
How does phenol differ from benzene?
Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: The phenol and benzene have both structural differences at only one carbon where the alcohol group is attached. One can elaborate on the differences in both the chemicals about the physical and chemical properties.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all, as we know both phenols and benzene are aromatic structures and they differ from each other in the attachment of a group of alcohol to one carbon. Now let us see each chemical structure in detail as below,
2) Phenol:
i) Structure of phenol:
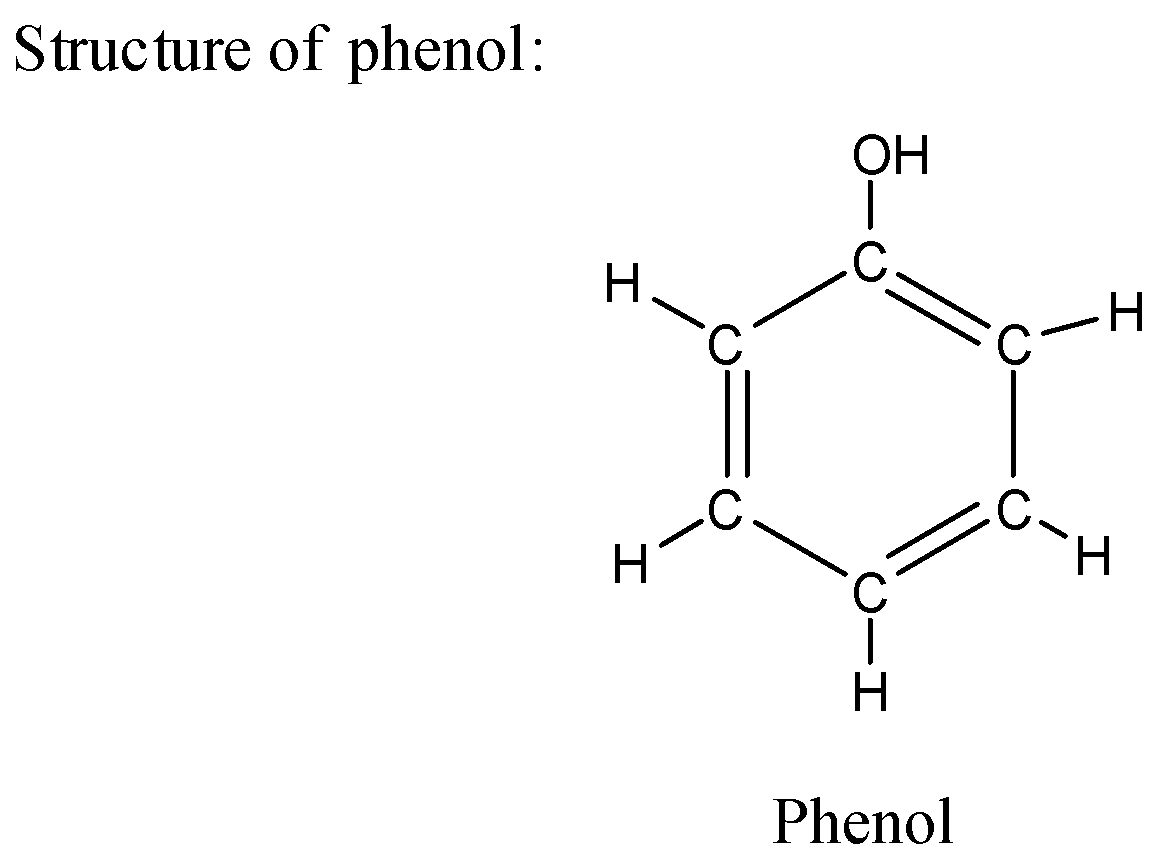
ii) The phenol has a molecular formula as ${C_6}{H_6}OH$ which has an alcoholic functional group in its structure.
iii) The phenol is present in solid form and has a white crystalline appearance.
iv) Phenol has a very strong odor which is very unique and can be detected in the lab easily by smell.
v) Phenol is acidic in nature which means it donates proton easily.
vi) Phenol is easily soluble in solvents like water.
