
What does P-wave represent in ECG?
A)End of systole
B)Contraction of both atria
C)Initiation of ventricular contraction
D)Beginning of systole

Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: In order to search for multiple heart problems, an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records an electrical signal from your heart. Electrodes are mounted on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to pound.
Complete answer:
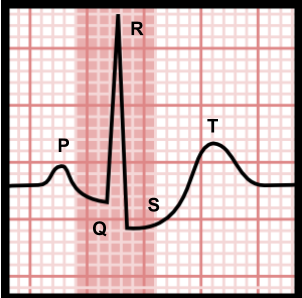
As described below, a normal ECG contains waves, intervals, segments, and one complex.
Wave: A positive or negative deflection suggesting a particular electrical event from the baseline. The P wave, Q wave, R wave, S wave, T wave and U wave are the waves on the ECG.
Interval: the time between two particular events of the ECG. PR interval, QRS interval (also called QRS duration), QT interval and RR interval are the intervals typically measured on an ECG.
Segment: The length between two ECG unique points which are expected to be at the baseline amplitude (not negative or positive). The PR section, ST segment and TP segment are the segments on an ECG.
Complex: The combination of the grouping of multiple waves. The QRS complex is the only primary complex on an ECG.
Point: On an ECG called the J point, which is where the QRS complex ends and the ST section starts, there is only one point.
There is a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave in the main part of the ECG. In this tutorial, each will be explained individually, as will each section and interval.
Atrial depolarization is demonstrated by the P wave. A Q wave, R wave and S wave are the QRS complex and reflect ventricular depolarization. After the QRS complex, the T wave arrives and shows ventricular repolarization.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There are 12 leads on the regular ECG. Six of the leads are known as "limb leads" since they are mounted on the individual's arms and/or legs. As they are put on the torso, the other six leads are called "precordial leads" (precordium).
Lead I, II, III, aVL, aVR and aVF are referred to as the six limb leads. As these leads are measured as a combination of leads I, II and III, the letter "a" stands for "augmented." The six precordial leads are called V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 and V6 leads.
Complete answer:
As described below, a normal ECG contains waves, intervals, segments, and one complex.
Wave: A positive or negative deflection suggesting a particular electrical event from the baseline. The P wave, Q wave, R wave, S wave, T wave and U wave are the waves on the ECG.
Interval: the time between two particular events of the ECG. PR interval, QRS interval (also called QRS duration), QT interval and RR interval are the intervals typically measured on an ECG.
Segment: The length between two ECG unique points which are expected to be at the baseline amplitude (not negative or positive). The PR section, ST segment and TP segment are the segments on an ECG.
Complex: The combination of the grouping of multiple waves. The QRS complex is the only primary complex on an ECG.
Point: On an ECG called the J point, which is where the QRS complex ends and the ST section starts, there is only one point.
There is a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave in the main part of the ECG. In this tutorial, each will be explained individually, as will each section and interval.
Atrial depolarization is demonstrated by the P wave. A Q wave, R wave and S wave are the QRS complex and reflect ventricular depolarization. After the QRS complex, the T wave arrives and shows ventricular repolarization.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: There are 12 leads on the regular ECG. Six of the leads are known as "limb leads" since they are mounted on the individual's arms and/or legs. As they are put on the torso, the other six leads are called "precordial leads" (precordium).
Lead I, II, III, aVL, aVR and aVF are referred to as the six limb leads. As these leads are measured as a combination of leads I, II and III, the letter "a" stands for "augmented." The six precordial leads are called V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 and V6 leads.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




