reach the receiver.
Now we use the Pythagoras theorem to find the value of the depth.
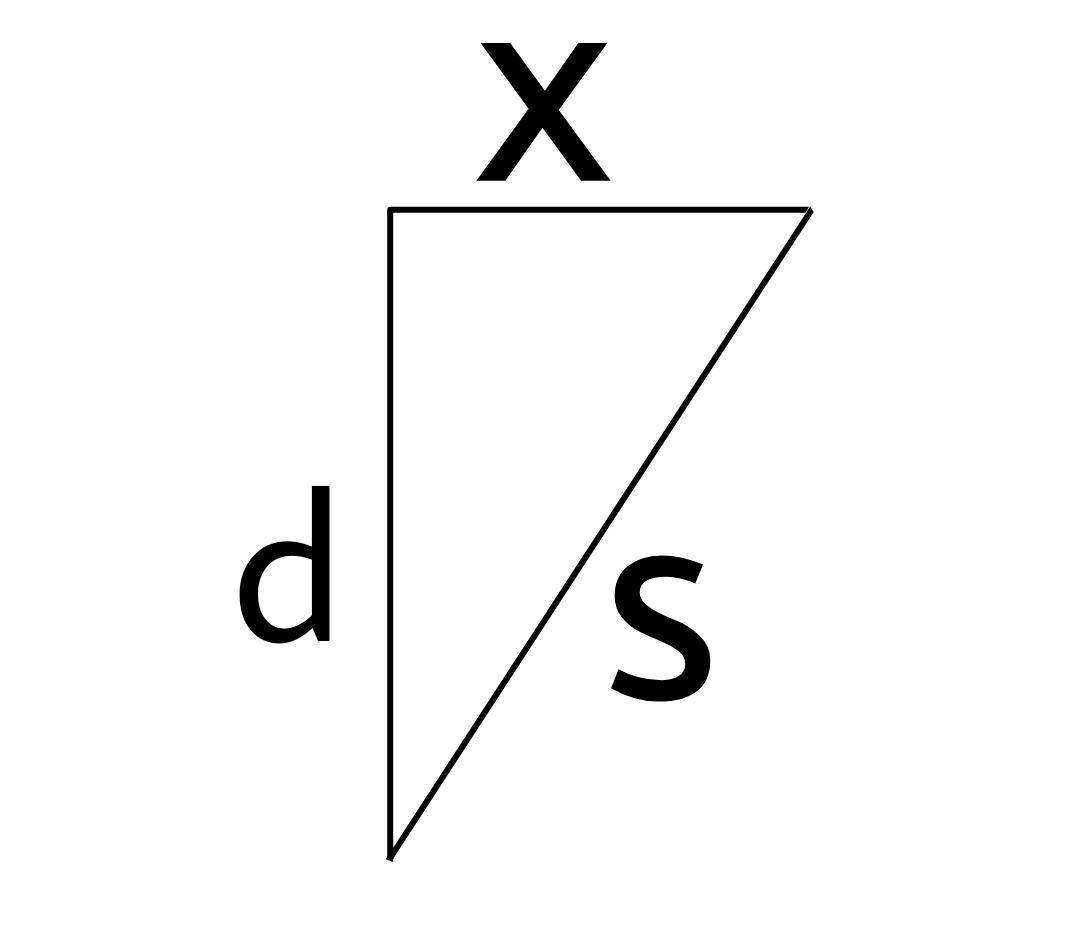
Now,
$ {s^2} = {x^2} + {d^2} $
$ {d^2} = {s^2} - {x^2} $
$ d = \sqrt {{s^2} - {x^2}} $
$ d = \sqrt {{{\left( {vt} \right)}^2} - {x^2}} $ substituting $ s = vt $
Thus, with the above formula we can find the depth of the sea.
Note:
Sometimes there can be rocks which can't give us the actual measurement of the depth so we send many rays in a particular large area in order to confirm the actual depth of the sea bed. And also at times If we know that the depth is too high and the distance between the transmitter and the receiver is very low we can neglect this distance as it the depth almost becomes equal to the distance the rays travelled $ \left( {s \cong d} \right) $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