3) Benzene:
i) Structure of benzene:
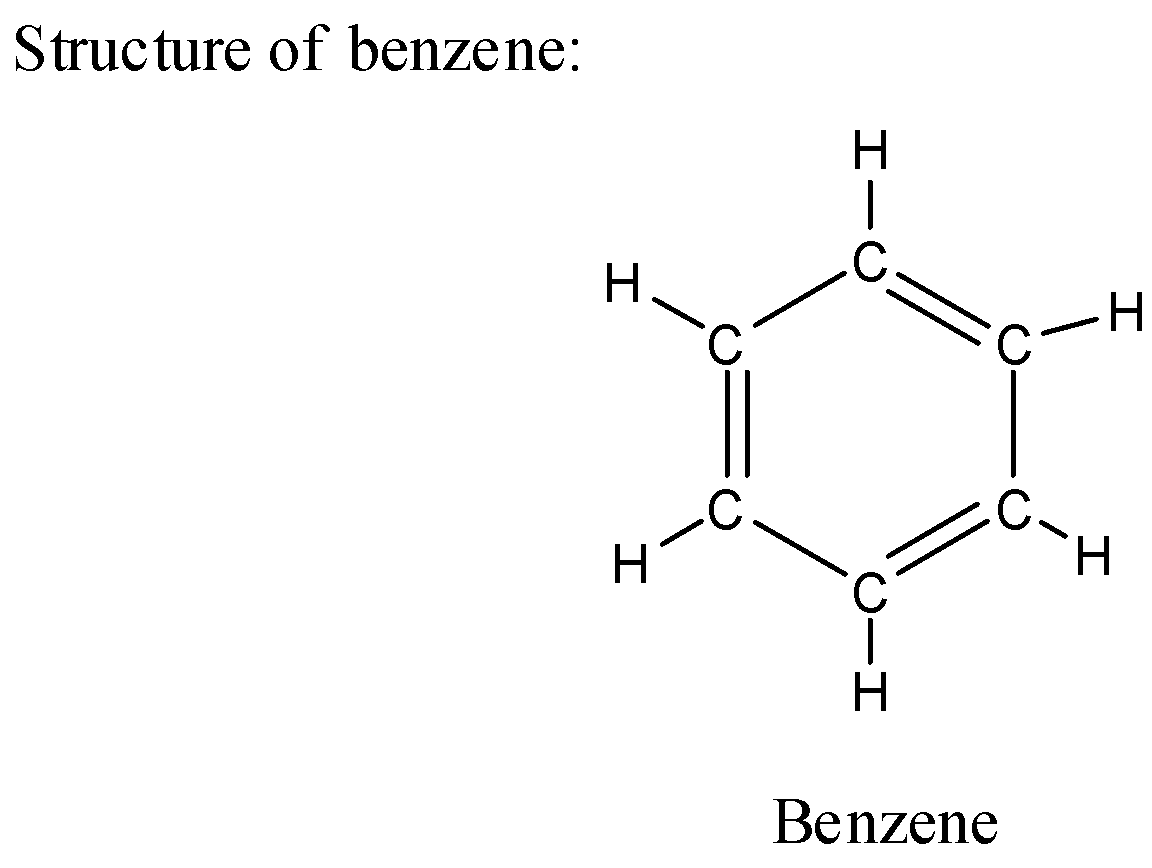
ii) The chemical structure of benzene has a molecular formula as ${C_6}{H_6}$ where each carbon in the ring has one hydrogen atom.
iii) The benzene is present in liquid form and is colorless in appearance.
iv) Benzene has a very sweet odor which is unique from other odors.
v) The benzene has neutral nature in chemical reactivity and hence it is mostly used as a solvent in many chemical reactions.
vi) The benzene is less soluble in water as compared to phenol which is more soluble in water.
Note:
The phenol is acidic in nature despite having an alcoholic group in its structure. The hydrogen atom donation forms a phenoxide ion which is stable due to aromaticity and that makes phenol acidic. Both the phenol and benzene are volatile where benzene has a faster rate of evaporation.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all, as we know both phenols and benzene are aromatic structures and they differ from each other in the attachment of a group of alcohol to one carbon. Now let us see each chemical structure in detail as below,
2) Phenol:
i) Structure of phenol:

ii) The phenol has a molecular formula as ${C_6}{H_6}OH$ which has an alcoholic functional group in its structure.
iii) The phenol is present in solid form and has a white crystalline appearance.
iv) Phenol has a very strong odor which is very unique and can be detected in the lab easily by smell.
v) Phenol is acidic in nature which means it donates proton easily.
vi) Phenol is easily soluble in solvents like water.
3) Benzene:
i) Structure of benzene:

ii) The chemical structure of benzene has a molecular formula as ${C_6}{H_6}$ where each carbon in the ring has one hydrogen atom.
iii) The benzene is present in liquid form and is colorless in appearance.
iv) Benzene has a very sweet odor which is unique from other odors.
v) The benzene has neutral nature in chemical reactivity and hence it is mostly used as a solvent in many chemical reactions.
vi) The benzene is less soluble in water as compared to phenol which is more soluble in water.
Note:
The phenol is acidic in nature despite having an alcoholic group in its structure. The hydrogen atom donation forms a phenoxide ion which is stable due to aromaticity and that makes phenol acidic. Both the phenol and benzene are volatile where benzene has a faster rate of evaporation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




