
Does it grow well in dry or moist conditions?

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The zygomycetes also known as the conjugation fungi are the division of fungi. Fungi are organisms that have a thallus body, and possess a definite cell wall of either cellulose or chitin or both but lack chlorophyll.
Complete answer:
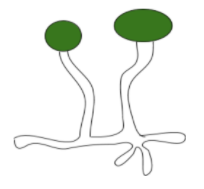
Thallus of zygomycetes is mycelial. Their hyphae are coenocytic i.e multinucleated and aseptate. Their cell is made up of chitin. One of the characteristic features of this division is the absence of any motile body. They do reproduce by asexual as well as sexual repodroduction. Asexual reproduction mainly occurs by formation of non-motile sporangiospores formed due to cleavage occuring in sporangia. Sexual reproduction takes place with the help of conjugation or gametangial copulation that occurs between two identical gametangia. Their gametes are non- motile and multinucleate. Sexual reproduction leads to the formation of diploid zygospore. This zygospore contains diploid nuclei and then divides by meiosis before it enters into a resting stage. On germination, this zygospore gives rise to a sporangium at the tip of it, which produces spores , called germ spores. Rhizopus and mucor are examples of this division. They are multi spored. Most of the saprophytic species that are responsible for causing any disease in plants and animals including human beings fall under this category. These grow very well in moist , dark and warm environmental conditions. In rainy seasons, they can be seen grown at very foodstuffs, clothes etc.
Note: Few species of rhizopus and mucor helps in alcoholic fermentation and in industrial production of several enzymes, lactic and citric acids. Zygomycetes are popularly known as conjugation fungi since they reproduce by conjugation in sexual reproduction.
Complete answer:
Thallus of zygomycetes is mycelial. Their hyphae are coenocytic i.e multinucleated and aseptate. Their cell is made up of chitin. One of the characteristic features of this division is the absence of any motile body. They do reproduce by asexual as well as sexual repodroduction. Asexual reproduction mainly occurs by formation of non-motile sporangiospores formed due to cleavage occuring in sporangia. Sexual reproduction takes place with the help of conjugation or gametangial copulation that occurs between two identical gametangia. Their gametes are non- motile and multinucleate. Sexual reproduction leads to the formation of diploid zygospore. This zygospore contains diploid nuclei and then divides by meiosis before it enters into a resting stage. On germination, this zygospore gives rise to a sporangium at the tip of it, which produces spores , called germ spores. Rhizopus and mucor are examples of this division. They are multi spored. Most of the saprophytic species that are responsible for causing any disease in plants and animals including human beings fall under this category. These grow very well in moist , dark and warm environmental conditions. In rainy seasons, they can be seen grown at very foodstuffs, clothes etc.
Note: Few species of rhizopus and mucor helps in alcoholic fermentation and in industrial production of several enzymes, lactic and citric acids. Zygomycetes are popularly known as conjugation fungi since they reproduce by conjugation in sexual reproduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




